FK506 Influence Glucose Metabolism by Short Chain Fatty Acid
1Urology, Capital Medical University Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Beijing, China, 2GI Divison, West China Hospital, Beijing, China
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C50
Keywords: FK506, Hyperglycemia, Post-transplant diabetes
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Complications: Late Graft Failure
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
Session Information
Session Name: Young Investigator Oral Communication Session
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:20pm-5:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:20pm-5:30pm
Location: Room 208
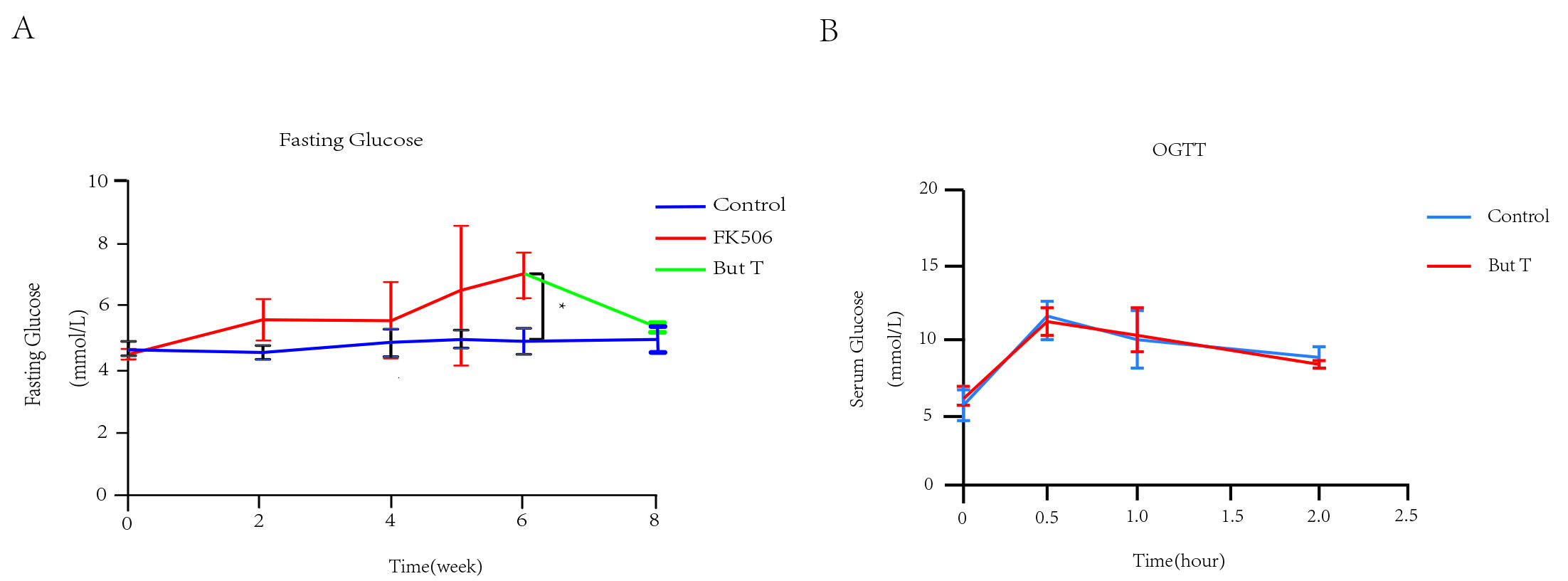
*Purpose: FK506 is one of the most common immunosuppressant drugs in organ transplantation, which have been demonstrated to cause glucose metabolism disorder and alterd the gut microbiota. Meanwhile glucose metabolism was reported influenced by gut microbiota and its metabolites, especially short chain fatty acids (SCFAs). In this article, we indicated the relationship of gut microbiota altered by FK506 and glucose metabolism in mice and also found the improvement in FK506 related glucose metabolism disorder by one of the SCFAs—butyrate.
*Methods: Mice models were established using C57BL6 mice. FK506 was used to induce glucose disorder model in mice. FK506 group(FK506 group)(n=4) were given 10mg/kg of FK506 by gavage each day; Butyrate treated group(But T group)(n=4) were given butyrate in drinking water by 150mM based on the established model; control group(Con group)(n=6) were given 10ml/kg water by gavage. Blood glucose was detected by fasting glucose and oral glucose tolerance test. Comparison of gut microbiota was analyzed by pyro sequencing the 16S rRNA genes. LEfSe(linear discriminant analysis) and PCA(Principal component analysis) were utilized to visualize significant differences in taxa between groups. PICRUSt(Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of unobserved States) analysis was performed to predict the functional capacity of the gut microbiota.
