Early And Late Borderline Lesions Exhibit Differential Outcomes In Renal Transplant Recipients
1University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 2The Christ Hospital, Cincinnati, OH
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C169
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: A major distinguishing factor in the risk of acute rejection episodes that markedly affects graft survival is the timing of the rejection episode. Early and late acute cellular rejection, antibody mediated rejection, and mixed acute rejection have been reported by several groups to pose differential risks to the renal allograft. However, temporal effects have not previously been analyzed for borderline lesions. Additionally, the roles of donor specific antibodies (DSA) and C4d staining positivity in borderline lesions are unknown. This study presents 5-year outcomes of borderline lesions based on early versus late time post-transplant and the presence of DSA and C4d positivity.
*Methods: Patients with a biopsy-proven borderline lesion from 2000 to 2014 who received rATG induction were included. All biopsies were for-cause. Patients with a prior biopsy-proven acute rejection (BPAR) or concurrent ABMR were excluded. Patients who were maintained on belatacept therapy or who received treatment for the borderline lesion other than increased maintenance immunosuppression (IS) or corticosteroid therapy were excluded. Early borderline lesions were defined as those diagnosed within the first 180 days post-transplant.
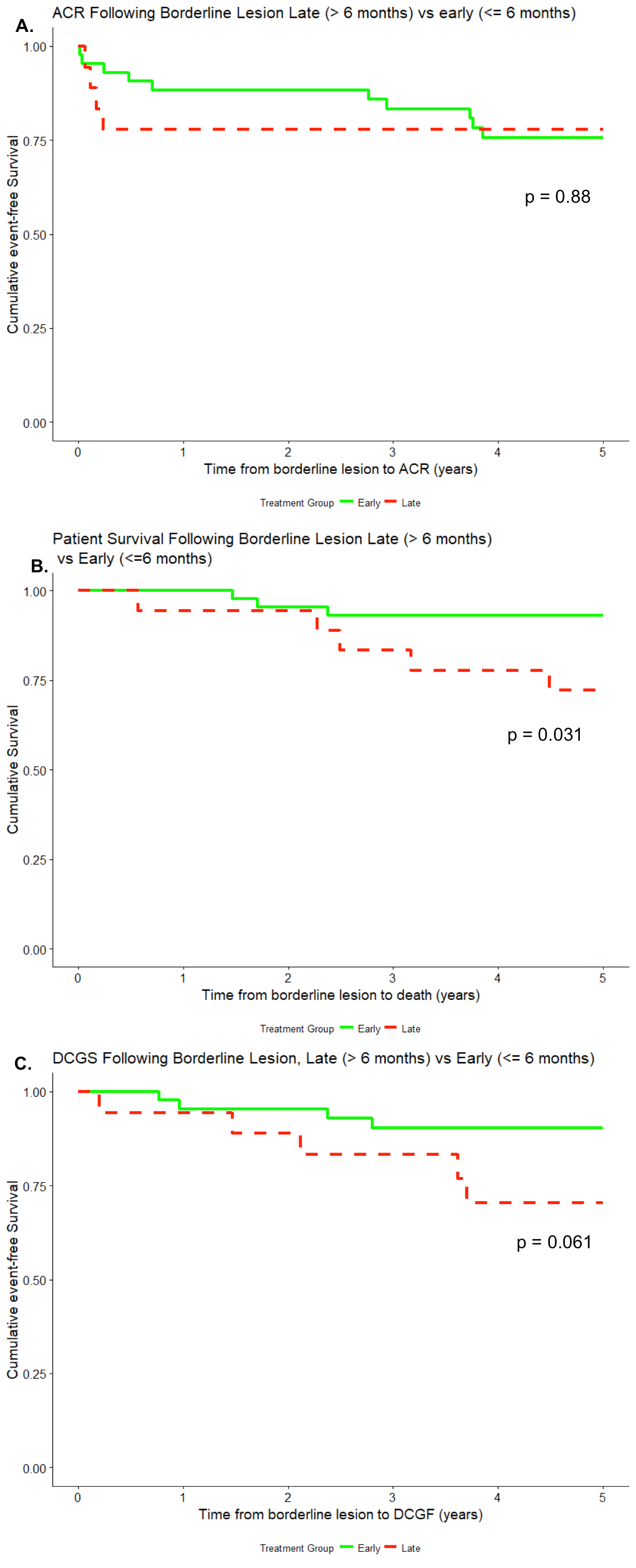
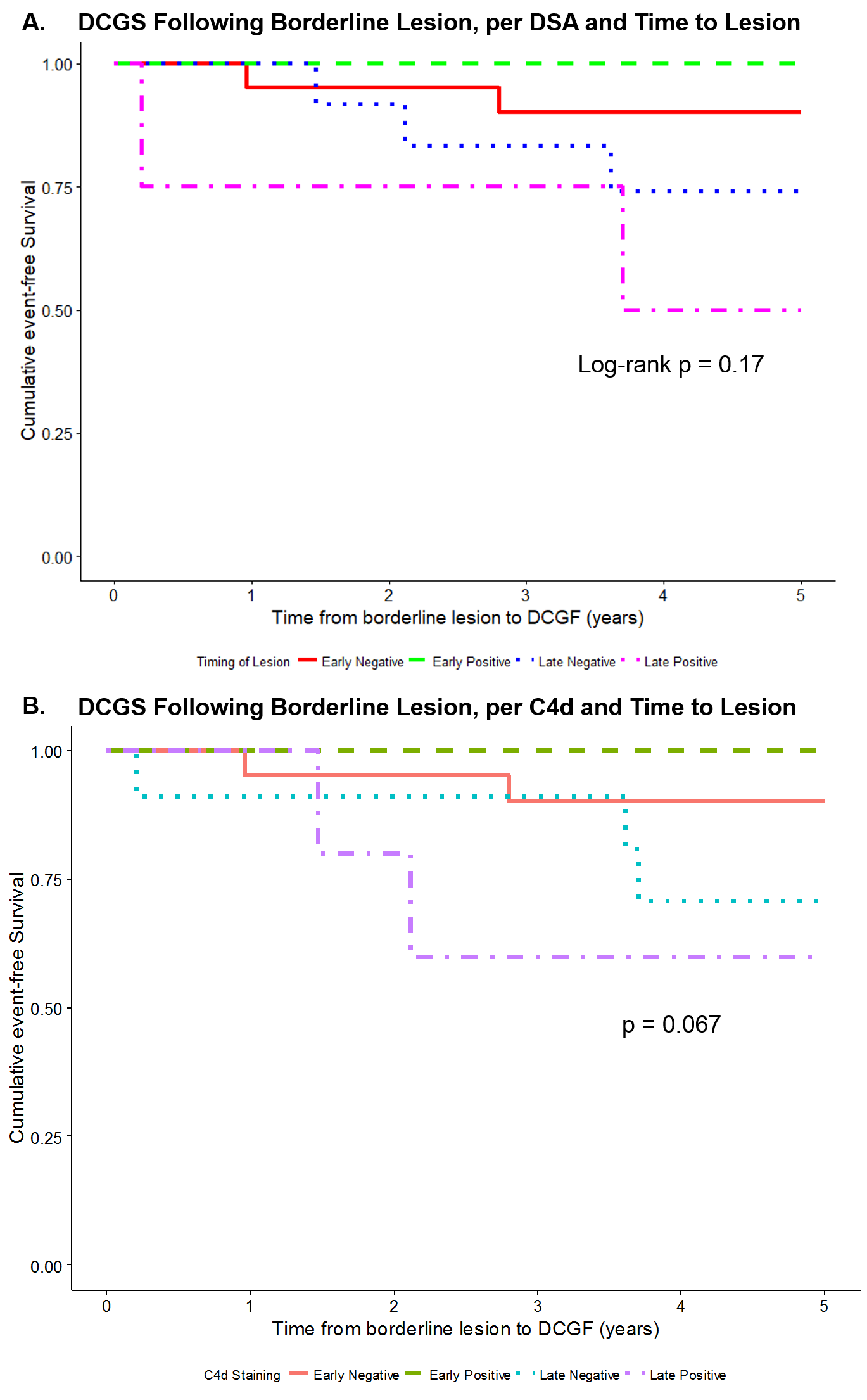
*Results: Table 1 shows patient demographics and immunosuppression information. Figure 1 shows Kaplan Meier curves for progression to ACR, death or graft loss. Figure 2 shows Kaplan Meier curves for graft loss based on the presence of DSA or C4d and time to lesion.
*Conclusions: Late borderline lesions conferred a greater risk to DCGS, and surprisingly, patient survival as compared to early borderline lesions. Late borderline lesions with concurrent DSA or C4d positivity had worse outcomes than those without C4d to DSA. No effect of timing was seen on progression to ACR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wilson NK, Tremblay S, Lee P, Bumb S, Alloway RR, Shields AR, Cardi M, Woodle ES. Early And Late Borderline Lesions Exhibit Differential Outcomes In Renal Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/early-and-late-borderline-lesions-exhibit-differential-outcomes-in-renal-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress