Does Simultaneous Liver Kidney Transplant in Patients with MELD ≥35 on Renal Replacement Therapy at the Time of Transplant Improve Outcome?
Transplant Hepatology, Univ. of Tennessee, Memphis, TN
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D185
Keywords: Kidney/liver transplantation, Renal failure
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Liver - Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Background: A significant proportion of patients with MELD ≥35 have renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy (RRT) at the time of transplant, and receive either Liver Transplant alone (LTA) or simultaneous liver and kidney transplants (SLK). We aim to evaluate if SLK in patients with MELD ≥35 on RRT (MELD ≥35 -RRT) improves outcomes comparted to LTA.
Methods: We reviewed 1200 patients from our center to identify 50 patients with MELD ≥35 -RRT. Baseline characteristics, duration of RRT prior to transplant and the wait time for transplant was collected. Renal outcome (based on GFR), length of stay and survival after transplant was assessed.
Results: 36 patients on RRT received LTA and 14 patients underwent SLK. The mean wait time was 3.4 ±1.5 days. LTA and SLK patients had similar baseline characteristics.
| LTA | SLK | |
| Age
Male % DM% Cr. 30 days pre Tx (mg/dl) * |
53.3 +/- 8.1
22 (61%) 5 (14%) 1.48 +/- 0.4 |
54.7 +/- 9.2
11 (78%) 4 (28%) 3.1 +/- 2.5 |
| Removal MELD
Days on RRT pre-Tx * Wait time after MELD ≥ 35 |
38.3 +/-1.8
6.6 +/- 5.5 3.3 +/- 1.8 |
38 +/- 1.7
34.2 +/-53 3.7 +/- 2.6 |
| LOS (days)
GFR post-Tx (ml/min) 3 month 6 month 12 month CKD-3 post Tx 1 year 3 year * |
17.3 +/- 11.1
73 +/- 31 67 +/- 32 67 +/- 31 14/29 ( 48 %) 4/12 (33 %) |
17.3 +/- 11.1
73 +/- 35 63 +/- 32 68 +/- 32 6/12 (50%) 6/12 (50%) |
SLK patients were on RRT for a longer period before transplant (39.8 ±53 vs. 6.6 ± 5.5 days; p= 0.0001) and had higher Cr 30 days prior to transplant (3.1±2.5 vs. 1.48± 0.4 mg/dl; p= 0.012). At 1-year, 48% patients with LTA and 50 % patients with SLK had CKD-3 but at 3 years more SLK patients had CKD-3 (50% vs. 33%, p=0.014). Kaplan Meier survival analysis (log rank test) did no show a difference in survival between the two cohorts. 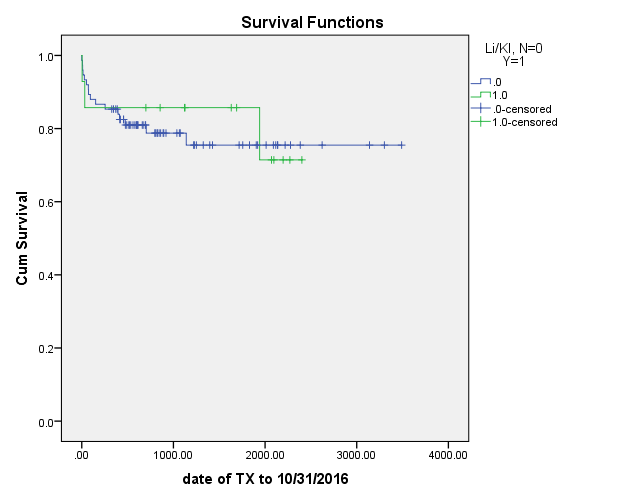 Conclusion: SLK does not improve renal outcomes or survival compared to LTA in patients with MELD ≥35 on RRT before transplant. Expedited transplant is likely responsible for good outcome in patients on RRT who receive LTA alone. Share 35 policy is likely to minimize the need for SLK.
Conclusion: SLK does not improve renal outcomes or survival compared to LTA in patients with MELD ≥35 on RRT before transplant. Expedited transplant is likely responsible for good outcome in patients on RRT who receive LTA alone. Share 35 policy is likely to minimize the need for SLK.
CITATION INFORMATION: Ali B, Gadiparthi C, Cholankeril G, Satapathy S, Eason J, Nair S. Does Simultaneous Liver Kidney Transplant in Patients with MELD ≥35 on Renal Replacement Therapy at the Time of Transplant Improve Outcome? Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ali B, Gadiparthi C, Cholankeril G, Satapathy S, Eason J, Nair S. Does Simultaneous Liver Kidney Transplant in Patients with MELD ≥35 on Renal Replacement Therapy at the Time of Transplant Improve Outcome? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/does-simultaneous-liver-kidney-transplant-in-patients-with-meld-35-on-renal-replacement-therapy-at-the-time-of-transplant-improve-outcome/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
