Exploring Individual Optimal Immunosuppression Management According to the Oncological Risk in Liver Transplanted Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, 2Massachusetts General Hospital, Belmont, MA, 3Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN, 4University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, 5Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1092
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » 56 - Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Post-Liver transplant (LT) immunosuppression management is the only modifiable factor to prevent hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) recurrence; however, the impact of immunosuppression on the HCC recurrence and optimal immunosuppression management strategy after LT for HCC is not full elucidated. This study aimed to explore the optimal immunosuppression management according to the individual oncological risk of HCC recurrence.
*Methods: This was a multicenter study, which included 1413 adult patients from four institutions. The inclusion criteria were defined as patients who underwent primary LT for HCC between 2002-2019. According to the previous study from the same study cohort, immunosuppression level was evaluated by the time-weighted average tacrolimus (TWAFK) level at 2 weeks after LT and administration of Induction therapy. The oncological risk of individual patients was estimated using HALT-HCC score, which was a continuous risk score consisting of tumor size/tumor number/AFP/MELD score. The predicted probability of recurrence was calculated using the logistic regression model.
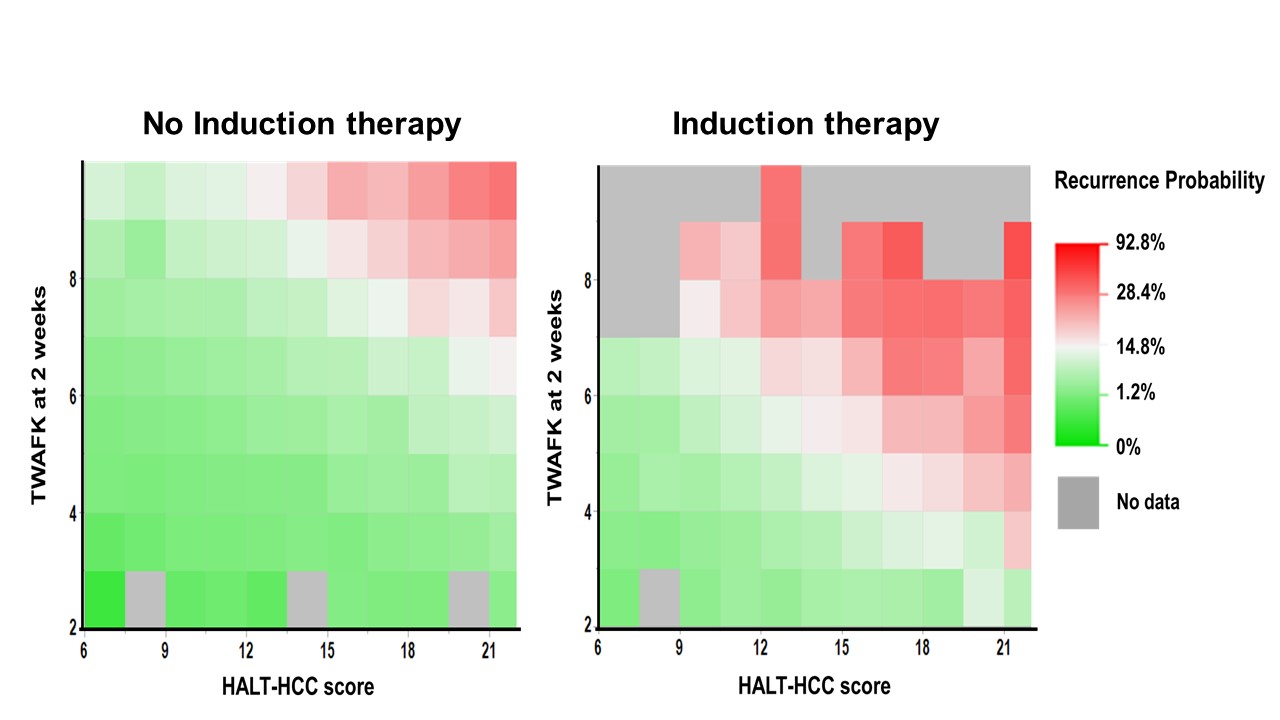
*Results: The median maximum tumor size, tumor number, and preoperative AFP were 2.5 cm, 1, 8 ng/ml, respectively. Pathological vascular invasion was seen in 21.0%. The median HALT-HCC score was 14. TWAFK level at 2 weeks was 6.3 and 8.2 % of patients received induction therapy. The rate of HCC recurrence was 14% of the overall cohort and 5-year recurrence-free survival was 70.9%. Heatmaps for recurrence probability based on HALT-HCC score and FK levels at 2 weeks were generated after separating the patient population into those with and without induction therapy (Figure). Individuals who had higher recurrence probability were demonstrated by the shades of red and those with low risk were demonstrated by the shades of green. According to the heatmaps, the recurrence rate can be reduced by decreasing TWAFK level even if patients have a higher risk of recurrence and vise versa.
*Conclusions: Postoperative immunosuppression management in HCC patients must be individualized according to the risk of recurrence.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sasakik K, Kimura S, Soma D, Tomiyama K, Matthew M, Fruscione M, Kubal C, Kwon D. Exploring Individual Optimal Immunosuppression Management According to the Oncological Risk in Liver Transplanted Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/exploring-individual-optimal-immunosuppression-management-according-to-the-oncological-risk-in-liver-transplanted-patients-with-hepatocellular-carcinoma/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress