Geographic Distribution of End-Stage Renal Disease in the US: The First Description of an “ESRD Belt”
1Surgery, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, 2Medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C-257
Keywords: Kidney, Morbidity, Renal failure
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Non-Organ Specific: Public Policy & Allocation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Previous research has demonstrated that population health is associated with organ supply and transplantation; this is particularly true in the southeastern United States, which comprises the majority of the Stroke Belt. End-stage renal disease (ESRD) is a known risk factor for stroke, but the presence of an “ESRD Belt” has not previously been described.
*Methods: This cross-sectional study used 2016 United States Renal Data System data to estimate ESRD period prevalence in 2014. Patients on dialysis 18-74 years of age were included and aggregated to the state level based on permanent residence. ESRD prevalence per million adult population was estimated using 2014 US Census data. Point prevalence of stroke history was obtained from the CDC Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. States were classified by location in the Stroke Belt, and Spearman’s correlation coefficient was used to assess the relationship between ESRD prevalence and history of stroke.
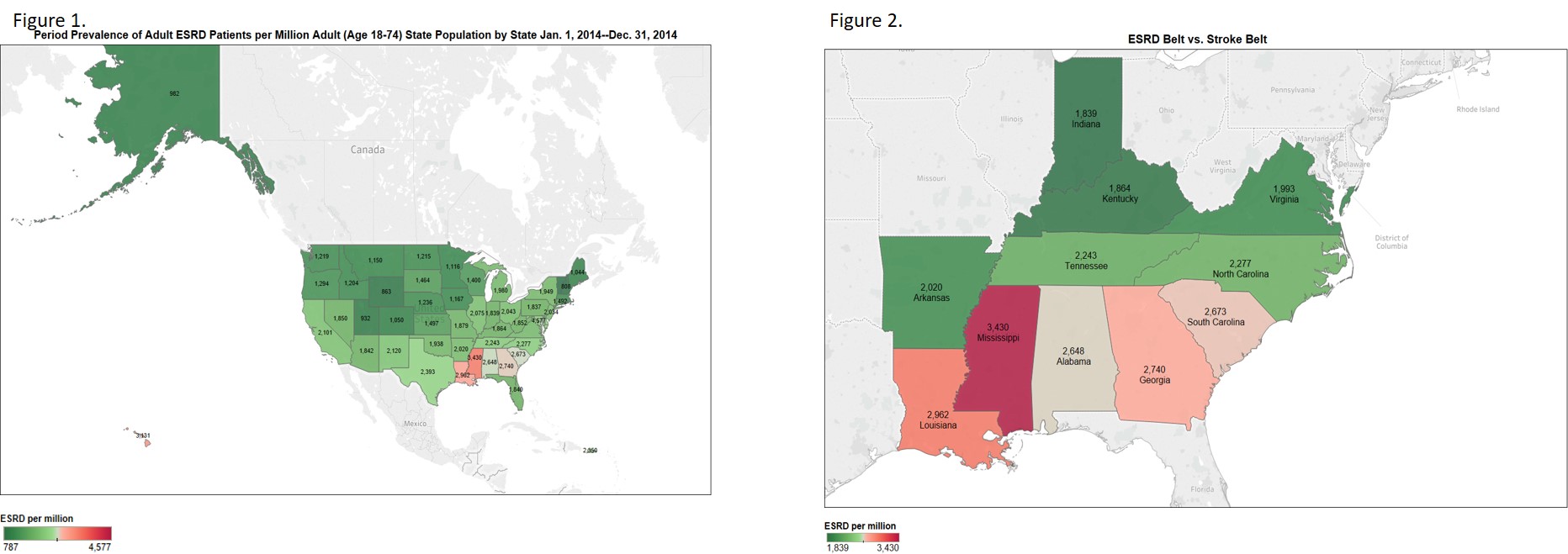
*Results: 450,828 patients with ESRD were included in our analyses. There was wide geographic variation in ESRD period prevalence per million adult population (Figure 1), with increased burden concentrated in the southeast. Of the ten states with the highest ESRD prevalence, five were located in the Stroke Belt (Figure 2). Prevalence of ESRD was significantly positively correlated with history of stroke at the state level (Spearman’s rho: 0.65147, p < 0.001).
*Conclusions: These findings of overlapping disease underscore the need to consider disease burden in conversations regarding organ supply and allocation, to ensure equitable access to transplantation and prevention of future comorbidity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reed RD, Qu H, MacLennan PA, Mustian MN, Anderson D, Kale AC, Orandi BJ, Shelton BA, Kumar V, Hanaway MJ, Locke JE. Geographic Distribution of End-Stage Renal Disease in the US: The First Description of an “ESRD Belt” [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/geographic-distribution-of-end-stage-renal-disease-in-the-us-the-first-description-of-an-esrd-belt/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress