Current Treatments for Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.
The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 20
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Clinical Science: Liver - Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:42pm-2:54pm
Presentation Time: 2:42pm-2:54pm
Location: E451b
Purpose: Numerous randomized controlled trials (RCTs) concerning treatments for small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have been reported. Herein, we conducted a network meta-analysis integrating current evidence to compare the efficacies of various therapies for small HCC.
Methods: PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, ClinicalTrials.gov, and the China Journal Full-text Database were searched. All published RCTs on treatments for small HCC were eligible and included in the analyses.
Results: We identified nineteen eligible RCTs with 2432 patients. In the direct meta-analysis, hepatic resection (HR) was superior to percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in 2-year DFS (odds ratio (OR) =1.58, 95%CI: 1.12-2.24, p<0.01), while the OR values of RFA was significantly higher than percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI) in most of the OS and DFS outcomes without heterogeneity. Percutaneous acetic acid injection (PAI) appeared to have higher OR values than PEI, but lower ORs than RFA in all of the outcomes according to the individual RCT. Furthermore, HR and RFA were significantly more effective than PEI in the DFS outcomes and showed better ranking probabilities and SUCRA in the network meta-analysis. The combination therapies (RFA+TACE, PEI+TACE, RFA+PEI) showed higher OR values over single therapies in both direct and multiple treatments comparisons. And the combination therapies had higher ranking probabilities and surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA) than the single therapies.
In the direct meta-analysis, hepatic resection (HR) was superior to percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in 2-year DFS (odds ratio (OR) =1.58, 95%CI: 1.12-2.24, p<0.01), while the OR values of RFA was significantly higher than percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI) in most of the OS and DFS outcomes without heterogeneity. Percutaneous acetic acid injection (PAI) appeared to have higher OR values than PEI, but lower ORs than RFA in all of the outcomes according to the individual RCT. Furthermore, HR and RFA were significantly more effective than PEI in the DFS outcomes and showed better ranking probabilities and SUCRA in the network meta-analysis. The combination therapies (RFA+TACE, PEI+TACE, RFA+PEI) showed higher OR values over single therapies in both direct and multiple treatments comparisons. And the combination therapies had higher ranking probabilities and surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA) than the single therapies. 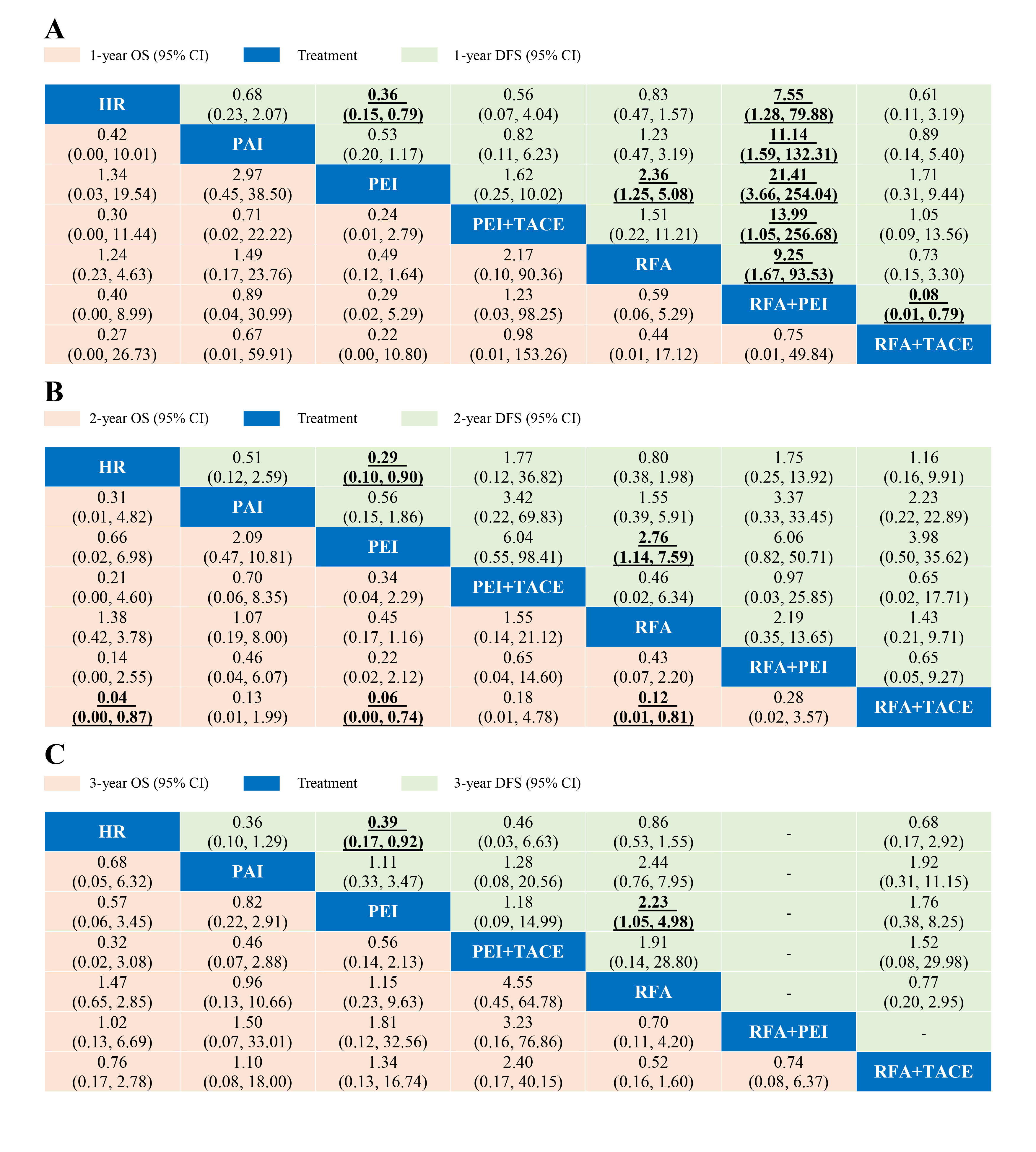 Conclusions: HR and RFA+PEI tend to be the optimum treatments for small hepatocellular carcinoma on improving the disease-free survival, while RFA+TACE is superior to any other treatments in overall survival outcomes.
Conclusions: HR and RFA+PEI tend to be the optimum treatments for small hepatocellular carcinoma on improving the disease-free survival, while RFA+TACE is superior to any other treatments in overall survival outcomes.
CITATION INFORMATION: Guo Z, Zheng Z, He X, Chen G. Current Treatments for Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guo Z, Zheng Z, He X, Chen G. Current Treatments for Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/current-treatments-for-small-hepatocellular-carcinoma-a-network-meta-analysis-of-randomized-controlled-trials/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
