Early Utilization of Telehealth in Kidney Transplantation
Transplant Institute, University Hospitals of Cleveland, Cleveland, OH.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D76
Keywords: Kidney, Outpatients, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney Complications: Late Graft Failure
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Introduction: Telehealth is an emerging strategy to improve outcomes and decrease emergency department visits and readmissions. Utility of telehealth in kidney transplantation hasn't been much explored.
Methods: This is a retrospective observational study where we compared kidney transplant recipients discharged on telehealth pilot to historical controls. Our center instituted a Telehealth Kidney Program (TKP) in 2014, which consists of a one time intensive home visit by a home care RN (after discharge from hospitalization for kidney transplantation), the installation of the telehealth monitor (Cardiocom), daily monitoring and a daily phone call by a telehealth nurse up to one to two weeks. After vital signs are transmitted daily, a detailed phone call with clinically relevant questions is placed by RN to the patient. All the information is then communicated to physician. We studied effect of telehealth on ED visits, early hospital readmission (within 30 days), biopsy proven acute rejection, and one year graft survival.
Results: 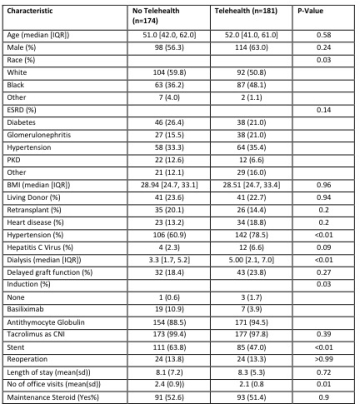 shows baseline characteristics of the study cohort stratified by telehealth utilization.
shows baseline characteristics of the study cohort stratified by telehealth utilization.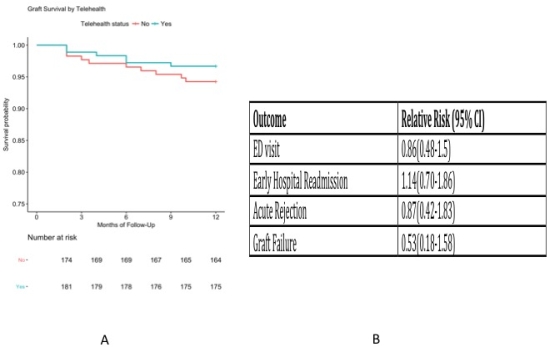 shows KM curves for graft failure stratified by telehealth, and relative risks of other outcomes for telehealth of multivariable model adjusted for baseline characteristics that had p-value of less than 0.2.
shows KM curves for graft failure stratified by telehealth, and relative risks of other outcomes for telehealth of multivariable model adjusted for baseline characteristics that had p-value of less than 0.2.
Telehealth resulted in slight reduction of ED visits, acute rejection, graft failure and slight increase in early hospital readmission but none of these reached statistical significance.
Conclusion: In this pilot study, utilization of telehealth didn't significantly change kidney transplant outcomes. However, its utilization needs to be further explored at a larger scale.
CITATION INFORMATION: Young T., Hricik D., Sanchez E., Sarabu N. Early Utilization of Telehealth in Kidney Transplantation Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Young T, Hricik D, Sanchez E, Sarabu N. Early Utilization of Telehealth in Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/early-utilization-of-telehealth-in-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
