Baseline Predictors of Antimicrobial Utilization in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
M. Govil1, D. Xie1, L. S. Hynan2, S. L. Spitznogle1, M. L. Monogue1, J. Sanders1, E. Bae1, J. B. Cutrell1, R. M. La Hoz1
1University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, 2University of Texas at Southwestern, Dallas, TX
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1347
Keywords: Multivariate analysis, Risk factors
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 24 - All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis) III
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Antimicrobial use (AU) is a major driver of antimicrobial resistance but is understudied in solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients. Our study sought to quantify and identify baseline predictors of AU among SOT recipients at a single transplant center.
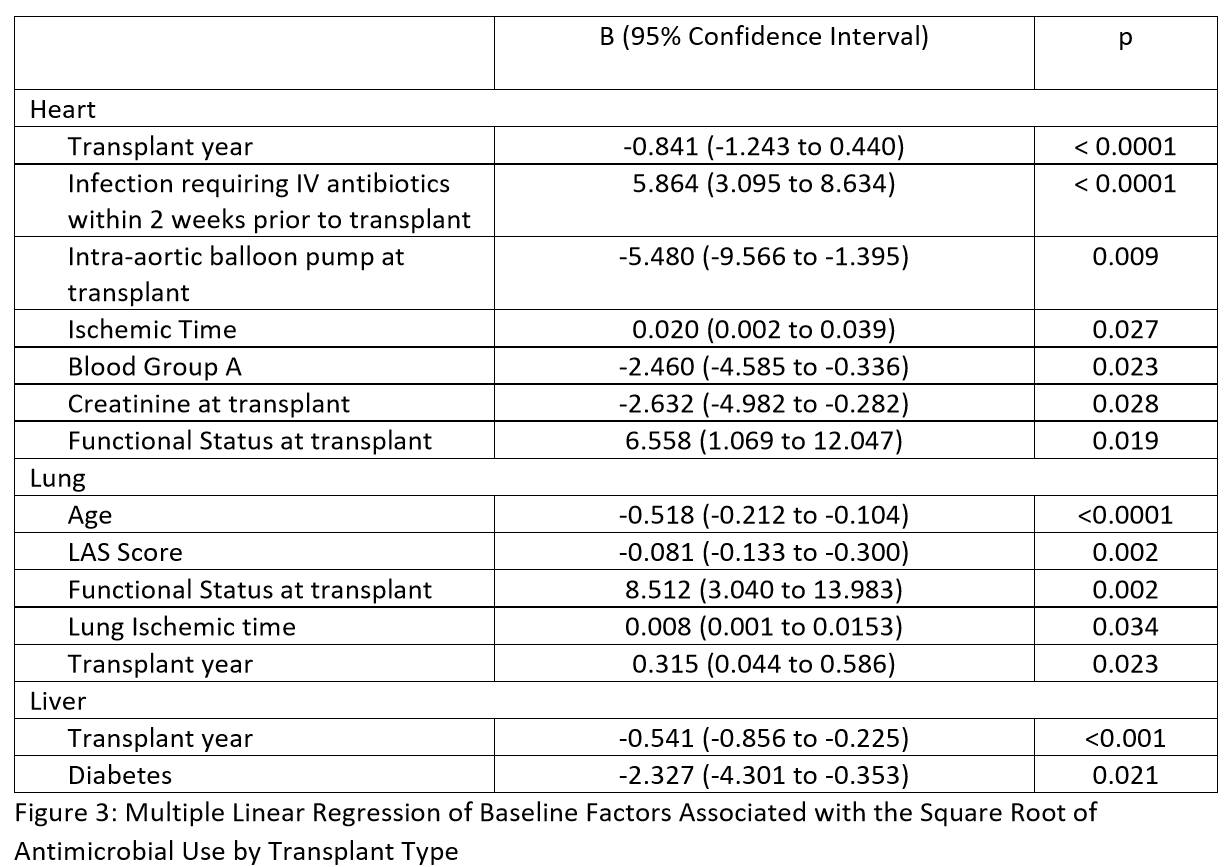
*Methods: We conducted a retrospective single-center cohort study of all first SOT at our institution from 2010 to 2019 using merged data from the Standard Transplant Analysis and Research files and the electronic health record. Inpatient AU during the first six months post-transplant was calculated as days of therapy per 1000 days present using National Healthcare Safety Network AU module definitions and antimicrobial class categories. Multiple linear regression was used to identify baseline factors associated with the square root of AU.
