Donor-Derived Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections: Risk Mitigation Strategy in Solid Organ Transplant Improves Recipients Safety and Could Expand Donor Pool
A. Mularoni1, E. Graziano1, M. Campanella1, A. Cervo2, M. Peghin3, F. Barbera1, P. Conaldi1, A. Luca1, P. A. Grossi4
1ISMETT, Palermo, Italy, 2Department of Infectious Diseases, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Policlinico of Modena, Modena, Italy, 3Division of Infectious Diseases, ASUFC, Udine, Italy, 4Infectious and Tropical Diseases Unit, University of Insubria, Varese, Italy
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 353
Keywords: Bacterial infection, Organ Selection/Allocation, Prophylaxis, Safety
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 24 - All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: Transplant Infectious Diseases: All Organs
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:50pm-6:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:50pm-6:00pm
Location: Hynes Ballroom B
*Purpose: We implemented an Active Surveillance System (ASS) to mitigate the risk of unexpected carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative (CRGN) donor-derived infection (DDI) in solid organ transplant recipient (SOTR). We describe the results of our ASS, evaluate risk factors and outcome of CRGN DDI in our cohort of SOTR.
*Methods: We performed a prospective observational study of all consecutive SOTR at ISMETT from December 2015 to July 2021 after the introduction of our ASS coordinated as follows: 1) microbiological analysis in our laboratory of donor (D) and preservation fluid (PF) samples; 2) in case of positivity, results were communicated to the infectious disease specialist (ID) and in case of GN, CARBA test was performed; 3) ID prescribed SOTR cultures and set a pre-emptive therapy, reassessed on definitive results. We defined R as high-risk (HR) for CRGN DDI all R from D with positive blood culture or PF, kidney R from D with positive urine culture and lung R from D with positive bronchoalveolar lavage. Whole Generation Sequencing was performed for DDI confirmation. We evaluated transmission rate, risk factors and the outcome (days of hospitalization and survival) in the population with CRGN DDI. In HR recipient we evaluated the appropriateness of antibiotic therapy.
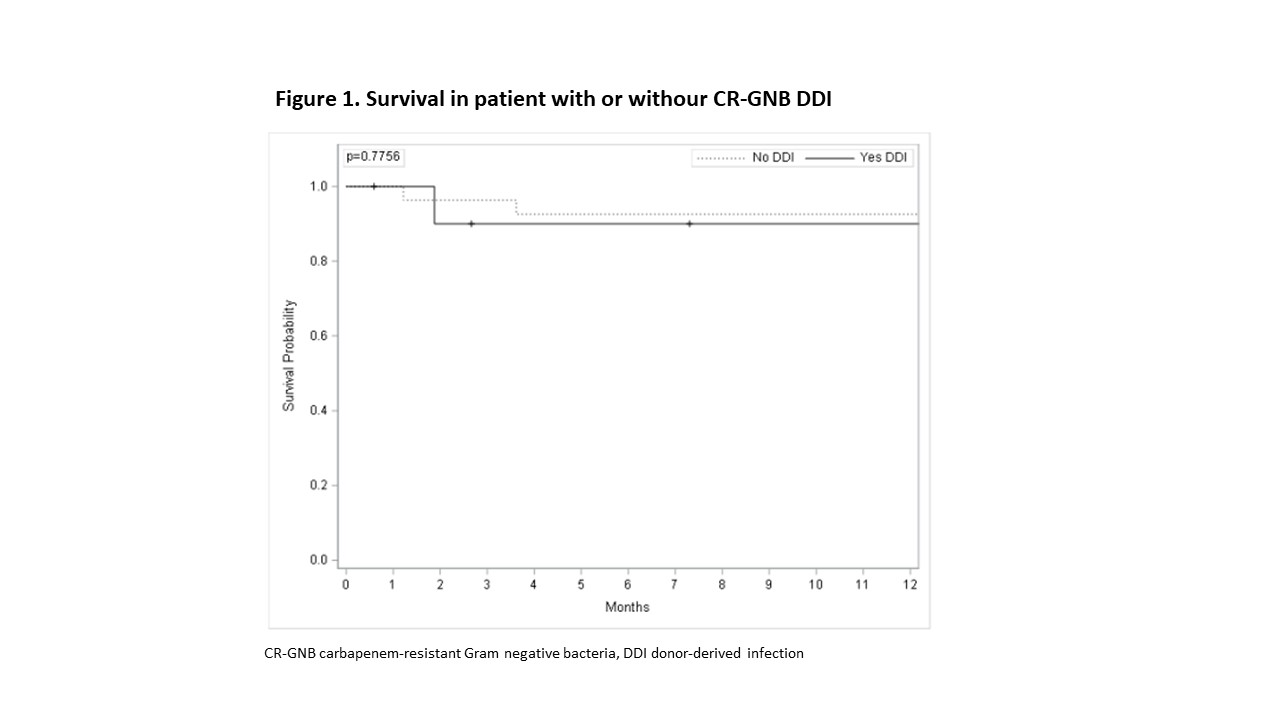
*Results: Of 791 recipients, 38 (4.8%) were HR for unexpected CRGN DDI, 25 for CR Enterobacterales (CRE) and 13 for CR Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB). Among 38 CR-GN HR recipients, in only 11 cases the transmission from D to R resulted in DDI (9/25 of CRE and 2/13 of CRAB). All R at HR for CRGN DDI received an appropriate therapy and DDI was detected as soon as donor culture turned positive. Risk factors for transmission were: D with CRGN bacteremia (p=0.019), CRGN with positive PF (p=0.0002), liver from a D with CRE bacteremia or positive PF (p=0.028). PF positivity for CRGN led to DDI in 87% of cases. Median length of stay in ICU and hospital and 60-day survival were not different between population with CRGN DDI and without DDI (p=0.2, p= 0.1, p=1).
*Conclusions: Our innovative active surveillance system demonstrated to be a useful tool in order to contain transmission rate, mitigate clinical impact of unexpected CRGN DDI and, with the new antibiotics, our system could expand the donor pool in endemic areas.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mularoni A, Graziano E, Campanella M, Cervo A, Peghin M, Barbera F, Conaldi P, Luca A, Grossi PA. Donor-Derived Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections: Risk Mitigation Strategy in Solid Organ Transplant Improves Recipients Safety and Could Expand Donor Pool [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/donor-derived-carbapenem-resistant-gram-negative-infections-risk-mitigation-strategy-in-solid-organ-transplant-improves-recipients-safety-and-could-expand-donor-pool/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress