Early Clinical Experience With Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir For Treatment Of Covid-19 In Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
1NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY, 2Long Island University, Brooklyn, NY, 3Pharmacy, NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY, 4Columbia University Irving Medical Center, Fort Lee, NJ, 5New York Presbyterian Hospital, Tenafly, NJ, 6Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, 7New York Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 9019
Keywords: COVID-19, Drug interaction, Immunosuppression
Topic: Clinical Science » Pharmacy » 29 - Non-Organ Specific: Pharmacokinetics / Pharmacogenomics / Drug interactions
Session Information
Session Name: Late Breaking: Clinical
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:40pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:40pm
Location: Hynes Room 313
*Purpose: Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir use has not yet been described in solid organ transplant recipients (SOTR) who become infected with COVID-19. The objective of our study was to evaluate outcomes among a heterogeneous population of SOTR and quantify the drug-drug interaction with commonly used immunosuppressive medications.
*Methods: This is an IRB-approved, retrospective study of all adult SOTR on a calcineurin inhibitor or mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor who were prescribed nirmatrelvir/ritonavir between 12/28/21 and 1/6/2022.
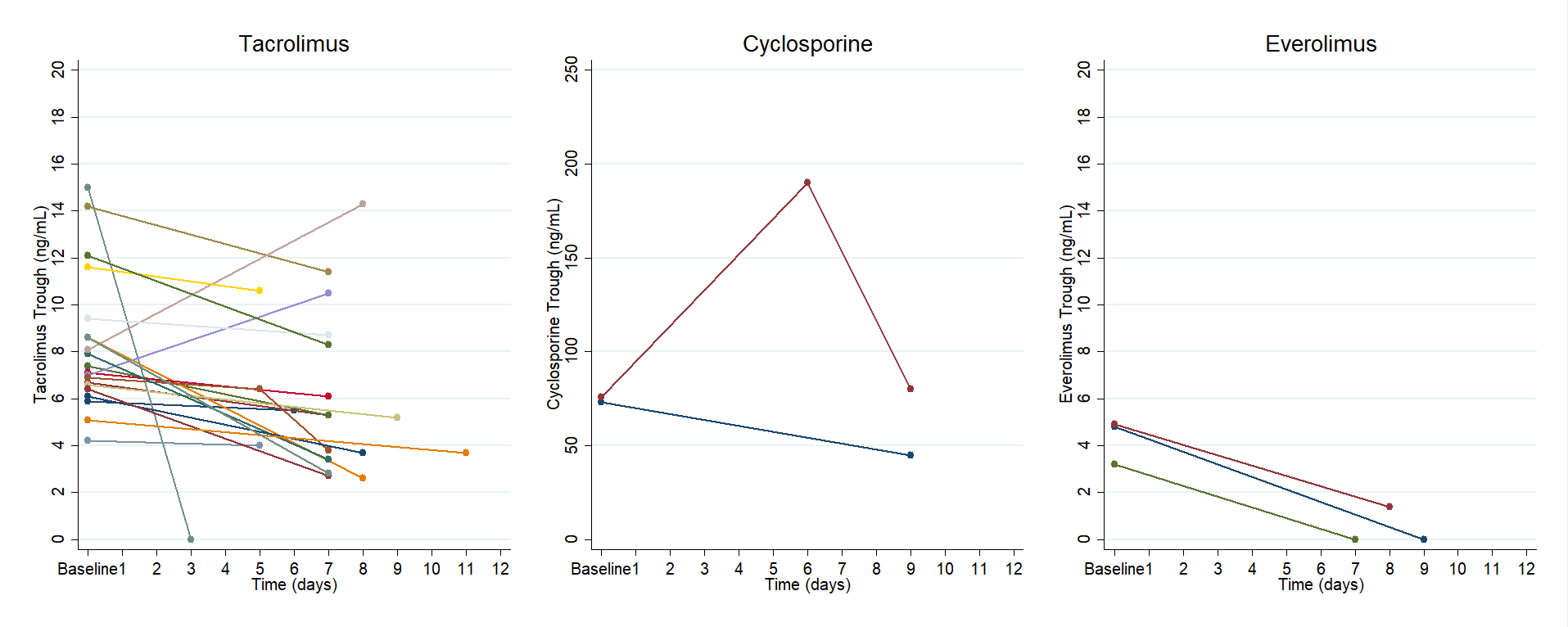
*Results: A total of 26 adult SOTR were included (n=20 tacrolimus, n=4 cyclosporine, n=3 everolimus, n=1 sirolimus). All patients were instructed to follow the following standardized protocol during treatment with 5 days of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir: hold tacrolimus, reduce cyclosporine dose to 20% of baseline daily dose, and/or hold everolimus/sirolimus. Two patients (7.7%) were hospitalized; one patient for symptoms related to COVID-19 and the other for infectious diarrhea. No patients died within 12 days of receipt of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir. Median time to first CNI trough from completion of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was 2 days (IQR, 1 – 3). Median tacrolimus trough concentration pre- and post-nirmatrelvir/ritonavir were 7.7 ng/mL (IQR, 6.6 – 8.6) and 5.3 ng/mL (IQR, 3.6 – 8.5), respectively. One patient on cyclosporine had trough concentrations pre- and post- nirmatrelvir/ritonavir of 73 ng/mL and 45 ng/mL (day 9), while the other patient had a trough of 75.9 ng/mL prior and 190 ng/mL and 80 ng/mL on days 6 and 9, respectively. Median everolimus trough concentration prior to receipt of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was 4.8 ng/mL (IQR, 3 – 4.9). Everolimus trough concentrations post-nirmatrelvir/ritonavir were undetectable in two patients on day 7 and day 9, and 1.4 ng/mL on day 8 in the third patient.
*Conclusions: Our results suggest that nirmatrelvir/ritonavir may be an effective therapy to prevent COVID-19-related hospitalization and death in SOTR. Furthermore, the clinically significant interaction between nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and immunosuppressive agents can be reasonably managed with a standardized dosing protocol.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Salerno D, Jennings D, Lange N, Kovac D, Shertel T, Chen J, Hedvat J, Scheffert J, Brown RS, Pereira M. Early Clinical Experience With Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir For Treatment Of Covid-19 In Solid Organ Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/early-clinical-experience-with-nirmatrelvir-ritonavir-for-treatment-of-covid-19-in-solid-organ-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress