Comparative Outcomes of Endovascular Interventions for Hepatic Artery Stenosis Following Adult Liver Transplantation
1Interventional Radiology, Albert Einstein Medical Center - Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, 2General Surgery, Albert Einstein Medical Center - Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, 3Transplant Surgery, Albert Einstein Medical Center - Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1074
Keywords: Angiography, Hepatic artery, Post-operative complications, Vascular disease
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » Liver: Retransplantation and Other Complications
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: Retransplantation and Other Complications
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: There is mounting evidence supporting interventional radiology (IR) treatment for hepatic artery stenosis (HAS) following liver transplantation to improve diminutive graft perfusion and to prevent progression to hepatic artery thrombosis. We aim to evaluate the safety and efficacy of direct hepatic artery interventions versus extrahepatic arterial embolization in the setting of HAS.
*Methods: We conducted an electronic search of all hepatic artery angiograms from September 12, 2012 to September 12, 2019, and cross-matched results with orthotopic liver transplant recipients. 91 angiograms for 65 patients were found. Demographics and clinical data were collected. Inclusion criteria consisted of patients with IR intervention within 1 year of transplant and definitive angiographic findings of diminutive hepatic arterial flow secondary to HAS. Decision for mode of intervention was made after intraoperative discussion between IR and transplant surgery physicians.
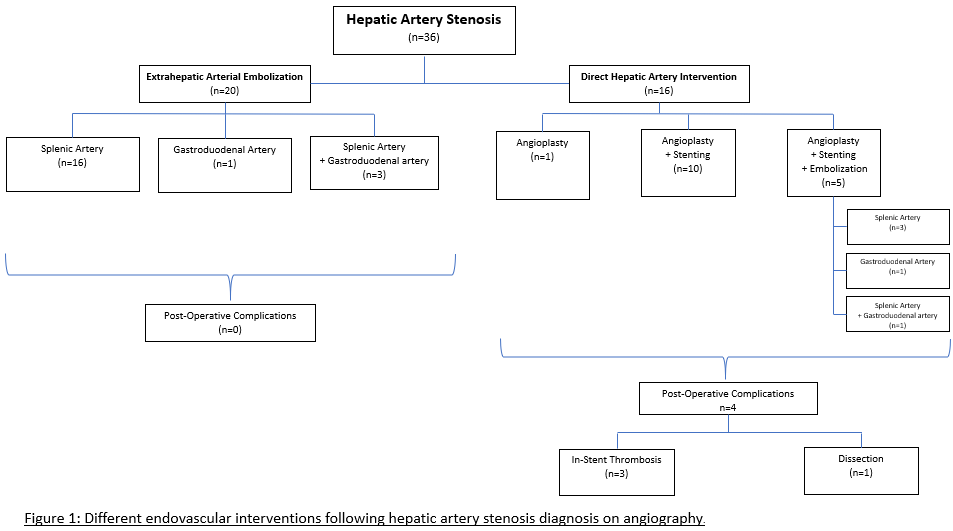
*Results: 36 patients undergoing 48 angiograms were included. 16 patients (average age 58 years; 62% male) underwent direct hepatic interventions and 20 patients (average age 55 years; 65% male) underwent extrahepatic embolization. Preprocedural clinical data shown in Table 1. Interventions for each treatment group illustrated in Figure 1. There was a significant difference in post-operative complications (25% vs 0%, p=0.018). Direct hepatic artery interventions had complications including dissection and in-stent thrombosis with incidence of 6.3% and 18.8%, respectively. There was no significant difference in number of additional procedures or 1- year survival (94% vs 95%).
*Conclusions: Extrahepatic arterial embolization provides a significantly better safety profile, with similar efficacy, versus direct hepatic artery intervention when considering treatment for hepatic artery stenosis post orthotopic liver transplant.
| Extrahepatic Embolization (n=20) | Direct Hepatic Artery Intervention (n=16) | p-value | |
| Time between transplant and intervention, days | 87 | 77.5 | 0.62 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 9.45 | 11.15 | 0.037 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 1.05 | 1.05 | 0.58 |
| ALT, U/L | 95 | 187 | 0.19 |
| AST, U/L | 44.5 | 107 | 0.14 |
| No complications | 20/20 (100%) | 12/16 (75%) | 0.018 |
| 1-year survival | 95% | 94% | 0.87 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Desai S, Crabtree D, Parsikia A, Ahuja R, Desai A, Natarajan B, Brady P, Kaul H, Khanmoradi K, Zaki R, Chandolias N. Comparative Outcomes of Endovascular Interventions for Hepatic Artery Stenosis Following Adult Liver Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/comparative-outcomes-of-endovascular-interventions-for-hepatic-artery-stenosis-following-adult-liver-transplantation/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress