Comprehensive Efficacy Analysis of Pancreas Transplantation Alone for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Y. Kudva,1 V. Dadlani,1 B. Smith,3 K. Bebjakova,1 P. Dean,2 M. Stegall.2
1Division of Endocrinology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
2Department of Transplantation Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
3Department of Health Sciences Research, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A332
Keywords: Hyperglycemia, Metabolic complications, Pancreas transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Pancreas and Islet: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Introduction: Pancreas transplantation alone (PTA) is an accepted procedure for selected patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D). However, limited data exist regarding long term effects on (i) insulin independence (ii) glycemic control including HbA1c and C-peptide; and (iii) reversal of metabolic crises such as severe hypoglycemia (SH), or diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA).
Methods: We studied 101 T1D recipients of PTA at a single center from 1998 to 2016. We analyzed 1) insulin independence 2) metabolic measures and 2) SH and DKA
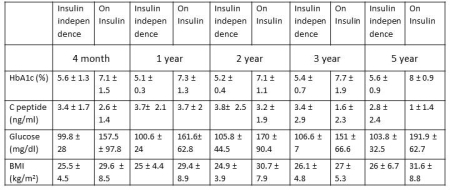
Results: Patients with T1D (Age 42.7 ± 10.6 years, gender F/M 61/40, HbA1c 9.0 ± 2.2%, creatinine 1.2 g/dl ± 0.5) who underwent PTA were followed for 7.3 (2.3-12.1) years. Insulin independence was achieved in 85%, 84%, 80%, 74%, and 68% of the patients at 4 months, 1, 2, 3 and 5 years respectively. HbA1c, fasting C-peptide, fasting plasma glucose and BMI for the cohort are shown in Table 1. SH occurred in 1 %, 1%, 6%, 6% and 7% at 4 months, 1, 2, 3 and 5 years respectively. DKA was observed in 1% and 3% at 2 and 3 years respectively. 16 patients with HbA1c <7.0% (mean 6.4 ± 0.4%) at baseline remained <7.0% at 4 months (mean 5.2 ± 0.6%), 1 year (mean 5.2 ± 0.3%) and at 5 years (mean 5.4 ± 0.6%). Of 85 patients with HBA1c >7.0% at baseline, HbA1c of <7.0% was achieved in 87% subjects at 4 months with mean HbA1c improved from 9.5 ± 2% at baseline to 5.8 ±1.4% at 4 months and 6.2 ±1.4% at 5 years
Discussion and conclusion: PTA provides durable glycemic control with independence from insulin for several years, sustained improvement in HbA1c and significant relief from SH and DKA. These data will provide sample size estimates for multi-center prospective studies of PTA
CITATION INFORMATION: Kudva Y., Dadlani V., Smith B., Bebjakova K., Dean P., Stegall M. Comprehensive Efficacy Analysis of Pancreas Transplantation Alone for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kudva Y, Dadlani V, Smith B, Bebjakova K, Dean P, Stegall M. Comprehensive Efficacy Analysis of Pancreas Transplantation Alone for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/comprehensive-efficacy-analysis-of-pancreas-transplantation-alone-for-type-1-diabetes-mellitus/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress