Bortezomib Impacts T-Cell Signaling and Regulatory Pathways
Med. Univ South Carolina, Charleston
Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland
Emory University, Atlanta
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D1705
Introduction/ Aims: Bortezomib (PS-341), a selective 26S proteasome inhibitor has been used to treat antibody mediated rejection (AMR) among allograft recipients. The efficacy of Bortezomib treatment of AMR has been reported in cases both with pure AMR and with mixed features of T cell mediated rejection (TCMR) and AMR. While the effect of Bortezomib on HLA-donor specific antibodies is largely attributed to its effects on plasma cells (PCs), the 26S proteasome is distributed in cells other than PCs. Bortezomib’s efficacy in mixed ACR/AMR raises the possibility that additional signaling pathways may be impacted by bortezomib. In the current study we used a peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMNC) model to investigate whether other signaling pathways are altered by bortezomib
Methods: Human PBMNC isolated from 2 normal healthy volunteers were treated with Bortezomib or vehicle control. cDNA microarray hybridization using four 42K genes slide array (Stanford University) was performed on RNA isolated from treated cells. Array normalization and analysis were performed using TIGR software. Pathways were analyzed using Onto-Express. Array results were validated with RT- PCR.
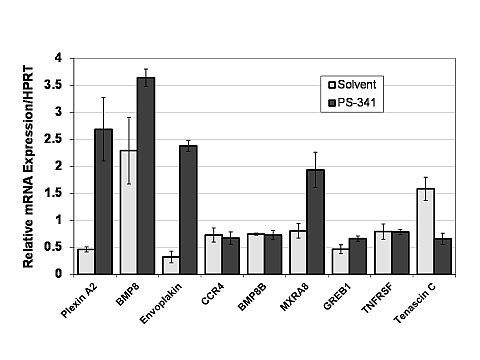
Results: In Bortezomib treated PBMNC, alteration in T cell activation and signaling pathways were observed in addition to pathways involving B cell signaling. Specifically, mRNA levels of Plexin A2, a Plexin-A subset of the semaphorin co-receptor family, was increased 5 fold [Figure 1]. Interestingly, Plexin A2 is a key negative regulator of T cell activity, proliferation,chemotaxis, differentiation, and cytokine production Additionally, tenascin C gene (a positive regulator of IL 17) expression was decreased with bortezomib treatment.
Conclusions:
Our findings point to significant effects of Bortezomib on T cell signaling pathways. We speculate that our observatons may explain the efficacy of Bortezomib in patients with mixed TCMR and AMR despite variable effect on alloantibody levels. Further studies are needed to document the novel pathways impacted by Bortezomib as potential targets of therapeutic intervention in AMR and mixed ACR/AMR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moussa O, Askar M, Gebel H, Flechner S, Taber D, Chavin K, Baliga P, Srinivas T. Bortezomib Impacts T-Cell Signaling and Regulatory Pathways [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/bortezomib-impacts-t-cell-signaling-and-regulatory-pathways/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
