Covid 19 Re-infection versus Re-activation in Two Renal Transplant Patients
L. Liriano-Ward, Y. Al Azzi, R. Bartash, C. Pynadath, M. Ajaimy, P. Loarte, J. Graham, S. Greenstein, M. Kinkhabwala, J. Rocca, E. Akalin
Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 789
Keywords: Infection, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Infectious Disease » Kidney Infectious Non-Polyoma & Non-Viral Hepatitis
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Infectious Non-Polyoma & Non-Viral Hepatitis
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Rare cases of potential COVID 19 re-infection have been reported throughout the world.
*Methods: We describe two renal transplant recipients with possible SARS-COV-2 re-infection.
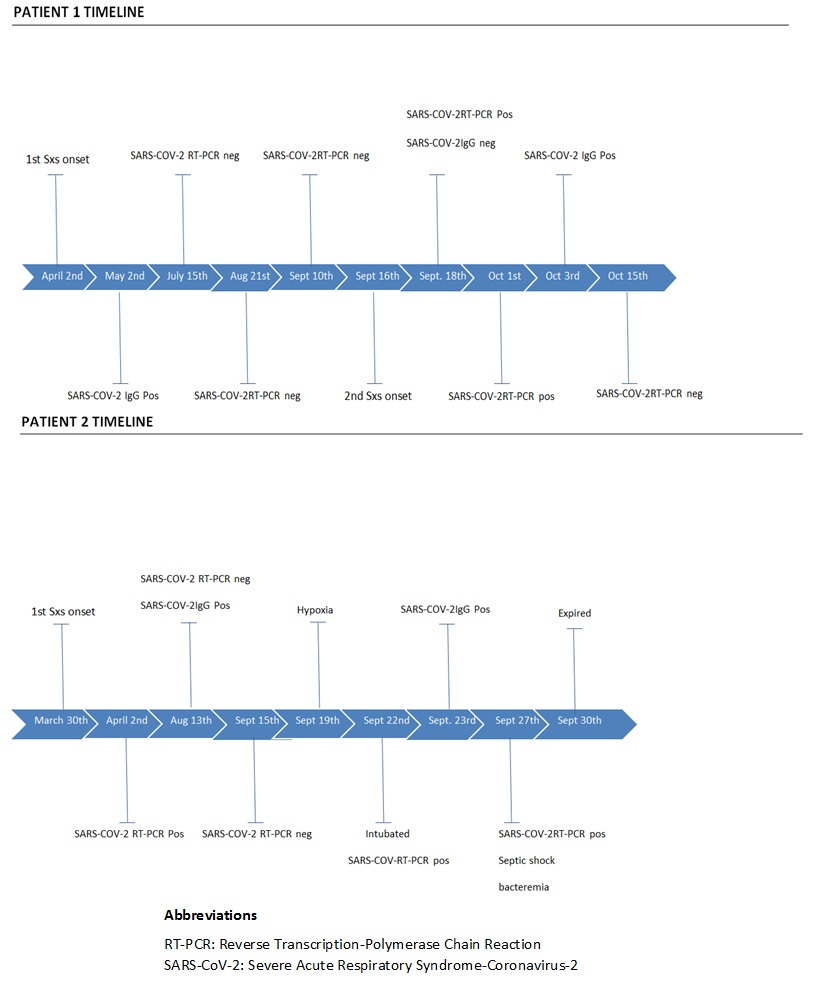
*Results: Patient #1 is a 63-year-old man with a history of renal transplant in February 2010, who initially experienced symptoms consistent with COVID-19 in April 2020 along with several family members. Due to limitations in outpatient testing, no SARS-CoV2 testing was able to be performed but he was treated as presumed COVID-19 infection due to high community prevalence and three weeks following his symptoms, SARS-CoV2 IgG was positive. The patient subsequently had four negative PCR tests from July-September 2020. In October, he was admitted for hypoxic respiratory failure and was found to be SARS-COV-2 positive by PCR and SARS-COV- IgG was negative (Figure 1). The patient was treated with Remdesivir and recovered. Patient #2 is a 64-year-old man with history of renal transplant in 2003, who was found to be SARS-COV-2 positive by RT-PCR in April 2020 after presenting with hypoxia. The patient had an uneventful hospital course and was discharged off supplemental oxygen. He had two negative SARS-COV-2 PCR tests in August and September and his SAR-COV-2 IgG was positive. In September, he was readmitted with hypoxic respiratory failure requiring intubation and ICU admission and was again found to be SARS-COV-2 positive by PCR. The patient had a complicated hospital course and expired on September 30th (Figure 1).
*Conclusions: Potential cases of SARS-COV-2 re-infection have been previously reported, but it is unclear whether these are true re-infections versus reactivation of a prior infection, prolonged viral shedding, or dynamic RT-PCR results. In our cases, we believe prolonged viral shedding from the initial infection or inaccurate testing is less likely given the prolonged time interval between the two events, the multiple negative tests in between, and the severity of the second episodes. While both of these patients were suspected of having re-infections, this could not be confirmed as genomic analysis was not performed. Future studies of similar cases are needed to determine factors contributing to re-infection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liriano-Ward L, Azzi YAl, Bartash R, Pynadath C, Ajaimy M, Loarte P, Graham J, Greenstein S, Kinkhabwala M, Rocca J, Akalin E. Covid 19 Re-infection versus Re-activation in Two Renal Transplant Patients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/covid-19-re-infection-versus-re-activation-in-two-renal-transplant-patients/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress