Current Dialysis, Previous Kidney Transplant, and Autoimmune Disease Increase Risk for Abnormal Pap Smear in Women Undergoing Kidney Transplant Evaluation
1Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH
2University Hospitals, Cleveland, OH.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D228
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Screening
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: PTLD/Malignancies: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
The USPSTF recommends Pap smears every three years for women 21-65, with optional combination Pap smear and HPV testing every five years for women 30-65. We sought to determine risk factors for abnormal Pap smears in women undergoing kidney transplant evaluation.
METHODS: We retrospectively examined 405 women undergoing kidney transplant evaluation from 2008-2011. Patients who were <21 or did not have Pap smears during evaluation were excluded. Patients were stratified based on normal cytology and atypical/malignant cytology.
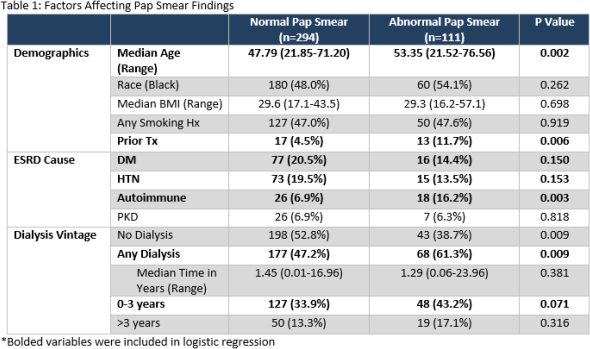
RESULTS: 294 (72.6%) patients had normal cytological findings, and 111 (27.4%) had abnormal findings, with median ages of 48 and 53, respectively (Table 1). On univariate logistic regression, patients who had ESRD with autoimmune etiology (OR=2.83, 95% CI: 1.52-5.28, p=0.001), who underwent dialysis prior to evaluation (OR=1.77, 95% CI: 1.15-2.73, p=0.010), or who had previous renal transplants (OR=2.79, 95% CI: 1.31-5.95, p=0.008) were more likely to have abnormal findings. Conversely, the diagnosis of DM or HTN was found to be somewhat protective (OR=0.52, 95% CI: 0.31-0.88, p=0.015). On multivariate logistic regression, patients who had ESRD with autoimmune etiology (OR=2.60, 95% CI: 1.35-5.00, p=0.04), who underwent dialysis prior to evaluation (OR=1.75, 95% CI: 1.12-2.71, p=0.013), or who had previous renal transplants (OR=2.81, 95% CI: 1.29-6.14, p=0.009) were more likely to have abnormal findings. An ESRD etiology of DM or HTN was found to be somewhat protective (OR=0.54, 95% CI: 0.33-0.89, p=0.015).
CONCLUSION: Risk factors such as current dialysis and previous transplant may affect cervical screening findings in women undergoing kidney transplant evaluation. Chronic inflammation, such as in the setting of autoimmune disease or longstanding chronic transplant rejection, may increase the risk of abnormal Pap smear results.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chaung K, Zheng Y, Martella A, Stoecker J, Cote D, Augustine J, Sanchez E, Humphreville V, Ammori J, Woodside K. Current Dialysis, Previous Kidney Transplant, and Autoimmune Disease Increase Risk for Abnormal Pap Smear in Women Undergoing Kidney Transplant Evaluation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/current-dialysis-previous-kidney-transplant-and-autoimmune-disease-increase-risk-for-abnormal-pap-smear-in-women-undergoing-kidney-transplant-evaluation/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
