COVID-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients in the Southeastern United States: A Single Center Experience
K. R. Kumm, S. H. Shawar, R. C. Forbes, B. P. Concepcion
Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 746
Keywords: Infection, Kidney transplantation, Pneumonia, Survival
Topic: Clinical Science » Infectious Disease » All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The novel coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or COVID-19, has emerged as a viral pandemic and brought unprecedented challenges worldwide on health care systems, including our transplantation community. Data on the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) remain uncertain. Here we describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of KTRs in the Southeastern US who contracted COVID-19.
*Methods: A retrospective review of KTRs who tested positive for COVID-19 from March 15th, 2020 until November 25th, 2020 and followed at our institution were included. Data including patient demographics, history, laboratory results, radiological findings, and clinical outcomes was collected from the electronic medical record. Summary statistics using Kruskal-Wallis and Chi-square tests were performed. Multivariable logistic regression was used to identify risk factors for inpatient admission.
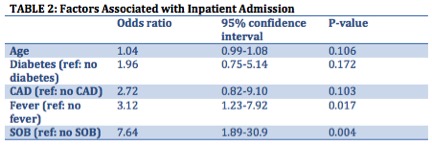
*Results: There were 104 patients who tested positive for COVID-19 either at our institution or a referring hospital (Table 1). Fifty-six (54%) patients required hospitalization. Labs on admission were: mean WBC 6.6±2.8 (x10^3/mcL), serum creatinine 2.3±1.7 (mg/dL), CRP 96±84 (mg/L), ferritin 1093±1052 (ng/mL), procalcitonin 0.62±1.0 (ng/mL), lactate 1.2±0.4 (mEq/L). Admitted patients were treated with dexamethasone (54%) and remdesivir (23%), and the anti-metabolite was held in 71%. Nineteen patients required ICU stay, 13 were intubated, 25 developed AKI and 12 died related to COVID-19 (11%). Mean length of inpatient stay was 11±13 days. After adjustment for age, DM and CAD status, the risk of admission due to COVID-19 was higher in those presenting with fever (OR 3.12, 95% CI 1.23-7.92, P-Value 0.017), and SOB (OR 7.64,95% CI 1.89-30.9, P-Value 0.004) (Table 2).
*Conclusions: The majority of KTRs with COVID-19 in our cohort required hospital admission. The mortality rate was 11% which is at the lower end of the spectrum of what has been previously reported. Despite this, COVID-19 remains a significant risk for our kidney transplant recipients with a high rate of hospital admission.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kumm KR, Shawar SH, Forbes RC, Concepcion BP. COVID-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients in the Southeastern United States: A Single Center Experience [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/covid-19-in-kidney-transplant-recipients-in-the-southeastern-united-states-a-single-center-experience/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress