Can Predonation Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Predict Postdonation Renal Function?
Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 565
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Living Donor: Other II
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:03pm-4:15pm
Presentation Time: 4:03pm-4:15pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Data on living kidney donor outcomes are of topical interest to the transplant community. Despite thorough pre-donation screening and risk assessment, a minority of living donors have suboptimal post-donation outcomes. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) is a common tool used to help determine living kidney donor candidacy. However, not much is known about ABPM as a predictor of postdonation renal function. This study sought to identify predictors of significant decline in post-donation estimated creatinine clearance (CrCl).
*Methods: Retrospective longitudinal cohort study of living donors who donated from 2015-2017. Baseline demographics and clinical parameters (24 hr ambulatory BP, clinic BP, SCr, UPCR) pre-donation and at 1, 6, 12, 24 months post-donation were obtained from the EMR. Predonation ABPM were grouped by sleep v. awake and systolic v. diastolic BP. The primary outcome was change in CrCl from predonation to latest postdonation value up to 24 months. Univariate and multivariable linear regression analyses were performed.
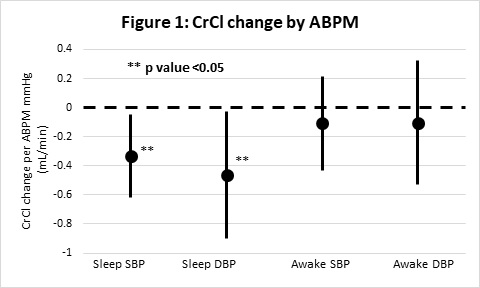
*Results: 93 living donors were included; 60 (65%) were female and 77 (86%) were Caucasian. After a mean follow-up of 18 months, 37 (40%) had a decline in estimated CrCl of greater than 30 mL/min and 27 (29%) had post-donation CrCl less than 70% of pre-donation values. Sleeping ABPM systolic and diastolic BPs were inversely associated with CrCl, but awake ABPM values were not (Figure 1). After adjusting for baseline demographics and clinical parameters, a pre-donation mean SBP >100 mmHg while sleeping assessed using 24-hr ambulatory BP predicted a 10.1 mL/min decline in estimated CrCl (95% CI 2.6 to 17.6 mL/min decline; p=0.009), while an in-clinic 24-month post-donation SBP >130 mmHg was correlated with a 10.9 mL/min decline in estimated CrCl (95% CI 0.8 to 21.1 mL/min decline; p=0.037).
*Conclusions: This observational data suggests that pre-donation 24-hr ambulatory BP assessment was most sensitive in predicting rate of estimated CrCl decline post-donation. It is also apparent that close BP monitoring post-donation is important to assess for potential further declines in CrCl estimations. This raises intriguing questions about possible links between asleep BP, post-donation BP, and postdonation renal function. Measures to screen for elevated BP and achieve tight BP control may optimize post-donation renal function among living donors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ahmed MMohamed, Salas MPosadas, Taber D, Rao V, Soliman K, Casey M. Can Predonation Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Predict Postdonation Renal Function? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/can-predonation-ambulatory-blood-pressure-monitoring-predict-postdonation-renal-function/. Accessed February 20, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress