Diabetes Significantly Impacts Quality of Life Following Kidney Transplant
Dept of Pharmacy Services, MUSC, Charleston, SC
Dept of Transplant Surgery, MUSC, Charleston, SC
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A764
Purpose: Kidney transplant (KTx) has the potential to substantially improve quality of life (QOL) through improvements in performance status and life expectancy. Few studies have evaluated the effects of demographic and clinical measures on patient perceptions of their QOL following KTx. The purpose of this analysis was to assess the impact of diabetes mellitus (DM) on subjective QOL outcomes following KTx.
Methods: This QOL analysis was conducted as part of a prospective, risk stratified, randomized, open label study of 200 KTx recipients. Pediatric, HLA-identical, and non-KTx patients were excluded as well as those with any positive cross-match or age > 75. All patients were randomized to receive rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin or an IL-2 receptor antagonist in addition to Fk, MMF, and corticosteroids. QOL surveys, including a visual analog scale (VAS) and short form-36 (SF-36), were to be administered at the time of KTx and months 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12.
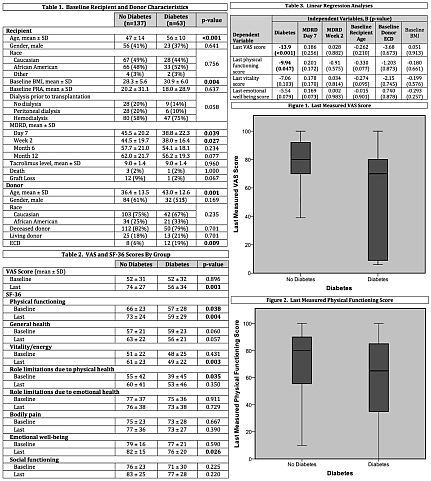
Results: Of the 200 patients included in the study, 63 (32%) had pre-existing DM. Baseline characteristics are displayed in Table 1. The only QOL metrics which differed between the two groups at baseline were physical functioning and role limitations due to physical health, which were significantly lower in the DM group (p=0.038, 0.043; Table 2). At the time of the last QOL measurements, the overall VAS as well as the SF-36 domains of physical functioning, vitality, and emotional well-being were all significantly lower in the DM cohort (Table 2). When controlling for significant differences in baseline characteristics (recipient age, BMI, MDRD at day 7 and week 2, donor age, and proportion of ECD donors), DM remained a significant predictor of both the overall VAS (<0.001) and SF-36 physical functioning (p=0.047) scores (Table 4, Figure 1).
Conclusion: Diabetes has a significant negative impact on KTx recipients’ overall perception of their health as well as physical functioning following KTx, and future efforts are warranted to study mechanisms to reduce this disparity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Musgrave C, Pilch N, Meadows H, McGillicuddy J, Bratton C, Chavin K, Baliga P, Taber D. Diabetes Significantly Impacts Quality of Life Following Kidney Transplant [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/diabetes-significantly-impacts-quality-of-life-following-kidney-transplant/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
