Evaluation of the Ability of the Integrative Box (ibox) to Predict Kidney Allograft Survival in a Cohort of Brazilian Patients
1Nephrology Division, Hospital do Rim, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2Research Centre for Organ Transplantation, Université de Paris, Paris, France, 3Research Centre for Organ Transplantation, Hospital do Rim, Sao Paulo, Brazil
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C-008
Keywords: Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Kidney transplantation lacks robust models to predict graft survival. The Paris Transplant Group recently developed the iBox system (NCT03474003), a prediction tool that accurately predicts allograft survival by integrating a large spectrum of factors. The iBox was generated on French centers patients and validated in European and North-American centers and 3 RCTs. The goal of this study was to evaluate the performance of the iBox in a South-American center
*Methods: Single center retrospective cohort of kidney recipients, older than 18 years at Hospital do Rim, in São Paulo. All patients underwent risk evaluation comprising a biopsy for cause (graded according to the Banff international classification), functional parameters (glomerular filtration rate and proteinuria), together with assessment of circulating anti-HLA DSA. These data were submitted to the iBox risk evaluation platform to evaluate its ability to predict allograft survival after transplantation
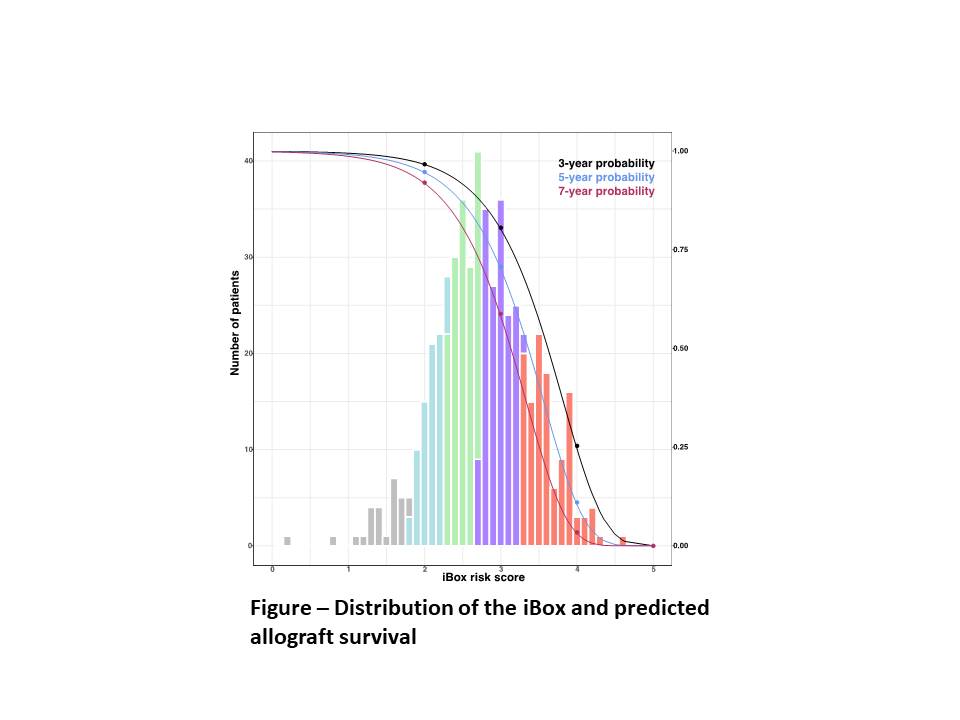
*Results: 536 renal transplant recipients were included in this study. The mean age was of 41.3 ± 14.8 years. The main underlying disease identified was glomerulopathy (19%), followed by diabetes (12.1%). Donors were mostly men (54.5%), with a mean age of 44.7 ± 15.4 years, with 77.2% being deceased and, of these, 26.1% were ECD. Median time from transplantation to iBox risk evaluation was 2.2 years (IQR 1.06 – 3.07). At the time of risk evaluation, the mean GFR was 34.5 ± 15.9 mL/min/1.73m2, with a mean proteinuria level of proteinuria of 0.87 ± 1.3 g/dL, 19.2% of patients presented with circulating anti-HLA DSA. Biopsies were graded according to the Banff criteria. After quality check procedure and database unification to be imported in the iBOx risk assessment platform, the probabilities of allograft survival were calculated with the iBox (Figure). The statistic of concordance was of 0.89, meaning that the iBox accurately separated patients who lose the graft from those who don’t. The calibration was also adequate, showing that the predictions adequately aligned with the observed number of allograft losses
*Conclusions: The iBox demonstrated great performances in predicting the risk of allograft survival in an independent cohort of Brazilian recipients and could be a useful tool to the clinician to adjust prognostic judgments in daily practice
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Linhares K, Raynaud M, Aubert O, Lefaucher C, Gomes G, Peixoto C, Villanueva L, Legendre C, Loupy A, Tedesco-Silva H. Evaluation of the Ability of the Integrative Box (ibox) to Predict Kidney Allograft Survival in a Cohort of Brazilian Patients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/evaluation-of-the-ability-of-the-integrative-box-ibox-to-predict-kidney-allograft-survival-in-a-cohort-of-brazilian-patients/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress