Creatinine Reduction Ratio at 2 Postoperative Day as a Predicting Factor of Long-Term Outcomes After Living Donor Kidney Transplantation
Division of Renal Surgery and Transplantation, Department of Urology, Jichi Medical University Hospital, Shimotsuke, Tochigi, Japan
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 951
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Living donor, Outcome, Prediction models
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » Kidney Living Donor: Long Term Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Living Donor: Long Term Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Creatinine reduction ratio from 1 to 2 postoperative days (CRR2) under 30% has been defined as a slow graft function (SGF) and used to predict long-term graft outcomes in some studies involving deceased donor kidney transplantation. However, the usefulness of the parameter involving living donor kidney transplantation (LDKT) remains uncertain. We retrospectively evaluated the relationship between CRR2 and graft survivals after LDKT and the risk factor for SGF.
*Methods: Clinical data on patients who underwent LDKT at Jichi Medical University Hospital in 2006-2019 were extracted from the medical records. After excluding patients who needed reoperation, dialysis, or anti-rejection therapy within 1 week after transplantation, patients were divided into 2 groups: immediate graft function (IGF) defined as patients with CRR2 > 30%, and SGF defined as patients with CRR2 ≤ 30%. CRR2 was calculated by the formula: (Cre1 – Cre2)×100/Cre1 (Cre1 and Cre2 refered serum creatinine level 1 and 2 postoperative days after transplantation).
