End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) Patients' Willingness to Accept Risks to Living Kidney Donors.
1Yale University, New Haven
2University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
3Northwestern University, Chicago.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C167
Keywords: Donation, Ethics, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Donor Evaluation and Donor Nephrectomy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background: While many potential living kidney donors (LKDs) are willing to accept high levels of ESRD risk, receipt of a living donor kidney is also contingent on recipient attitudes about risks to donors. Therefore we explored potential recipients' acceptance of ESRD risks for LKDs.
Methods: We conducted a single center, prospective study of ESRD patients being evaluated for kidney transplantation. Using a novel 10,000 dot diagram, participants indicated the highest chance of a LKD getting ESRD that they were willing to accept (WTA ESRD). They also completed surveys related to risk taking behavior and demographics. Due to a non-normal distribution, WTA ESRD was analyzed as a categorical variable in quartiles. Ordinal logistic regression assessed factors associated with WTA ESRD.
Results: Our study includes 52 potential kidney transplant recipients (response rate 68%). Participants were 54% male, 52% completed some college; the mean age was 54 years. Thirty-seven percent were employed and 65% earned <$65,000/year. Half were on dialysis (median 15 months).
Recipients were willing to accept a median of 1% chance that a LKD develop ESRD. 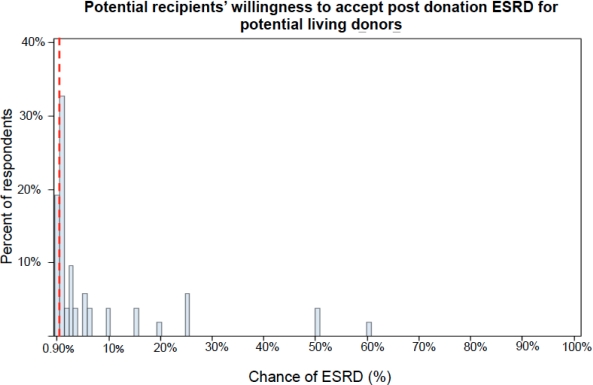 21% accepted a maximum risk at or below 0.9%, the documented chance that donors develop ESRD. In unadjusted analysis, having a potential LKD was associated with higher WTA ESRD (OR 5.84, p<0.001). Dialysis status, time on dialysis, education, and risk-taking propensity were not associated with WTA ESRD. After adjusting for these variables, having an identified potential donor remained significantly associated with increased WTA ESRD (OR 6.70, p<0.001).
21% accepted a maximum risk at or below 0.9%, the documented chance that donors develop ESRD. In unadjusted analysis, having a potential LKD was associated with higher WTA ESRD (OR 5.84, p<0.001). Dialysis status, time on dialysis, education, and risk-taking propensity were not associated with WTA ESRD. After adjusting for these variables, having an identified potential donor remained significantly associated with increased WTA ESRD (OR 6.70, p<0.001).
Conclusion: Most (79%) potential recipients accept at least the current level of 0.9% ESRD risk for potential LKDs (Muzaale 2014); 21% of potential recipients are more averse to LKD risks. Future research should assess why transplant candidates are willing to accept greater risks if they have a potential LKD. Transplant professionals' understanding of candidates' attitudes about risks to LKDs will enhance informed consent and facilitate dialogue between potential donors and recipients.
CITATION INFORMATION: Gannon J, Thiessen C, Yu K, Skrip L, Reese P, Gordon E, Kulkarni S. End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) Patients' Willingness to Accept Risks to Living Kidney Donors. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gannon J, Thiessen C, Yu K, Skrip L, Reese P, Gordon E, Kulkarni S. End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) Patients' Willingness to Accept Risks to Living Kidney Donors. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/end-stage-renal-disease-esrd-patients-willingness-to-accept-risks-to-living-kidney-donors/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
