Effects of Everolimus and Tacrolimus Exposure on Efficacy and Renal Function in Liver Transplant Recipients at 24 Months in a Randomized Trial (H2304)
For the H2304 Study Group, Hamburg, Germany
Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 282
Purpose: The present analysis aims to explore the effect of everolimus (EVR) and tacrolimus (TAC) exposure on efficacy and safety events of interest in de novo liver transplant recipients (LTxR).
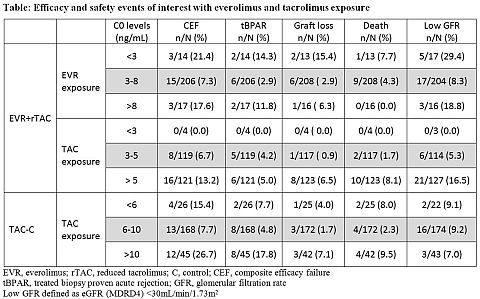
Method: The H2304 trial is a 24-month (M), multicenter, open-label study (NCT00622869) in de novo LTxR. 719 study patients were randomized after a 30-day run-in period with TAC ± mycophenolic acid to receive either EVR (C0 3-8 ng/mL) with reduced TAC (C0 3-5 ng/mL; EVR+rTAC, N=245) or EVR (C0 6-10 ng/mL) with TAC withdrawal (TAC-WD; N=231) at M4 or standard TAC (C0 6-10 ng/mL; TAC-C, N=243); all with steroids. Here we present effects of EVR and TAC exposure (calculated as time-normalized trough level averages) on composite efficacy failure (CEF; treated biopsy-proven acute rejection [tBPAR]/graft loss/death) and its individual components, and low estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR by MDRD4; low eGFR defined as <30 mL/min/1.73m2).
Results: Enrollment in TAC-WD arm was prematurely terminated due to a higher rate of acute rejection. At M24, EVR+rTAC group showed comparable CEF rates and superior renal function compared to TAC-C (mean difference 6.66 mL/min/1.73m2, p=0.0018). In the EVR+rTAC arm the target EVR exposure of 3-8 ng/mL was associated with fewer efficacy failure rates and less incidences of low eGFR compared to EVR exposure of <3 ng/mL and >8 ng/mL (table). The target TAC exposure of 3-5 ng/mL in EVR+rTAC arm had fewer incidences of low eGFR compared to target TAC exposure of 6-10 ng/mL in TAC-C arm. The Cox model showed a higher risk of developing CEF (hazard ratio [HR]=1.30, p<0.001) or tBPAR (HR=1.29, p=0.014) or low eGFR (HR=1.32, p<0.001) with higher TAC exposure in the EVR+rTAC arm. The EVR exposure was not significantly correlated with renal function events (HR=1.139, p=0.247).
Conclusion: EVR C0 3-8 ng/mL with TAC C0 3-5 ng/mL provided good efficacy and renal function. Higher TAC C0 levels have a detrimental impact on renal function.
Fischer, L.: Grant/Research Support, Novartis, Astellas, Gilead. Koneru, B.: Grant/Research Support, Proteonomix, Inc. Durand, F.: Grant/Research Support, Gilead, Roche, Other, Novartis, Consultant, Astellas, Consultant. Heaton, N.: Grant/Research Support, Astellas, Speaker’s Bureau, Novartis. Shetty, K.: Grant/Research Support, Gilead, Ikaria, Beckman Coulter, Bayer, Novartis, Speaker’s Bureau, Salix, Gilead, Merck, Onyx. Dong, G.: Employee, Novartis. Lopez, P.: Employee, Novartis. Junge, G.: Employee, Novartis. Kovarik, J.: Employee, Novartis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fischer L, Kaiser G, Koneru B, Toselli L, Durand F, Heaton N, Shetty K, Dong G, Lopez P, Junge G, Kovarik J. Effects of Everolimus and Tacrolimus Exposure on Efficacy and Renal Function in Liver Transplant Recipients at 24 Months in a Randomized Trial (H2304) [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/effects-of-everolimus-and-tacrolimus-exposure-on-efficacy-and-renal-function-in-liver-transplant-recipients-at-24-months-in-a-randomized-trial-h2304/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
