Combined Liver-Kidney Transplantation in Adults With End-Stage Liver Disease: Risk Factors in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3-5, Not on Maintenance Dialysis
University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1086
Keywords: Kidney/liver transplantation, Liver cirrhosis, Multivariate analysis, Renal dysfunction
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » Liver: Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: We aimed to identify the risk factors for combined liver-kidney transplantation (CLKT) vs. liver transplantation alone (LTA) in end stage liver disease (ESLD) patients with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60 ml/.min, not on dialysis.
*Methods: Using OPTN data, we studied adult ESLD patients who received deceased-donor CLKT [N=2016 (12.9%] or LAT [N=13,588 (87.1%)] in July 2002-Mar 2016 with a 4-point modification of renal disease (MDRD) equation-estimated glomerular filtration rate (e-GFR) of below 60 ml/min (stratified into CKD stage 3: 30-59 ml/min, CKD stage 4: 15-39 ml/min, and CKD stage 5: <15 ml/min) and not on maintenance dialysis (NOD). The outcome of the study was CLKT or LAT. We reported odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for CLKT vs. LTA associated with recipient, donor, and clinical variables.
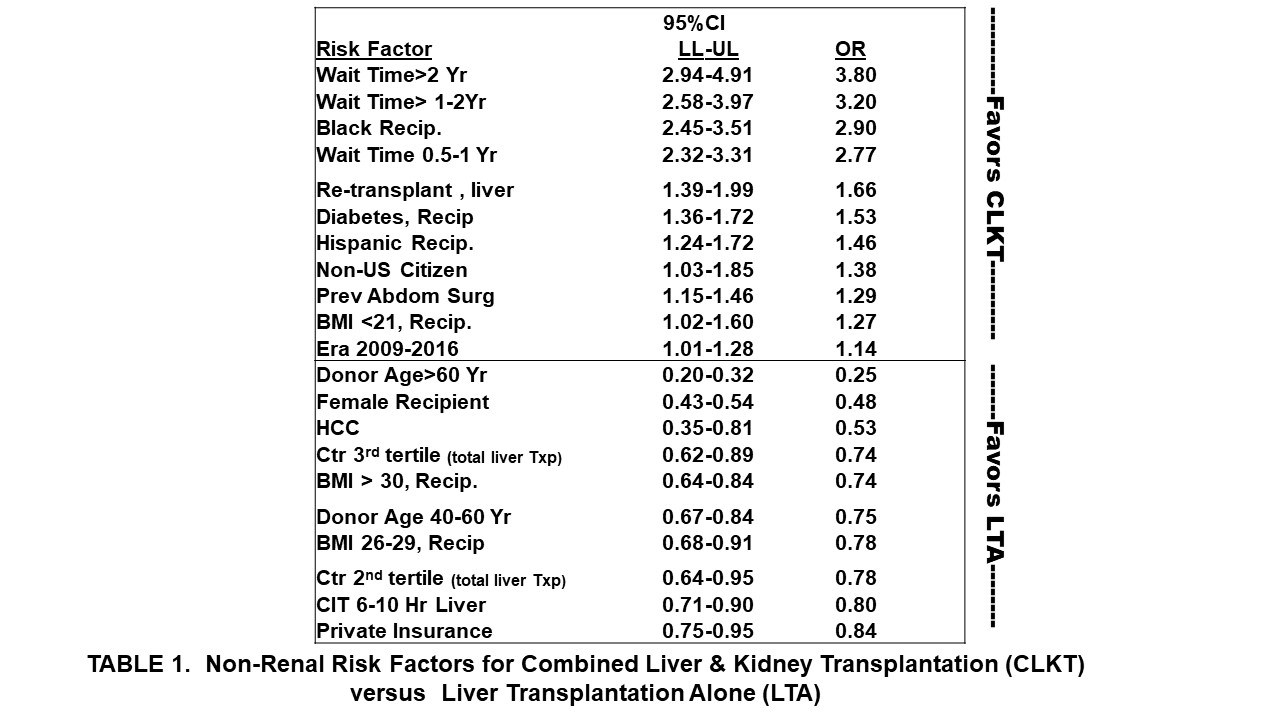
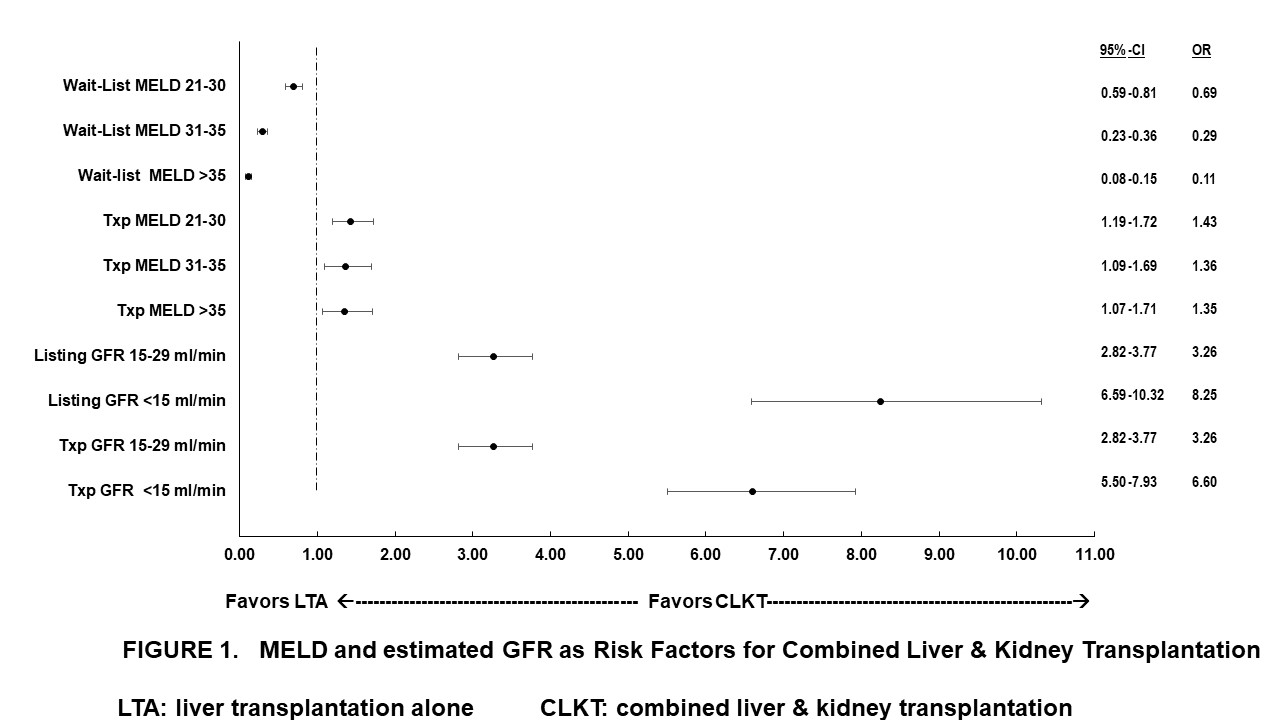
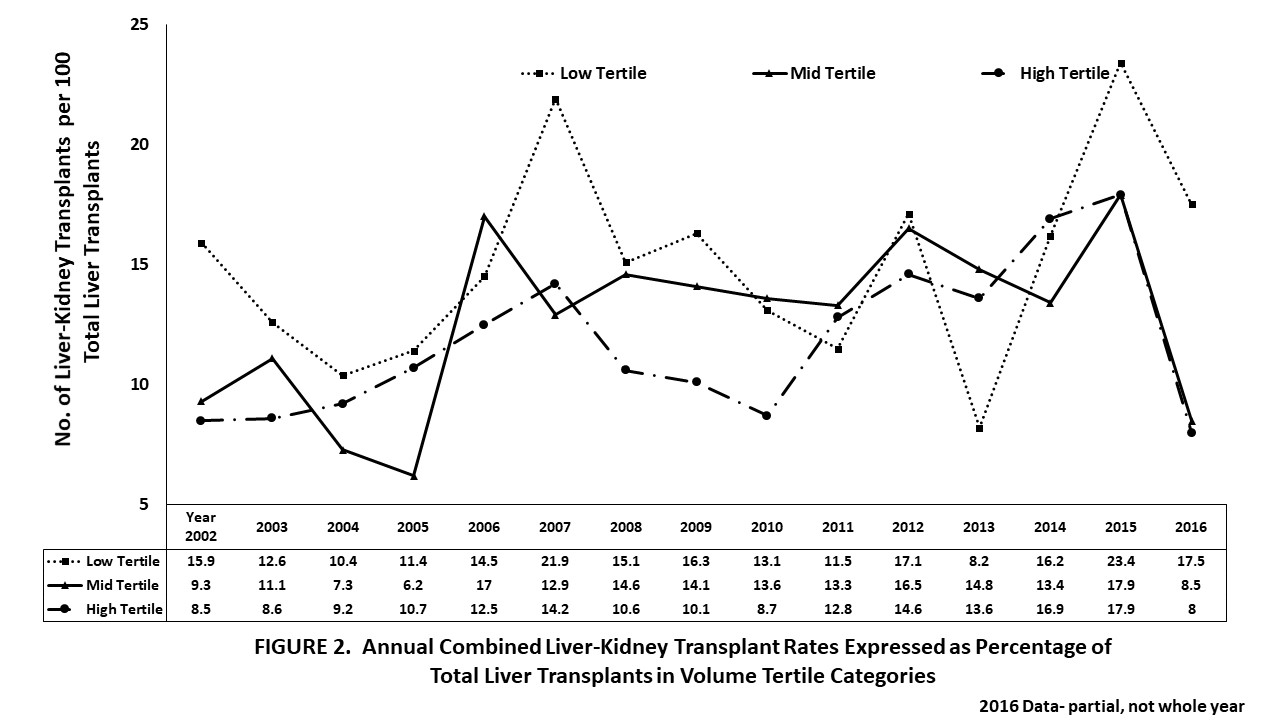
*Results: Out of 15, 604 CLKT and LTA recipients with MDRD-eGFR <60 ml/min. 8,784 (56.3%) had CKD stage 3; 4,916 (31.5%) had CKD stage 4; and 1,891 (12.1%) had CKD stage 5. CKD stages 5 and 4 at WL and transplant were the strongest risk factors for CLKT vs. LTA (FIG.1). Strong non-renal risk factors for CLKT vs. LTA were WL-time, Black recipients, liver re-transplant, and DM (TAB. 1). Factors associated with stronger likelihood of LTA vs. CLKT were WL-MELD >35, donor age>60 years, WL-MELD 31-35, female recipient’s sex, and hepatocellular carcinoma (FIG. 1 & TAB 1). Transplant center volume rank in the middle or highest tertile was associated with a lower likelihood of CLKT vs. LTA than the lowest tertile (FIG. 2, TAB. 1).
*Conclusions: Advanced CKD, waitlist time, AA ethnicity, previous liver transplant and DM are strong risk factors favoring CLKT vs. LTA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Santos A, Bueno E, Leghrouz M. Combined Liver-Kidney Transplantation in Adults With End-Stage Liver Disease: Risk Factors in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3-5, Not on Maintenance Dialysis [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/combined-liver-kidney-transplantation-in-adults-with-end-stage-liver-disease-risk-factors-in-patients-with-chronic-kidney-disease-stages-3-5-not-on-maintenance-dialysis/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress