Effect of Vasodilators on Organ Function during Normothermic Machine Perfusion of Porcine DCD Liver, The
Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B1143
Introduction: Shortage of donor livers and prolonged wait list mortality has lead to the need of using extended criteria donors. Donation after Cardiac Death (DCD) livers with prolonged Warm Ischemia Time (WIT) represents a wide pool of organs for clinical use. Organs that have been transplanted from DCD donors have shown a significant increase in the formation of biliary strictures 6-12 months after transplant. Here we show the effect of using different vasodilators during normothermic machine perfusion (NMP), on the microcirculation and rate of bile production in porcine DCD livers.
Materials and methods: Livers from 8 Female Yorkshire pigs (30-40 kg) were subjected to 60 minutes of WIT followed by 10 hours of NMP. In Group A (n=4) Epoprostenol sodium (Prostaglandin I2) was used as a vasodilator and Adenosine was used in group B (n=4). Livers were assed in terms of bile production hepatic enzyme levels and histological micro-architecture at the end of perfusion.
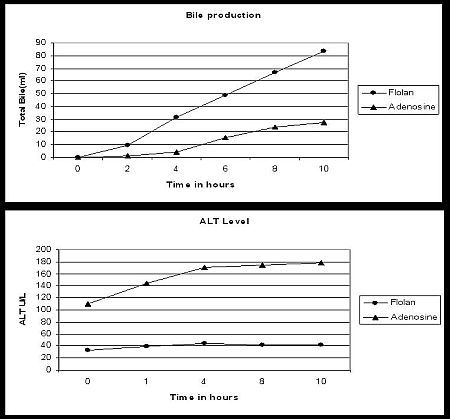
Results: Group A livers showed a significantly higher rate of bile production (101.75±16.5 ml) than group B livers (27.5±22ml), p= 0.002. ALT level was (43±10 U/L) for group A and (179±80 U/L) for group B, p= 0.04.
Histological samples of group A showed preserved hepatic architecture while those of group B showed some areas of sinusoidal dilatation and hemorrhage.
Conclusion: Vasodilators used during NMP can significantly affect the rate of bile production and improve the hepatic micro-architecture of DCD livers.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nassar A, Liu Q, Farias K, Tom C, D'Amico G, Bennett A, Abu-Elmagd K, Fung J, Miller C, Quintini C. Effect of Vasodilators on Organ Function during Normothermic Machine Perfusion of Porcine DCD Liver, The [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/effect-of-vasodilators-on-organ-function-during-normothermic-machine-perfusion-of-porcine-dcd-liver-the/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
