CHBP Suppresses Acute Rejection by Inhibition Maturation of Dendritic Cells though Jak-2/STAT3/SOCS1 Signal in Rat Kidney Transplantation
1Urology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
2Biomedical Research Center, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
3CAS Key Laboratory of Receptor Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 152
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Peptides, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: T Cell Mediated Rejection: Animal Models
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 4:00pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:12pm-5:24pm
Presentation Time: 5:12pm-5:24pm
Location: Room 120-ABC
Background. Renal acute rejection (AR) affects both allografts and recipients survival. We recently synthesized a novel proteolysis-resistant cyclic helix B peptide (CHBP), which exerts promising renoprotective effects. Dendritic cells (DCs) play an activate role for AR. Thus the present study was designed to study effects of CHBP on DCs in a rat kidney transplant model.
Materials and Methods. The left kidney was retrieved from male Lewis rats and transplanted into Wistar rats with or without CHBP treatment. For in vitro experiments, LPS was used to stimulate bone marrow (BM)-derived DCs from Wistar rats with or without CHBP treatment. The phenotype and function of DCs were then evaluated.
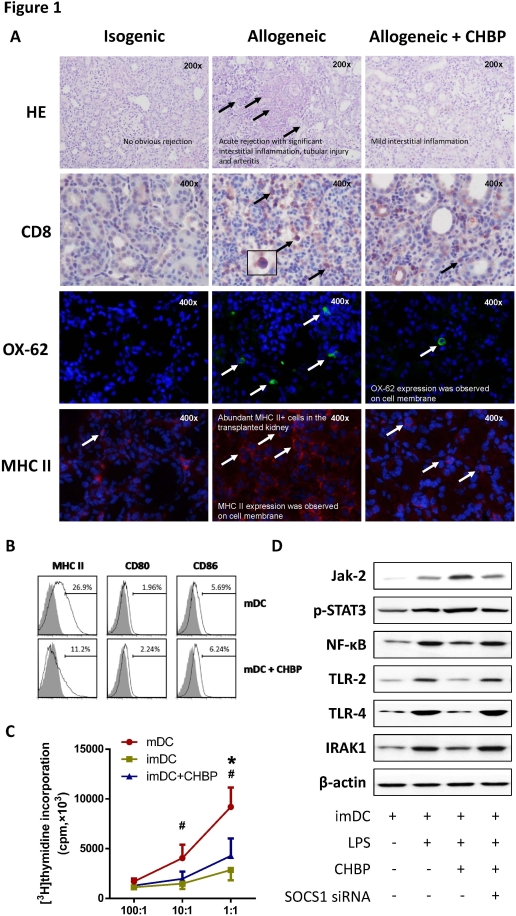
Results. Five days after transplantation, CHBP significantly ameliorated AR with less histologic injury, CD4 and CD8 T cells infiltration and apoptosis in the allograft kidney. CHBP reduced IFN-γ and IL-1β, but increased IL-4 and IL-10 protein levels in serum. The amount of DCs was significantly decreased in the transplant kidney treated with CHBP, shown as reduced expressions of OX-62, MHC-II and CD86. Incubation BM-derived DCs with CHBP led to reduction of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-12 and IL-17, but increased in IL-10 protein expression in supernatant. Furthermore, CHBP remarkably inhibited DC maturation and increased SOCS1 expression, with activated Jak-2/STAT3 signaling and inhibited TLR-2/4 signaling in cultured DCs.
Conclusion. CHBP suppresses renal transplant AR by inhibiting maturation of DCs via Jak-2/STAT-3/SOCS1 signaling pathway, suggesting that CHBP could be an effective therapeutic drug for renal transplant AR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yang C, Zhang Y, Wang J, Li L, Wang L, Xu M, Long Y, Rong R, Zhu T. CHBP Suppresses Acute Rejection by Inhibition Maturation of Dendritic Cells though Jak-2/STAT3/SOCS1 Signal in Rat Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/chbp-suppresses-acute-rejection-by-inhibition-maturation-of-dendritic-cells-though-jak-2stat3socs1-signal-in-rat-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
