Early Hospital Readmisison Among Older Kideny Transplant Recipients.
Surgery, Johns Hopkins University, School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C257
Keywords: Elderly patients, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Poster Session 1: Kidney Complications-Other
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
BACKGROUND: We previously established 31% of all kidney transplant (KT) recipients experience early hospital readmission (EHR). We hypothesized that rates of EHR might be higher for older (>65) KT recipients, and that risk factors might be different.
METHODS: We used USRDS data to study 70,852 adult Medicare primary first time older KT recipients from December 1999–October 2011. EHR was any hospitalization within 30 days of initial KT discharge. Modified Poisson Regression was used to determine the association between readmission and patient characteristics. Empirical Bayes estimation was used to explore variation in readmission of older recipients by center.
RESULTS: The crude incidence of readmission for older KT recipients was 34.2%, which is slightly higher than for KT recipients younger than 65 (31.8%, p <0.001). In a sub-group analysis of older KT recipients, age was associated with readmission such that there was no increase in baseline risk from age 65 to 70 (IRR 1.00, 95% CI: 0.99-1.02, p=0.7), however over the age of 75 each one year increase in age was associated with a 2% increased risk of readmission (1.02, 95%CI 1.01-1.03, p=0.001). For example, readmission rates among 80+ year olds were 45.6%. African American race, obesity, diabetes, history of cancer, dialysis vintage, donor age, extended criteria donor, and transplant length of stay were also associated with higher readmission rates.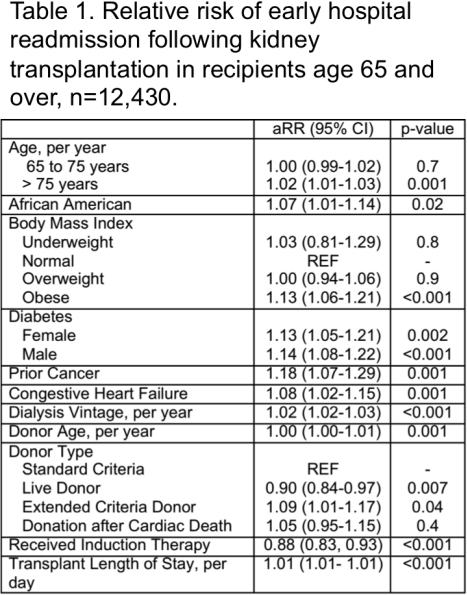 After adjusting for patient-level risk, there was little variation across centers in the incidence of readmission for older recipients.
After adjusting for patient-level risk, there was little variation across centers in the incidence of readmission for older recipients.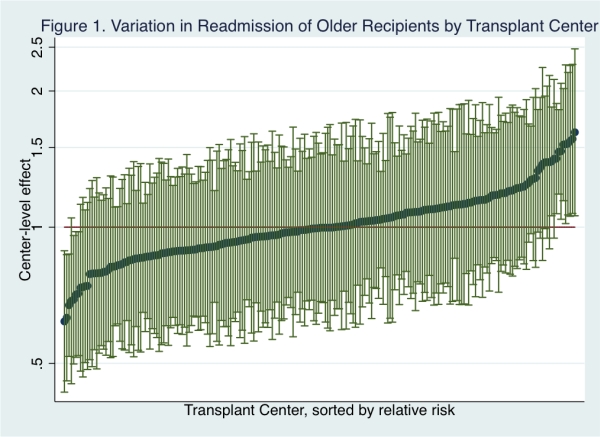
CONCLUSIONS: Rates of readmission and risk factors for readmission among older KT recipients were similar to readmission among KT recipients of all ages. The oldest KT recipients were more vulnerable to readmission and may benefit from more regular outpatient follow-up after KT discharge.
CITATION INFORMATION: King E, Kucirka L, McAdams-DeMarco M, Al-Ammary F, Segev D. Early Hospital Readmisison Among Older Kideny Transplant Recipients. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
King E, Kucirka L, McAdams-DeMarco M, Al-Ammary F, Segev D. Early Hospital Readmisison Among Older Kideny Transplant Recipients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/early-hospital-readmisison-among-older-kideny-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
