Gender Disparity in Infections After Kidney Transplantation
Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MD.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 355
Keywords: Infection, Kidney transplantation, Medicare
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Disparities in Donation and Transplant Outcomes
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 2:15pm-3:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:27pm-3:39pm
Presentation Time: 3:27pm-3:39pm
Location: Room 115-C
BACKGROUND: Female gender has been suggested as a risk factor for infection after kidney transplant (KT). Preliminary studies have reported that sex hormones such as estradiol may modulate immune responses. The goals of our study were to: 1) investigate gender disparities in risk of post-KT infections, and 2) examine whether the effect was attenuated in post-menopausal women.
METHODS: We studied 89355 first-time kidney transplant (KT) recipients with Medicare as their primary insurance from 1999-2010 as captured in USRDS. Infections that occurred in the year post-KT were ascertained via ICD-9 codes. Cox proportional hazards models were built to compare the hazard of infection by gender, adjusting for potential confounders. Analyses were stratified by age 50 to see whether gender differences were attenuated in post-menopausal women.
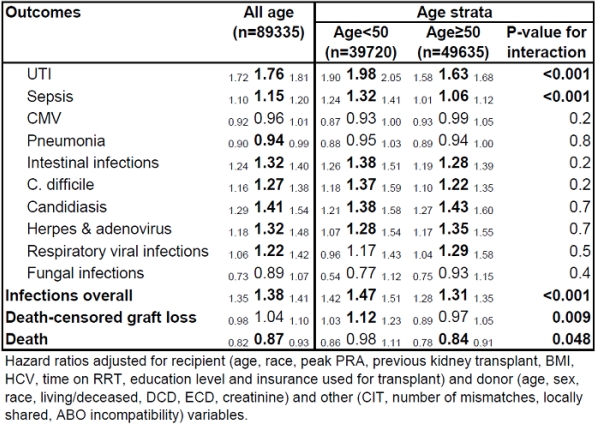
RESULTS: Females had higher hazards of UTI, sepsis, intestinal infections, C.difficile, candidiasis, herpes and adenoviruses, and respiratory viral infections (Table). There was no difference in the hazard of CMV and fungal infections, and females had a slightly lower hazard of pneumonia. Despite the higher hazard of infection, females had a similar hazard of death-censored graft loss and a lower risk of death. When stratified by age, gender disparities in sepsis and UTI were attenuated in those ≥ 50 (p<0.001). Although slightly attenuated, the gender disparities were still observed in those ≥ 50.
CONCLUSION: Female kidney recipients have higher hazards of infection. This gender disparity is attenuated but not eliminated in those ≥ 50.
Table. Adjusted hazard ratio of infections comparing females to males
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bae S, Kucirka L, Durand C, Orandi B, Avery R, Segev D. Gender Disparity in Infections After Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/gender-disparity-in-infections-after-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