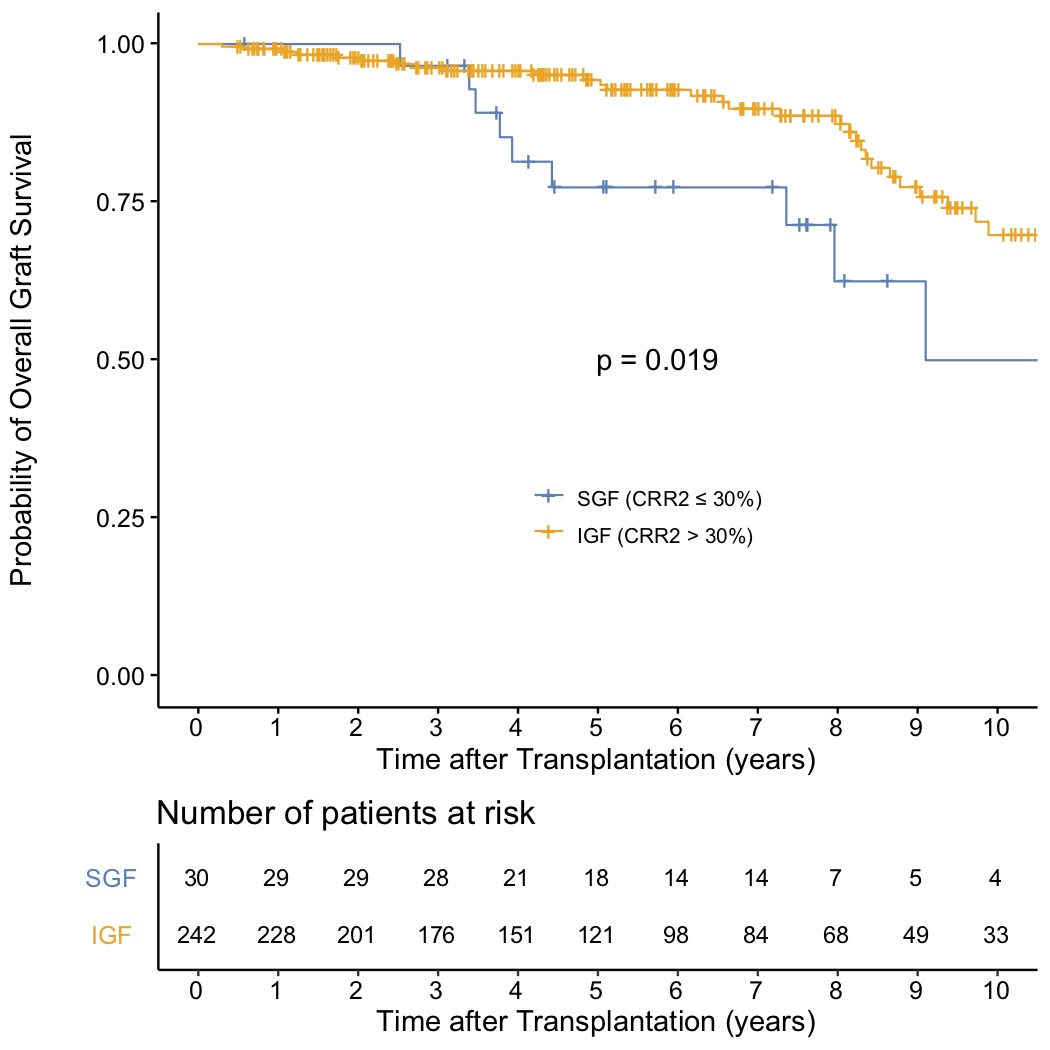
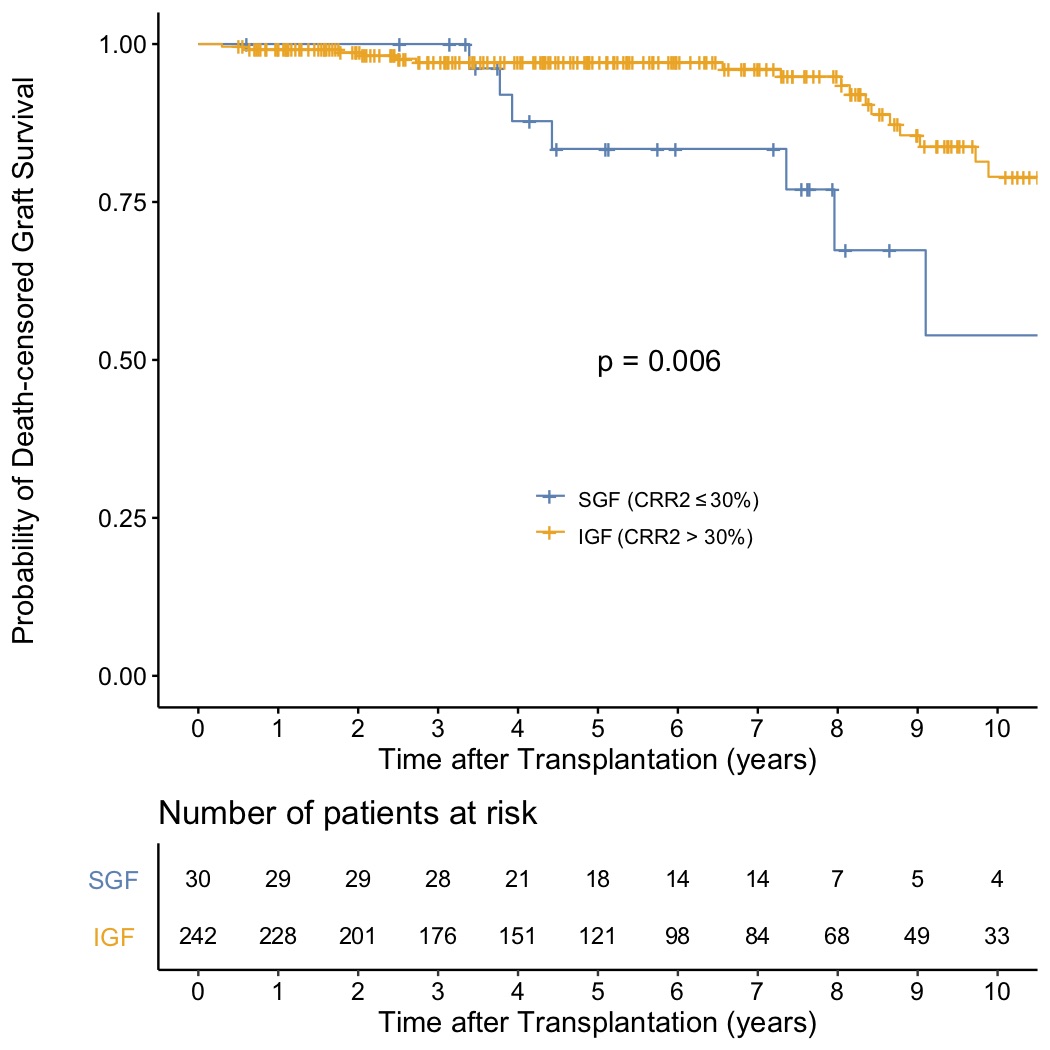
*Results: Of the 272 patients, 242 were IGF group and 30 were SGF group. Regarding the relationship between CRR2 and graft survivals, the log-rank test and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analyses showed a significantly higher incidence of overall and death-censored graft loss in SGF group (Hazard ratio = 2.5 and 2.8, p = 0.025 and 0.035, respectively), after adjusting for background characteristics including age, sex, duration of dialysis, ABO compatibility, donor-specific antibody positivity, and medically complex donor. Regarding the risk factor for SGF, in the logistic regression analysis using the aforementioned covariates and intraoperative factors including total ischemia time, warm ischemia time, renal artery reconstruction, and right donor kidney, using 225 complete cases without missing value, only renal artery reconstruction was associated with SGF (Odds ratio = 2.8, p = 0.043).
*Conclusions: CRR2 as a definition of SGF could be used to predict long-term graft outcomes. Renal artery reconstruction could be the risk factor for SGF.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kinoshita Y, Shinzato T, Shimizu T, Iwami D. Creatinine Reduction Ratio at 2 Postoperative Day as a Predicting Factor of Long-Term Outcomes After Living Donor Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/creatinine-reduction-ratio-at-2-postoperative-day-as-a-predicting-factor-of-long-term-outcomes-after-living-donor-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress