Benefit of Anti-Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin(HBIG) Monotherapy Compared to HBIG Combined with Entecavir in Long Term Renal Function
J. Lee,1 D. Kim,1 J. Lee,2 S. Kim,3 H. Lee,4 S. Song,5 J. Lee,1 M. Ju,1 G. Choi,1 D. Joo,1 J. Choi,1 S. Kim,1 Y. Jung.1
1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University of College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2Department of Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, Seongnam, Republic of Korea
3Department of Surgery, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Republic of Korea
4Department of Surgery, Ilsan Hospital, Ilsan, Republic of Korea
5Department of Surgery, Ehwa Wonmen Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D243
Keywords: Renal dysfunction
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Liver: Viral Hepatitis
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
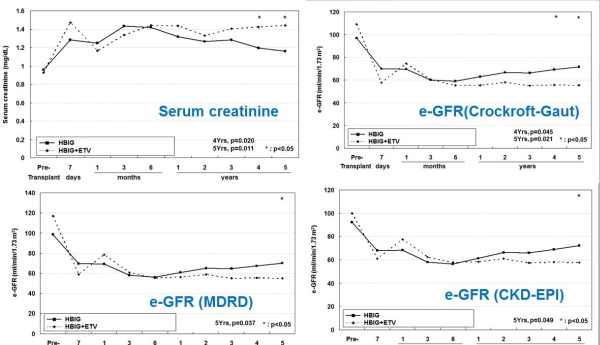
Background: To reduce the HBV reinfection after liver transplantation, anti-hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) alone or combination with antiviral nucleotide analogues are usually used regimen. However, antiviral nucleotide analogues have nephrotoxicity, which is a critical issue because renal dysfunction frequently happens after liver transplantation.
Method: Medical records of 171 liver recipients with HBV who underwent liver transplantation between Sep. 2005 and Dec. 2012 were retrospectively reviewed. The difference of renal function of HBIG mono-therapy group (HBIG) and HBIG combined with Entecavir group (HBIG+ETV) were analyzed.
Results: There was no significant difference in age, gender, body mass index, intraoperative blood loss, and MELD score between the two groups. But the patients who had preoperative ascites, mean preoperative AST level, preoperative GFR level, and the applying event of CRRT was significantly different between the groups. The decrease of eGFR between preoperative and 1 year after transplantation was 31.5±27.2 mL/min/1.73m2 (p<0.001), in HBIG group and 40.0±45.9 mL/min/1.73m2 (p<0.001) in HBIG+ETV group. Also, the eGFR decrease between preoperative and 4-year after transplantation was 24.5±29.9 mL/min/1.73m2 (p<0.001) in HBIG group and 38.9±56.8 mL/min/1.73m2 (p<0.001) in HBIG+ETV group.
Conclusion: There was no difference of recurrence rate of HBV. However, HBIG+ETV combination regimen showed more declination of eGFR in long-term period after liver transplantation than HBIG alone.
CITATION INFORMATION: Lee J., Kim D., Lee J., Kim S., Lee H., Song S., Lee J., Ju M., Choi G., Joo D., Choi J., Kim S., Jung Y. Benefit of Anti-Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin(HBIG) Monotherapy Compared to HBIG Combined with Entecavir in Long Term Renal Function Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee J, Kim D, Lee J, Kim S, Lee H, Song S, Lee J, Ju M, Choi G, Joo D, Choi J, Kim S, Jung Y. Benefit of Anti-Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin(HBIG) Monotherapy Compared to HBIG Combined with Entecavir in Long Term Renal Function [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/benefit-of-anti-hepatitis-b-immunoglobulinhbig-monotherapy-compared-to-hbig-combined-with-entecavir-in-long-term-renal-function-2/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress