Does CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) Equation Have Stronger Predictive Power for Long-Term Kidney Graft Survival?
Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Select One, Korea
Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Select One, Korea
The Research Institute for Transplantation, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Select One, Korea
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 461
Background: eGFR measured by the CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) equation is well-known to be more accurate than MDRD equation in chronic renal disease patients. There has not been any study with large population of kidney recipient and evaluation for long-term graft survival. Thus, we designed this study to evaluate the predictive power of the CKD-EPI equation compared with the MDRD with large single center kidney recipients.
Patients and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 3,026 adult kidney recipients who were followed up for at least 1 year after transplantation. We analyzed discrepancy of eGFR between the two equations, and compared long-term graft survival according to the CKD stage divided by each equation.
Results: Of the 3,026 kidney recipients, living donor kidney transplantations were 2,779 and deceased donor kidney transplantations were 247. Mean age of recipients and donors were 39.3±10.8 and 37.4±11.6 years. Mean follow up duration was 128.6±83.4 months. In terms of discrepancy of the CKD stage at 1 year after transplantation, there was no difference in stage 1 in both equations. The stage 2, 3A, 3B and 4 by the MDRD had 18.3%∼44.1% discrepancy with the CKD stage by the CKD-EPI equation. Graft survival rate according to the CKD stage categorized by the MDRD and CKD-EPI at 1 year after transplantation was different from each other. Graft survival rates sequentially distributed according to the stage categorized by the CKD-EPI but the MDRD did not. The CKD stage 3A and 3B by the CKD-EPI showed significantly different survival rate.
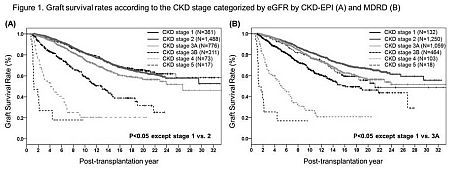
Conclusion: Our data support that CKD-EPI equation has stronger predictive power for long-term kidney graft survival in the transplantation settings. Thus, we recommend that eGFR by the CKD-EPI should be used for evaluation of graft function after kidney transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Joo D, Lee A, Lee S, Kim M, Huh K, Ju M, Kim S, Kim Y, Kim B. Does CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) Equation Have Stronger Predictive Power for Long-Term Kidney Graft Survival? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/does-ckd-epidemiology-collaboration-ckd-epi-equation-have-stronger-predictive-power-for-long-term-kidney-graft-survival/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
