Complement Fixing HLA Antibodies Predict Outcome in HLA Incompatible Renal Transplantation
Imperial College Renal and Transplant Centre, Hammersmith Hospital, London, United Kingdom
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1
HLA incompatible [HLAi] transplantation is associated with a higher incidence of antibody mediated rejection [AMR] and Transplant Glomerulopathy [TG]. In this study, we show that HLAi patients with complement fixing donor specific antibodies [C1q+DSAbs] have a higher incidence of AMR than patients with non-complement fixing DSAbs [C1q-DSAbs].
18 HLAi patients [m3, f15, mean age 47.9±13.83 years] underwent desensitisation [DS] with plasma exchange, IVIg and monoclonal antibody induction pre transplant and Tacrolimus, MMF and a week of steroids post-transplant. All patients were FXM+ prior to DS and FXM- at operation. Rejection was diagnosed by biopsy. Stored serum samples from patients pre and post DS and at the time of rejection were retrospectively analysed with a C1q assay [One Lambda] to determine C’fixing IgG and IgM DSAbs. Death censored graft survival was 100% at 1 year and 77.8% at 5 years. 4 patients lost their grafts [3 from rejection; all had C1q+DSAbs].
10/18 (55.6%) patients had C1q+DSAbs and patients with C1q+DSAbs were significantly more likely to develop rejection compared with C1q-DSAbs patients [(fig 1) 90% vs. 25%, p=0.01].
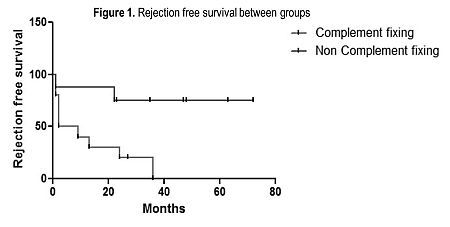
8/11 patients who developed rejection had complement fixing antibodies at the time of their first rejection episode; 1 C1q-DSAbs patient became C1q+DSAbs at the time of rejection.
Table 1 shows that C1q+DSAbs patients had poorer allograft function and more proteinuria than C1q-DSAbs patients [p<0.001]. Peritubular capillaritis [p=0.01] and glomerulitis [p=0.01] were more common in C1q+DSAbs patients. 4 patients with C1q+DSAbs progressed to TG; no C1q-DSAbs patients developed TG.
| Mean Creat at 12 months | Mean Creat at 24 months | Mean Creat at 36 months | Mean Urine PCR at 12 months | Mean Urine PCR at 24 months | Mean Urine PCR at 36 months | |
| C1q+DSAbs | 142 mmol/L | 190 mmol/L | 190 mmol/L | 133 | 246 | 156 |
| C1q-DSAbs | 95 mmol/L | 113 mmol/L | 102 mmol/L | 118 | 95 | 58 |
This study shows that HLAi transplant patients with C1q+DSAbs have a significantly higher incidence of rejection and graft loss; pre-screening for C1q+DSAbs identifies high risk patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Clarke C, Brookes P, Lawrence C, Willicombe M, Dodd P, Santos-Nunez E, Galliford J, Taube D. Complement Fixing HLA Antibodies Predict Outcome in HLA Incompatible Renal Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/complement-fixing-hla-antibodies-predict-outcome-in-hla-incompatible-renal-transplantation/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
