Diagnostic Bronchoscopy in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Acute Respiratory Failure: Risk or Value?
Nephrology, Charité
Universitaetsmedizin, Berlin, Germany
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A195
Keywords: Bacterial infection, Fungal infection, Kidney transplantation, Lung infection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Complications I
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, April 29, 2017
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall D1
Introduction:
Few data evaluates the differential diagnostic value of bronchoalveolar lavages (FO-BAL) in kidney transplant recipients (KTR) with acute respiratory failure (ARF). We describe the results of FO-BAL and the respiratory consequences in KTR with ARF.
Methods:
This retrospective single center study included all adult KTR with ARF and diagnostic FO-BAL 2004-2014.
Results:
Overall, 154 FO-BAL were performed in 129 KTR (mean age 53 years) with ARF. The causes of ARF were: infections (bacterial (45%), fungal (16%), viral (7%), pneumocystis pneumonia (8%)) and mTOR-associated pneumonitis (14%). In 10% of FO-BALs no certain cause of ARF could be identified. The results of laboratory parameters and differential cytologic analysis of BAL fluids are presented in Table 1.
| bakterial infektion | mTOR-
associated |
PCP | fungal infections | viral infections | other | |
| Blood tests (median) | ||||||
| Leukocytes, /nL | 7.3 | 5.8 | 6.8 | 9.1 | 4.5 | 7.6 |
| CRP, mg/dL | 53.7 | 33.9 | 68.8 | 73.6 | 42.1 | 23.6 |
| PCT, [micro]g/dL | 0.53 | 0.13 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.2 | 0.12 |
| LDH, U/L | 281 | 331 | 428 | 311 | 292 | 244 |
| BAL cytology (median) | ||||||
| Macrophages, % | 45 | 52 | 38 | 50 | 48 | 65 |
| Lymphocytes, % | 7 | 23 | 24 | 11 | 26 | 18 |
| Neutrophils, % | 29 | 9 | 27 | 18 | 9 | 3 |
| CD4/CD8 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 1.6 |
In case of ARF due to pulmonary infection, FO-BAL contributed to identification of the pathogenic agent in 51.3% of cases while respiratory deterioration after FO-BAL with the need of ventilation support occurred in 19.5% of patients, including 12.3% of patients who required invasive ventilation. 5-year survival by pathogenic entity is presented in Fig.1.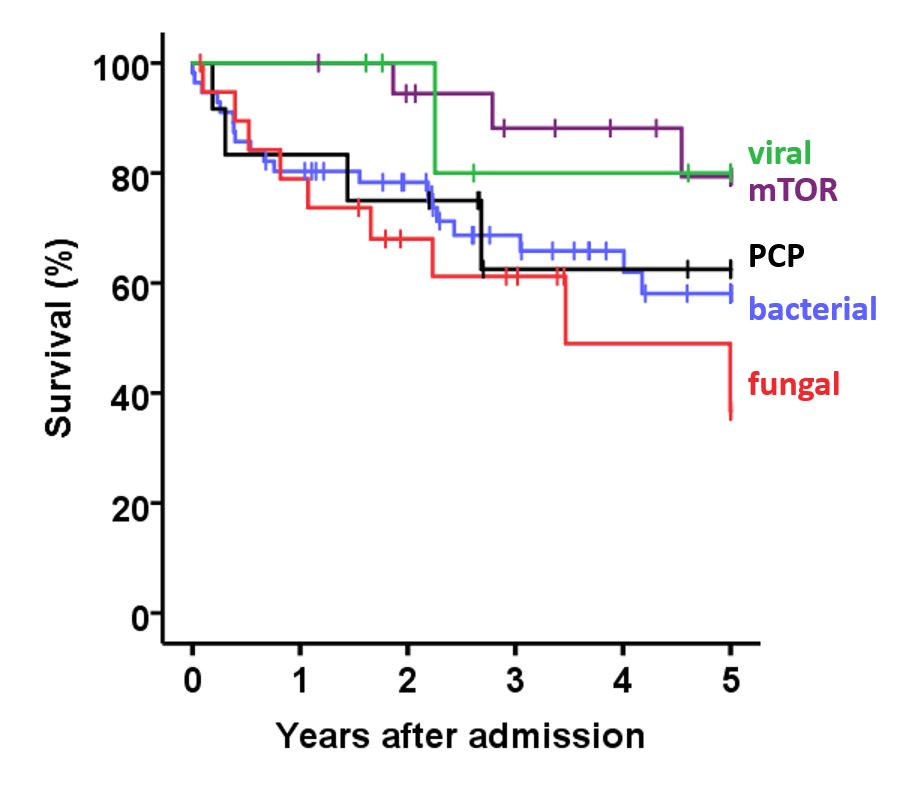 Conclusion: In KTR patients with ARF, a diagnostic strategy that includes FO-BAL may be limited by atypical presentation of findings but frequently exposes the patients to additional risk of respiratory deterioration.
Conclusion: In KTR patients with ARF, a diagnostic strategy that includes FO-BAL may be limited by atypical presentation of findings but frequently exposes the patients to additional risk of respiratory deterioration.
CITATION INFORMATION: Khadzhynov D, Deissler J, Halleck F, Lehner L, Budde K, Staeck O. Diagnostic Bronchoscopy in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Acute Respiratory Failure: Risk or Value? Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khadzhynov D, Deissler J, Halleck F, Lehner L, Budde K, Staeck O. Diagnostic Bronchoscopy in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Acute Respiratory Failure: Risk or Value? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/diagnostic-bronchoscopy-in-kidney-transplant-recipients-with-acute-respiratory-failure-risk-or-value/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
