Epidemiology of Post Transplant Diabetes Mellitus
S. Al Rasbi, I. Salmi
Renal Medicine Department, The Royal Hospital, Bausher, Oman
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 794
Keywords: Hyperglycemia, Kidney, Metabolic complications, Obesity
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 35 - Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 4, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a common non-communicable disease and have serious metabolic complications that contribute to death, major cardiovascular events, organs failure, and increased medical costs. The development of DM post kidney transplant (PTDM) is a serious health concern among our patients. Hence, this study aims to explore the epidemiology of PTDM among patients and examines the demography, clinical data, and investigatory tests for glucose control among transplant patients.
*Methods: This is an observational retrospective study of all non-diabetic patients who underwent kidney transplant and followed-up at the Royal Hospital, a tertiary care hospital in Muscat, Oman during (2010-2020). All clinical, laboratory, and radiological data were collected from patients’ electronic medical record system. Patients who had DM before the kidney transplant were excluded.All statistical tests were performed at a significance level of P = 0.050.
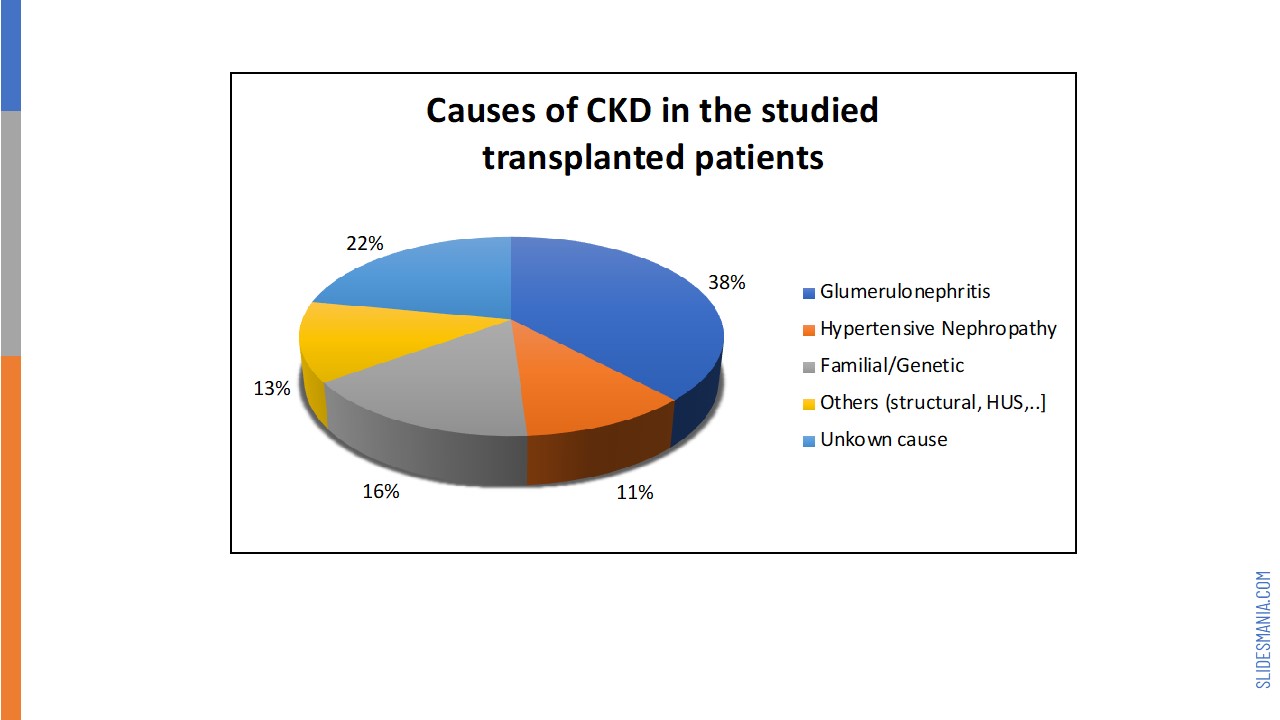
*Results: there was a total of 204 patients, 57.4% were male with a median age of 44.7 years (range: 15-82). The commonest cause of chronic kidney disease was glomerulonephritis (38.2%). PTDM developed in 69 (33.8%) patients with a mean of 43.0 months from time of transplantation. Body mass index (BMI), family history of DM, age at transplantation, renal replacement therapy prior to transplant, and donor type were statistically significant risk factors for PTDM. In the multivariant analysis, older age (odd ratio (OR) = 1.046, gender (OR = 1.797;and BMI (OR = 1.079 were significant risk factors for the development of PTDM. Death was observed in six patients, four in PTDM group. While graft rejection occurred in 18 patients, six in PTDM group. PTDM was treated differently and most of them were managed by oral hypoglycaemic agents and insulin.
*Conclusions: age, gender, and BMI are the main risk factors for development of PTDM. Hence, an early (pre-transplant period) healthy lifestyle changes including exercise, diet, and weight reduction may decrease the risk of development of PTDM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rasbi SAl, Salmi I. Epidemiology of Post Transplant Diabetes Mellitus [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/epidemiology-of-post-transplant-diabetes-mellitus/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress