Efficacy and Safety of PCSK-9 Inhibitor, Evolocumab for Lipid Management in Kidney Transplant Recipients
J. Pandav1, R. Saranu1, S. Muhsin1, N. Murakami1, S. Gabardi1, K. Safa2, A. Chandraker1
1Renal division, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, 2Renal division, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 770
Keywords: Dyslipidemia, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 35 - Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 4, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Dyslipidemia is common in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs). KDIGO guidelines suggest all KTRs should be treated with statins due to the high risk of ischemic heart disease. However, due to myopathy, hepatotoxicity, and interactions with calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs), statins are less well tolerated in KTRs. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/Kexin type 9 (PCSK-9) inhibitors is a novel FDA-approved medication class used for the treatment of low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C). The use of these agents has not been studied in KTRs. Our study was aimed at evaluating the efficacy and safety of PCSK-9 inhibitor, Evolocumab in KTRs.
*Methods: KTRs at least 1-year post-transplant with baseline LDL-C levels >100 mg/dL or >70 mg/dL with risk factors such as diabetes, coronary artery disease, or smoking were eligible for the study. Baseline lipid panel was checked and ASCVD scores were calculated after which they were started on Evolocumab 140 mg subcutaneously every 2 weeks. Patients previously on statin therapy were asked to continue their medication. At the end of 3 months, lipid panel, ASCVD scores, and kidney function were checked. The total target enrollment is 120 patients with a follow-up period of 1 year. Lipoprotein A, Apolipoprotein A1/B, CPK, and LFTs and tacrolimus levels are also being followed. Currently, 30 patients are consented and 12 patients have completed 3 months follow up.
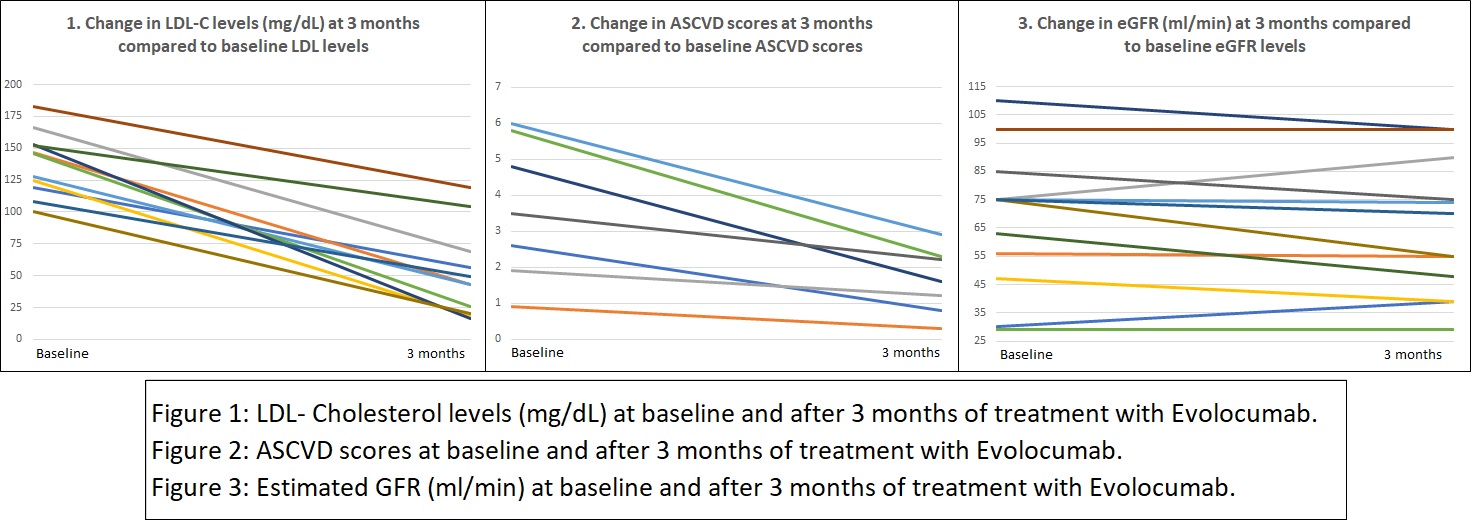
*Results: At the end of 3 months of treatment, all 12 patients demonstrated a significant drop in their LDL-C levels (35% to 90%). There was also a remarkable reduction in ASCVD scores (37% to 80%). The mean eGFR for all patients was stable. Overall, Evolocumab was well tolerated by all patients. One patient had a local allergic reaction, treatment was stopped and they were excluded from the study. None of the other 12 patients reported any major adverse reactions.
*Conclusions: PCSK-9 inhibitors are very effective for the reduction of LDL-C levels in KTRs. They have a favorable side effect profile and do not interact with immunosuppressive medications. Their effect on the reduction of LDL-C levels also correlates with an improvement in ASCVD score, which was clearly demonstrated in this study. Unlike statins, which have shown cardiovascular benefits in long-term studies, there is no data regarding PCSK-9 inhibitors as trials are still underway. Our analysis is a part of an ongoing prospective study that is aimed at studying the long-term benefits of PCSK-9 inhibitors on LDL-C levels and allograft function.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pandav J, Saranu R, Muhsin S, Murakami N, Gabardi S, Safa K, Chandraker A. Efficacy and Safety of PCSK-9 Inhibitor, Evolocumab for Lipid Management in Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-pcsk-9-inhibitor-evolocumab-for-lipid-management-in-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress