Estimation of Mortality on the Wait List
Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, TX.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 355
Keywords: Allocation, Mortality, Prediction models, Waiting lists
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Liver: MELD, Allocation and Donor Issues - 1
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:18pm-5:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:18pm-5:30pm
Location: Room 6B
Background: Since the introduction of MELD and MELDNa, the waitlist population has changed. Further, serum creatinine is a poor surrogate of renal dysfunction in patients with liver disease. Recently we developed and validated a novel equation for GfR Assessment In Liver disease (GRAIL, bun, cr, alb, inr, gender, race, www.bswh.md/grail). We examined (1) whether MELD and MELDNa perform well in a contemporary cohort and (2) whether incorporation of eGFR instead of creatinine improves performance of predictive models.
Methods: Using data submitted to the SRTR, we examined 2 cohorts (2000-2004, n=23,852 and 2011-2012, n=13,912) of adult candidates awaiting LT. Primary outcome was mortality w/n 90 days of listing. Cox proportional-hazards analyzed the association between MELD, MELDNa, GRAIL-MELD (br,inr,grail), GRAIL-MELDNa (br,inr,na,grail) and WL mortality. Discrimination (Harrel's concordance statistic) and calibration (difference in observed vs. predicted mortality) was assessed.
Results: MELD (c=0.82) and MELDNa (c=0.79) were excellent predictors of WL mortality in 2000-2004. However, the performance was worse in 2011-2012 (c statistic=0.72). Discrimination across strata of MELD score were poor (c<0.6) and was 0.5 in the highest MELD groups.(Table)
Incorporation of estimated GFR (GRAIL) had better performance in both historical (c=0.83) and contemporary datasets (c=0.72). Performance was higher for GRAIL-MELDNa across all strata, especially at higher MELD scores.(Table)
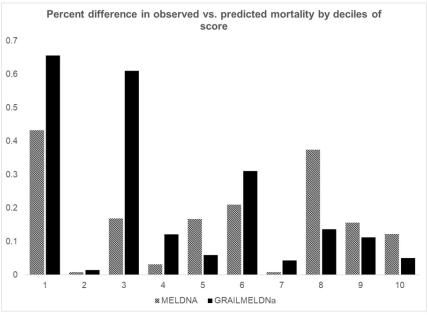
Calibration: GRAIL-MELDNa had lower percent difference between observed and predicted mortality across higher deciles of the score as compared to MELDNa.
Conclusion: Performance of MELD and MELDNa is worse in recent era, especially across higher scores, yet used for organ allocation. Incorporation of eGFR, in GRAIL-MELDNa improves discrimination and calibration and likely captures true GFR better than serum creatinine or Na alone.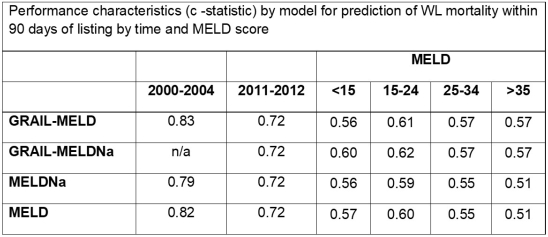
CITATION INFORMATION: Asrani S., Jennings L., Trotter J., Klintmalm G. Estimation of Mortality on the Wait List Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Asrani S, Jennings L, Trotter J, Klintmalm G. Estimation of Mortality on the Wait List [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/estimation-of-mortality-on-the-wait-list/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
