Efficacy of Everolimus with Reduced Cyclosporine in Japanese De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients: 24-Month, Randomized, Multicenter Study
Niigata University, Niigata, Japan
Aichi Medical University, Aichi, Japan
Osaka University, Osaka, Japan
Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan
International University of Health and Welfare, Atami Hospital, Shizouka, Japan
Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland
Jichi Medical University, Tochigi, Japan
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B944
Introduction: Results from study A1202 showed that everolimus (EVR) plus reduced dose cyclosporine (rCsA) prevents acute rejection, preserves renal function, and reduces incidence of viral infections in Japanese de novo renal transplant recipients (RTxR). Here, we present 24 month (M) data from A1202E1, an extension to the core study evaluating longer-term efficacy and safety of EVR with rCsA vs. mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) with standard dose CsA (sCsA). Selected M48 results for the EVR group are also presented.
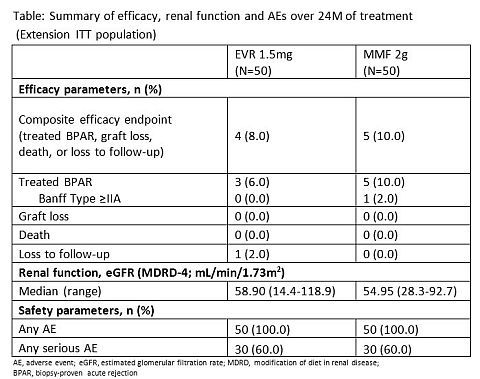
Methods: A1202E1 is a 24M, randomized, open-label, multicenter study wherein RTxR (rolled over from core study) were randomized (1:1) to receive either EVR (C0 3-8ng/mL)+rCsA (N=50) or MMF (2g/day)+sCsA, (N=50). All patients received basiliximab and corticosteroids. Key endpoints were composite efficacy failure rate (tBPAR, graft loss, death, or loss to follow-up), renal function (eGFR; MDRD-4), and safety comparisons between EVR and MMF groups at M24.
Results: At M24 median CsA C0 in the EVR group was 48% lower than for the MMF group. Consistent with the 12M results, median eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2) was numerically higher with EVR (58.90) vs. MMF (54.95; p=0.226) at M24. Renal function was maintained in patients who continued on EVR to M48 (median; 59.80). Composite efficacy failure rate was comparable in EVR and MMF over 24M. Overall incidence of AEs and serious AEs at M24 were similar in both groups and comparable to M12 post-Tx (table). Viral infections were less frequent in EVR vs. MMF, due to higher incidence of CMV NOS in the MMF group (20% vs. 72%). No graft loss or death was observed.
Conclusion: The 24M results confirm that EVR (C0 3-8ng/mL) plus rCsA provides numerically higher renal function and overall comparable efficacy and safety to MMF with sCsA treatment in Japanese de novo RTxR.
Saito, K.: Speaker’s Bureau, Novartis. Uchida, K.: Speaker’s Bureau, Novartis. Takahara, S.: Speaker’s Bureau, Novartis. Yoshimura, N.: Speaker’s Bureau, Novartis. Teraoka, S.: Speaker’s Bureau, Novartis. Cornu-Artis, C.: Employee, Novartis. Kobayashi, E.: Grant/Research Support, Novartis, Speaker’s Bureau, Novartis, Other, Novartis, Advisor, Otsuka, Advisor. Takahashi, K.: Speaker’s Bureau, Novartis, Other, Novartis, Advisor.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Saito K, Uchida K, Takahara S, Yoshimura N, Teraoka S, Cornu-Artis C, Kobayashi E, Takahashi K. Efficacy of Everolimus with Reduced Cyclosporine in Japanese De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients: 24-Month, Randomized, Multicenter Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/efficacy-of-everolimus-with-reduced-cyclosporine-in-japanese-de-novo-renal-transplant-recipients-24-month-randomized-multicenter-study/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