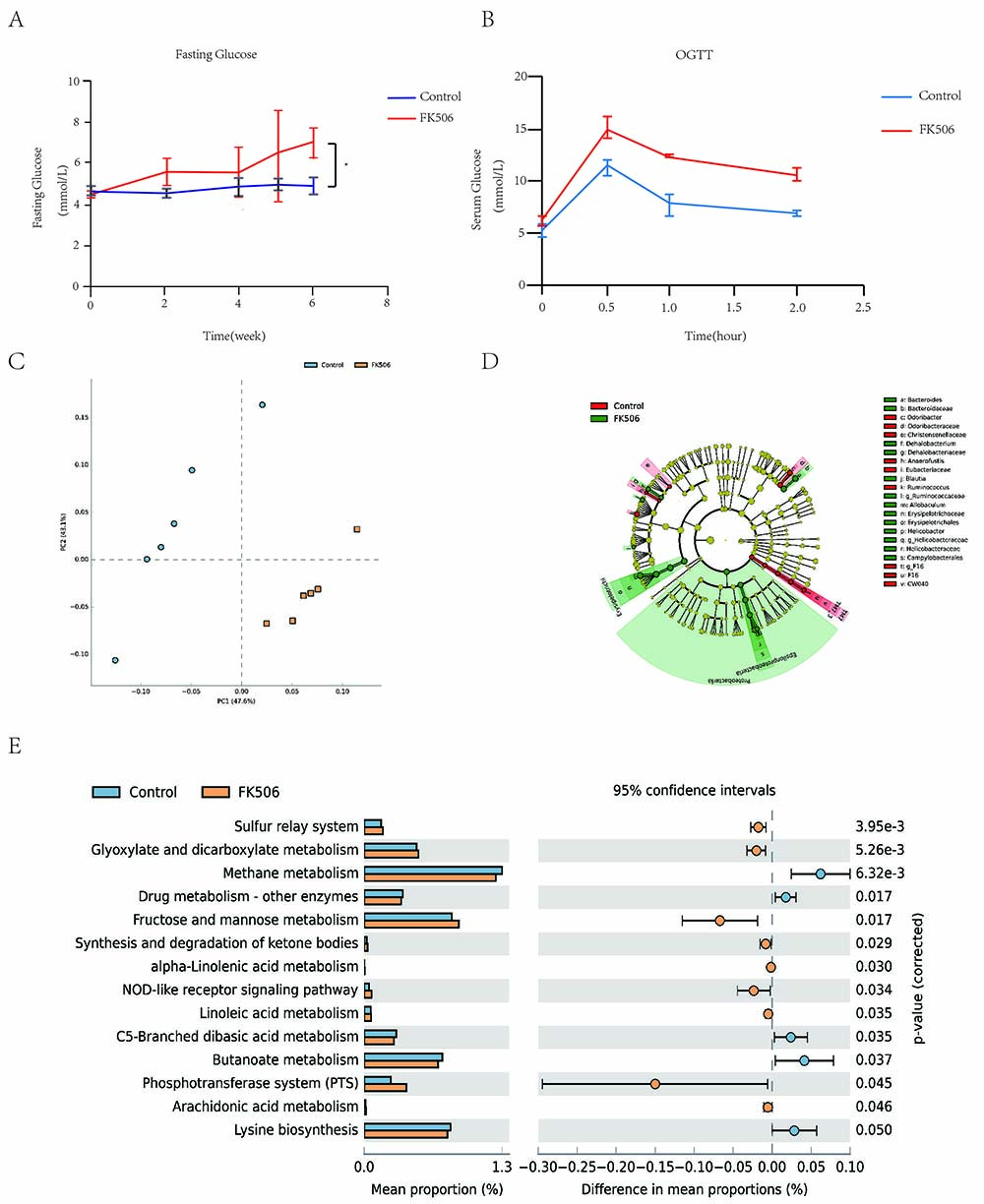
*Results: Glucose disorder model was established at 6th week(Figure 1A1B). We found FK506 group showed significant difference to Con group in phylogenetic classification(Figure1C). The differences in the overall community compositions between FK506 and Con group had shown by LEfSe and PCA(Figure 1C1D). PICRUSt analysis was performed based on the 16S rRNA OTUs table enriched 13 pathways included in 7 metabolic functions’ change(Figure1E).
*Conclusions: According to these findings, the FK506 related glucose metabolism disorder could be efficaciously improved by butyrate orally in mice. Butyrate or the SCFAs could be a newly potential therapeutic target of the post transplantation diabetes mellitus.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jiao W, Zhang Z, Liu L, Hu X. FK506 Influence Glucose Metabolism by Short Chain Fatty Acid [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/fk506-influence-glucose-metabolism-by-short-chain-fatty-acid/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress