Gut Microbiota, Mycophenolate Mofetil, and Post-Transplant Diarrhea in Kidney Transplant Recipients
J. Lee,1 M. Magruder,1 L. Zhang,1 D. Dadhania,1 M. Satlin,1 L. Westblade,1 A. Robertson,1 Y. Taur,2 L. Ling,2 E. Pamer,2 M. Suthanthiran.1
1Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY
2Memorial Sloan Kettering, New York, NY.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 141
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Toxocity
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic - 1
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Location: Room 303
INTRODUCTION. The etiology of post-transplant diarrhea is often unknown and attributed to mycophenolate mofetil dosage.
METHODS. We recruited 71 kidney transplant recipients for serial collection of fecal specimens in the first 3 months of transplantation and profiled the gut microbiota in 199 fecal specimens using 16S rRNA deep sequencing of the V4-V5 hypervariable region. Twenty-five subjects developed post-transplant diarrhea (Diarrhea Group), contributing 28 diarrheal fecal specimens; forty-six subjects did not develop post-transplant diarrhea (No Diarrhea Group), contributing 111 fecal specimens.
RESULTS. Microbial diversity was lower in the 28 diarrheal fecal specimens than in the 111 fecal specimens from the No Diarrhea Group. 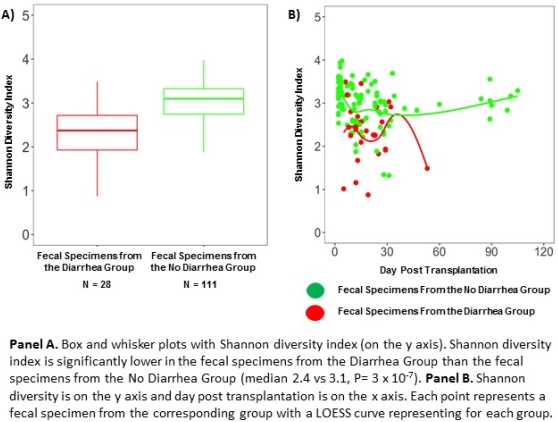
Nine taxa at the family level were significantly different between the 28 diarrheal fecal specimens and the 111 fecal specimens from the No Diarrhea Group (FDR < 0.15, Wilcoxon rank-sum test). 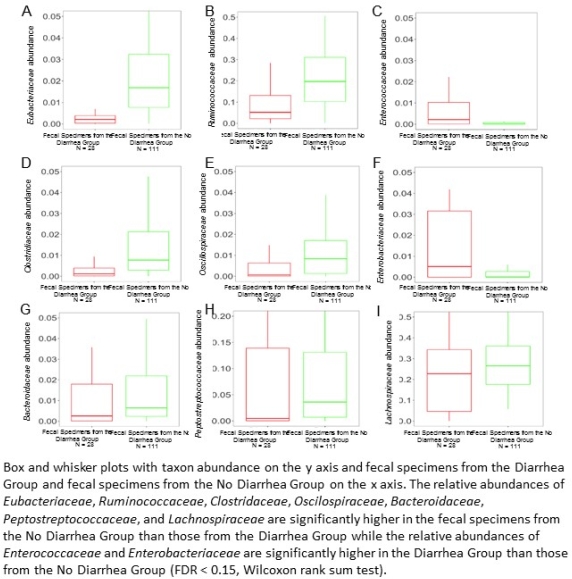
Comparison of the fecal specimens based on mycophenolate mofetil dosage (1000 mg/day vs. 2000 mg/day) did not reveal significantly different taxa when stratified by diarrhea status. Multiplex PCR testing using the FilmArray™ GI PCR Panel was negative for common bacterial, viral, fungal, and protozoa pathogens in 26 of the 28 diarrheal fecal specimens.
CONCLUSIONS. The abundance of commensal bacterial taxa was significantly lower in the post-transplant diarrheal fecal specimens and this decrease was not associated with mycophenolate mofetil dosage. Given the lack of pathogen identification via multiplex PCR testing, our data supports modulation of gut microbiota via probiotics or prebiotics to prevent and/or treat post-transplant diarrhea.
CITATION INFORMATION: Lee J., Magruder M., Zhang L., Dadhania D., Satlin M., Westblade L., Robertson A., Taur Y., Ling L., Pamer E., Suthanthiran M. Gut Microbiota, Mycophenolate Mofetil, and Post-Transplant Diarrhea in Kidney Transplant Recipients Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee J, Magruder M, Zhang L, Dadhania D, Satlin M, Westblade L, Robertson A, Taur Y, Ling L, Pamer E, Suthanthiran M. Gut Microbiota, Mycophenolate Mofetil, and Post-Transplant Diarrhea in Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/gut-microbiota-mycophenolate-mofetil-and-post-transplant-diarrhea-in-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
