Big Data Predictive Solution to Optimize Kidney Transplant Outcome and Resource Utilization.
MUSC, Charleston.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 111
Keywords: Economics, Medicare, Multivariate analysis, Resource utilization
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Impact of New Allocation Systems and Novel Tools for Performance Enhancement in Abdominal Transplantation
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: Room 210
Objective: Transplant (Tx) programs often use data in reaction to regulation vs. optimizing outcomes through data driven clinical care. Tx specific issues can detract from primary care (PC) needs (cardiac, metabolic) of patients. We demonstrate an EHR sited Big Data solution to optimize outcomes by cueing clinical workflow to appropriate care teams-PC vs Tx focus.
Methods: Predictive models for graft loss (GL) in yrs 1 and 3, and 3-yr mortality using baseline and follow up structured/unstructured data were developed in a QAPI on adult kidney tx recipients (2007-15). Structured data (labs) were directly taken from electronic records (EHR, UNOS, Txp database (Velos)) and Natural Language Processing (IBM Watson) was applied to unstructured text (rejections,vitals). We used IBM SPSS Modeler and Essentials for R for analysis.
Daily, data refresh the predictive model and are driven to the EHR, in a concise clinician-facing view. These views cue the right teams (PC vs. Tx focus) to deploy appropriate care pathways through the EHR workflow.
Results: Significant mutable factors associated with 1 and 3 yr GL and death fell into 2 groups: Immunologic factors, (Tx nephrology skill), and patient-level risk factors not directly Tx related, cardiovascular and behavioral risk (PC skill). Patient-level factors (non-Tx) associated with increased risk of GL at 1-yr (n=22/45) included cardiac /vascular events (OR=3.2) or active smoking (OR=3.5)). Acute MI (OR=10.5) or cardiac/vascular events (OR=2.5) dominated GL at 3 ys (n=40/89)). Cardiac/ vascular events significantly associated with 3-yr death (OR=2.6) with a 21.6 % 3-yr cardiovascular mortality rate( 50.7% of overall death). These results led us to design data systems and workflow built into the EHR that cue appropriate ( eams, PC focused vs. Tx focused) 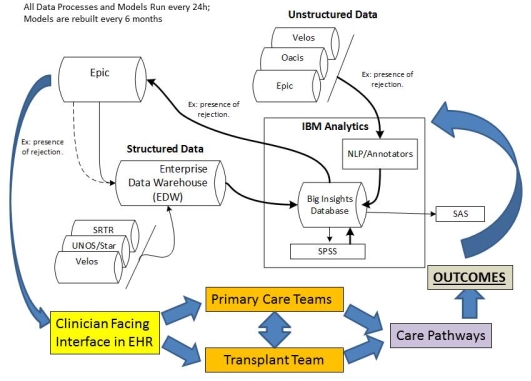 .
.
Conclusions: Transplant and Primary care teams can synergize in a Big Data driven daily deployable EHR sited clinician interface curating multiple data sources and vectoring the right skills to patients using predictive models. Our solution allows programs to optimize outcomes proactively by using data to cue intervention and allocate resources rather than react to regulatory stress.
CITATION INFORMATION: Srinivas T, Northrup D, Mauldin P, Taber D, Su Z, Zhang J, Daniels M, Moran W. Big Data Predictive Solution to Optimize Kidney Transplant Outcome and Resource Utilization. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Srinivas T, Northrup D, Mauldin P, Taber D, Su Z, Zhang J, Daniels M, Moran W. Big Data Predictive Solution to Optimize Kidney Transplant Outcome and Resource Utilization. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/big-data-predictive-solution-to-optimize-kidney-transplant-outcome-and-resource-utilization/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
