Ex-Vivo Perfusion with UW Cold Storage Solution Improves DCD Rat Liver Preservation
Surgery, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D-279
Keywords: Donation, Donors, non-heart-beating, Liver failure, Liver preservation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Ischemia Reperfusion & Organ Rehabilitation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
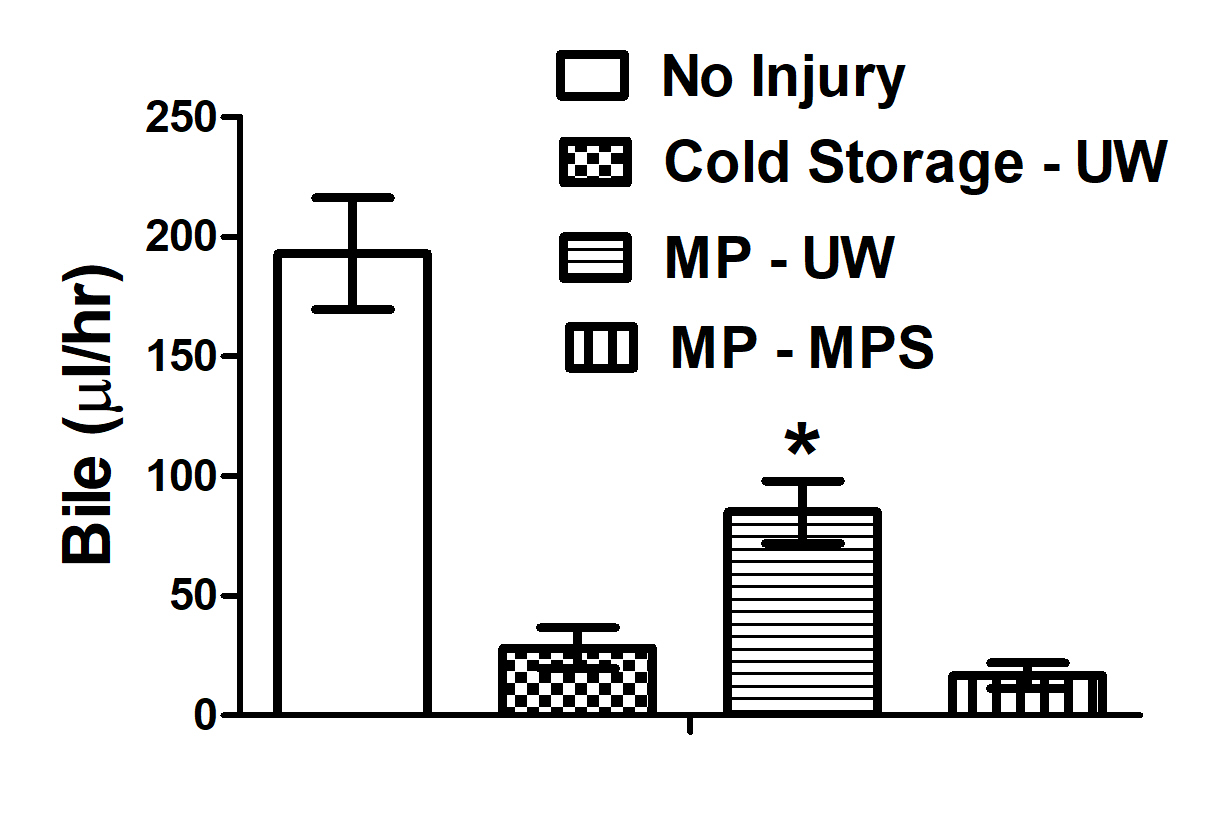
*Purpose: The donor pool of livers can be expanded by the successful use of donor livers recovered under DCD conditions. It is assumed that perfusion preservation using Belzer Machine Perfusion Solution (MPS) is required since it is used for kidneys. However, UW cold storage solution includes different cell impermeants that target mitochondrial failure from calcium overload. Lactobionic acid in UW solution also chelates divalent cations. Since warm ischemia associated with DCD conditions causes calcium overload and mitochondrial injury, we speculated that perfusion with UW solution would be superior to MPS. Therefore, the goal of this study was to determine if machine perfusion with UW cold storage solution was superior to Belzer MPS in rat livers recovered under DCD conditions.
*Methods: Rat livers with 0 or 30 minutes of cardiac arrest ischemia were flushed with UW cold storage solution and randomly assigned to groups: 1.) Sham- Recovered immediately after death and reperfused with Krebs buffer on the isolated perfused liver machine (IPL) to simulate reperfusion after transplantation, 2.) Cold Store-Livers flushed with UW solution, 3.) MP-UW- Livers machine perfused (MP) at 15° C with UW solution, and 4.) MP-MPS- Livers machine perfused at 15° C with Belzer MPS solution. After 4 hours of preservation, all livers were reperfused at 37° C on the IPL for 60 min to assess preservation injury. Outcomes were perfusate flow, oxygen consumption (VO2), Bile synthesis, LDH release, and total tissue water (TTW). Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (P<0.05).
*Results: All outcomes of preservation injury were worse in preserved DCD livers compare to the shams. Perfusate flow, VO2, bile production, and LDH release were all significantly improved when livers were machine perfused with UW cold storage solution compared to MPS. Bile density and TTW were not improved. Machine perfusion with MPS was not significantly different from cold storage with UW solution.
*Conclusions: We conclude that machine perfusion of DCD livers with UW cold storage solution is far superior to perfusion with MPS and should be utilized in clinical reanimation of DCD livers. We speculate that the salutary effect is attributable to the change in calcium chelating impermeants in UW that sequesters intracellular calcium to protect mitochondria and improve bioenergetics at reperfusion. Funded by 1R01DK087737
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fyffe-Freil R, Wickramaratne N, Khoraki J, Kang H, Chmielewski C, Li R, Mangino MJ. Ex-Vivo Perfusion with UW Cold Storage Solution Improves DCD Rat Liver Preservation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/ex-vivo-perfusion-with-uw-cold-storage-solution-improves-dcd-rat-liver-preservation/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress