Evaluation Of Typical Renal Transplant Infections In Simultaneous Heart-kidney Transplant Recipients
E. J. Henricksen1, U. Wang1, R. Lee1, R. Imai1, A. Puing2, A. Couture2, A. Multani3, Y. Moayedi4, C. Lenihan5, K. K. Khush6, J. J. Teuteberg5
1Pharmacy, Stanford Healthcare, Stanford, CA, 2Infectious Diseases and Geographic Medicine, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, 3Infectious Diseases, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, 4Cardiology, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada, 5Department of Medicine, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, 6Medicine, Stanford University, Stanford, CA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C-184
Keywords: Bacterial infection, Heart transplant patients, Infection, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Simultaneous heart-kidney transplant (SHKT) is an increasingly utilized treatment for patients with end stage heart failure and advanced kidney disease. Data regarding infectious complications in this population are limited. The purpose of this study was to examine the incidence of kidney transplant/urinary tract infection after SHKT.
*Methods: This was a retrospective analysis of adult SHKT recipients at a single institution between January 2008 and September 2019. All patients received induction with either antithymocyte globulin or daclizumab, and Pneumocystis jirovecii (PJP) prophylaxis with either trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) or atovaquone was given for 1 year post SHKT. Kidney transplant /urinary tract infections were categorized as 1) urinary tract infection (UTI), 2) BK polyomavirus viremia (BKVV) and 3) urinary adenovirus infection. UTI was defined as a positive urine culture with > 105 cfu/mL warranting treatment. BKV viremia was defined as a positive plasma BKV PCR assay and urinary adenovirus infection was defined as a positive urine adenovirus PCR assay. Primary outcome was incidence of UTI while on PJP prophylaxis. Descriptive statistics were performed on incidence of UTIs, BKV and adenovirus.
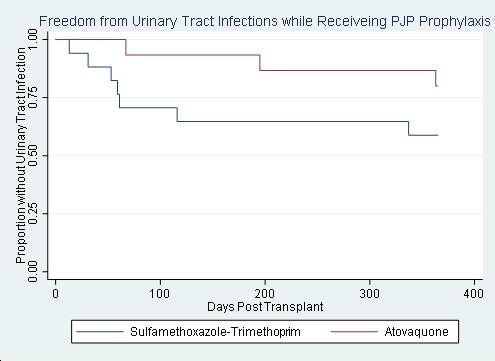
*Results: Of the 32 SHKT recipients, 13 (41%) developed UTI, 7 (22%) were positive for BKVV and 0 (0%) were positive for adenovirus. All UTIs were bacterial, with 10 (77%) occurring while receiving PJP prophylaxis. There was no significant difference in the proportion of patients with UTIs, when comparing agents for PJP prophylaxis (p=0.14) (Figure). Median time to initial UTI was 116 days (59-363). 4 (31%) patients developed 2 or more UTIs. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics between groups.
*Conclusions: A significant number of SHKT recipients develop bacterial UTIs and BKVV post-transplant, with the majority occurring within the first year. We found no urinary adenovirus infections in our cohort. We found no significant difference in UTIs between PJP prophylaxis regimens, although this study was likely underpowered to assess this outcome. Heart transplant providers must remain cognizant of potential renal infections when caring for SHKT recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Henricksen EJ, Wang U, Lee R, Imai R, Puing A, Couture A, Multani A, Moayedi Y, Lenihan C, Khush KK, Teuteberg JJ. Evaluation Of Typical Renal Transplant Infections In Simultaneous Heart-kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/evaluation-of-typical-renal-transplant-infections-in-simultaneous-heart-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress