Dialysis Patient Perspectives on Obesity as a Barrier to Kidney Transplantation
S. S. Hingorany, A. Klassen, B. Milliron, J. Sweeting, J. Lee, R. HaileSelasse, B. Gunen, M. N. Harhay
Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 767
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Obesity
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 35 - Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 4, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Although obesity is a known barrier to kidney transplantation (KT) and associated with delayed graft function and graft loss, guidance is lacking on optimal methods to support patients with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) who require or desire weight loss. Knowledge about patient experiences with obesity care and counseling and attitudes about body mass index (BMI) limits for KT will help to inform patient-centered obesity interventions.
*Methods: We conducted purposive sampling of dialysis-dependent adults with obesity and held 90-minute phone-based open-ended interviews (N=40) to explore perspectives about ESKD-specific obesity counseling, weight management strategies, and BMI limits for KT. Interviews were audio-recorded, transcribed verbatim, and analyzed using inductive and deductive thematic analysis by a research team with expertise in ESKD, social science, and nutrition.
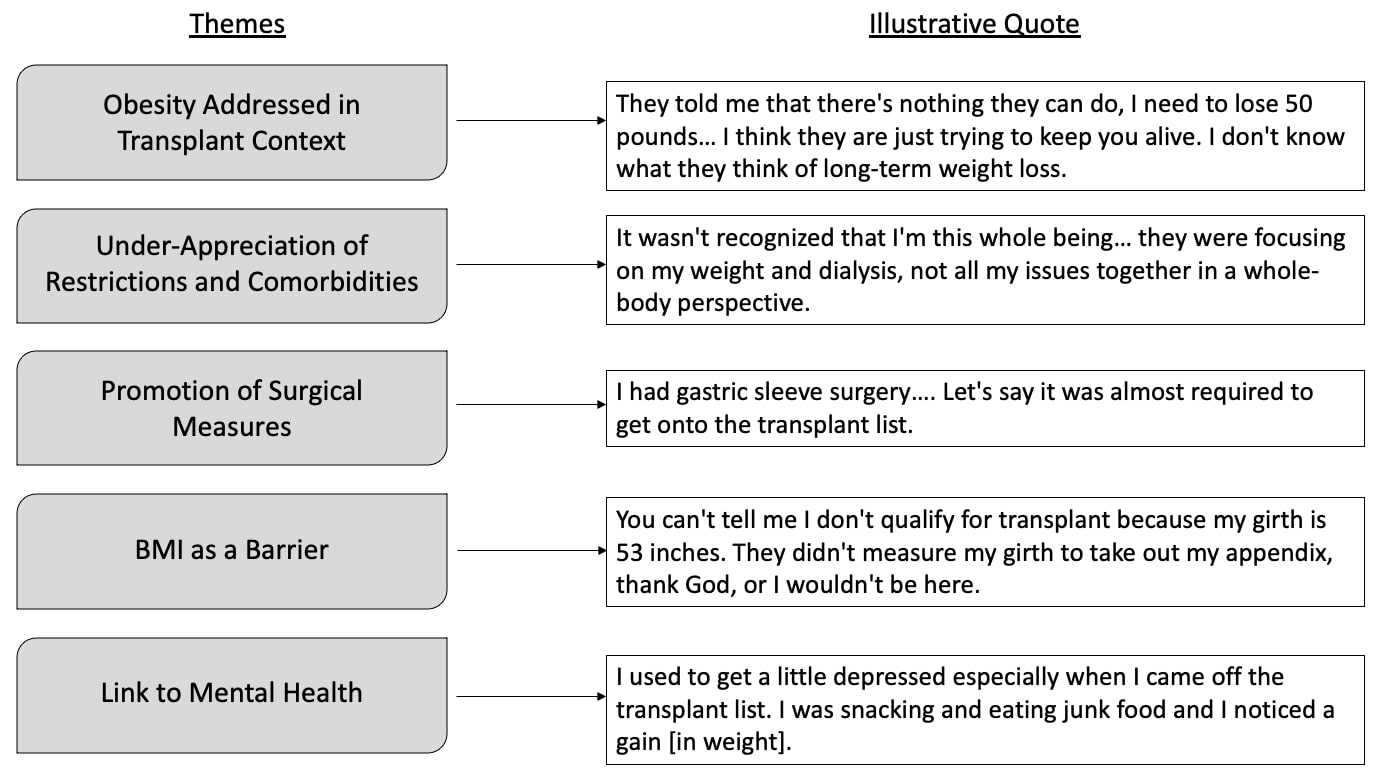
*Results: Respondents resided in 22 US states. The average age was 55.6 (±11.5) years, average BMI was 39.2 (±6.0) kg/m2, 59% were female, 31% were Black, and 20% were waitlisted for KT. We identified five major themes related to obesity management in the context of ESKD and BMI limits for KT, respectively (Figure): 1) ESKD and KT health care professionals usually only discuss obesity with patients if weight loss is needed to meet KT acceptance criteria; otherwise, obesity is not a central focus of typical ESKD patient care 2) health care professionals often under-appreciate how ESKD dietary restrictions, exhaustion and comorbidities make it harder to lose weight via diet and exercise 3) surgical weight loss measures are strongly promoted but are not aligned with many patients’ preferences for non-surgical weight loss strategies 4) BMI requirements are an arbitrary barrier for a life-saving procedure, and 5) mental health is strongly linked to food choices and eating behaviors.
*Conclusions: These findings suggest that obesity is rarely addressed in ESKD clinical encounters and that many patients consider BMI limits for KT to be unjustified and arbitrary. Obesity management strategies for KT candidates should be tailored to the ESKD lifestyle and address common physical and mental health challenges.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hingorany SS, Klassen A, Milliron B, Sweeting J, Lee J, HaileSelasse R, Gunen B, Harhay MN. Dialysis Patient Perspectives on Obesity as a Barrier to Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/dialysis-patient-perspectives-on-obesity-as-a-barrier-to-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress