Effect of Human Adipose Derive Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Regeneration in Humanized Mice, The
University of Massachusetts, Worceste
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C1297
Liver ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a well-known cause of morbidity and mortality following Liver transplantation. Effective treatment strategies aimed at reducing hepatic IRI injury and accelerating liver regeneration could offer major benefits in LT.
Recent reports have demonstrated the capacity of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to specifically be involved in the repair of organ tissue. We investigated the effect of human adipose derive MSC (HAD-MSC) on IRI and liver regeneration.
HAD-MSC were isolated from the perinephric fat of living kidney donors. Humanized mice (NOD-scid ILr2gnull ) were subjected to 30 minutes of 70% partial IRI with and without 70% partial hepatecotomy (PH). Animals were treated with intravenous HAD-MSC (1-2x 106) or normal saline. IRI injury was evaluated using serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), serum interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1, TNF-alpha and specific markers of regeneration (BrdU staining and PCNA) and hematoxylin and eosin staining.
Histology, serum IL-6, IL-1, TNF-alpha and ALT release revealed that HAD-MSC provided significant protection against IRI+-PH compared with controls Improved animal survival and increased number of BrdU positive cells were observed in treated animal which underwent IRI/PH compared to control group.
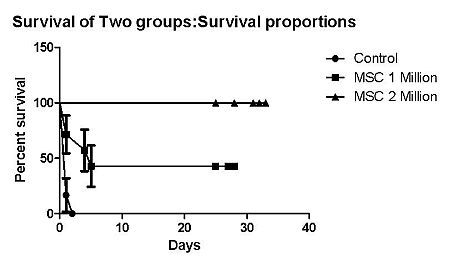
These data indicate that HAD-MSC plays a key role in IRI and liver regeneration. HAD-MSC represents a potential strategy to reduce IRI and promote regeneration in liver transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Saidi R, Rajeshkumar B, Walter O, Shariftabrizi A, Dresser K, Movahedi B, Jabbour N, Bozorgzadeh A. Effect of Human Adipose Derive Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Regeneration in Humanized Mice, The [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/effect-of-human-adipose-derive-mesenchymal-stem-cells-on-liver-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-and-regeneration-in-humanized-mice-the/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