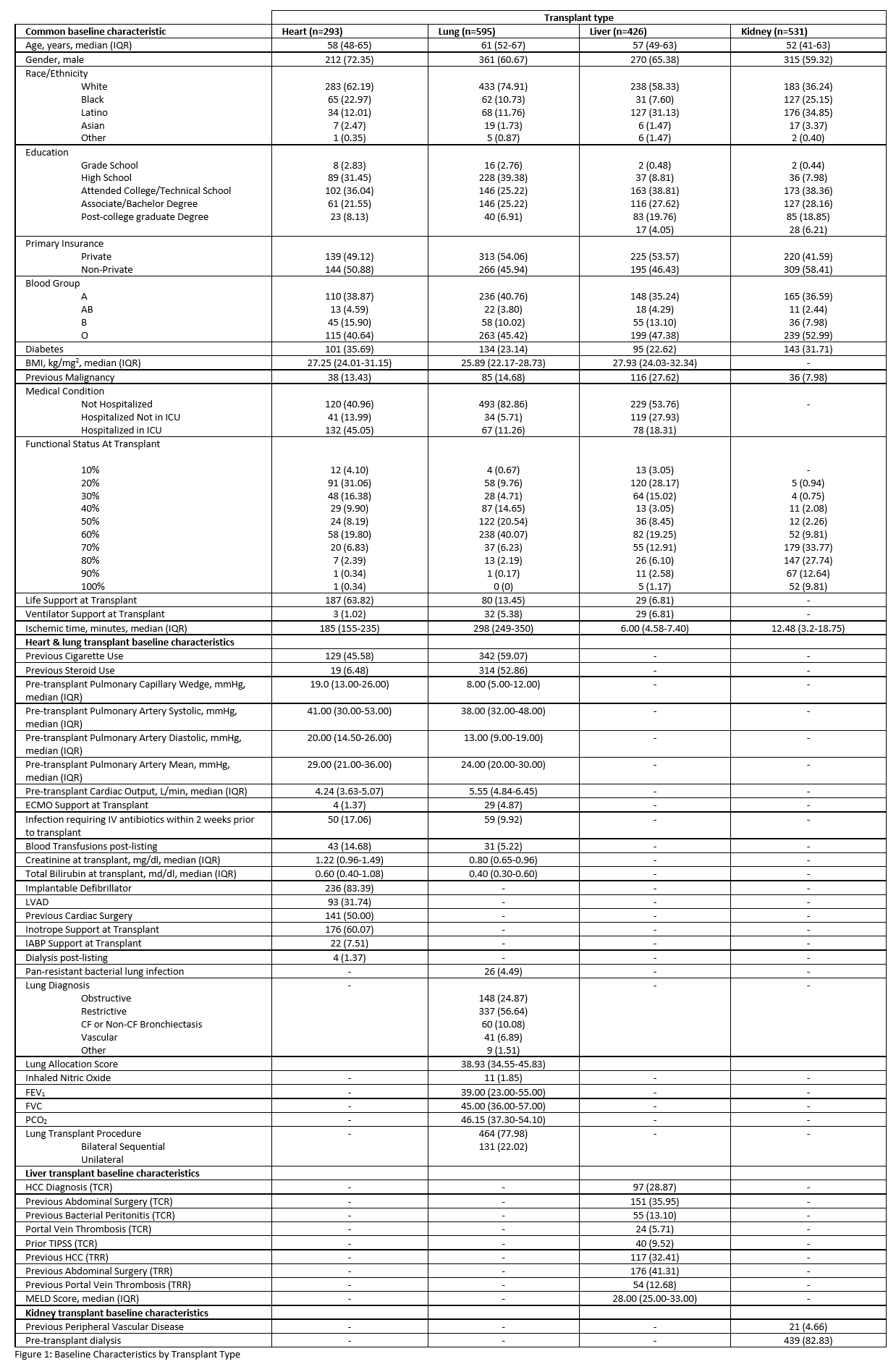
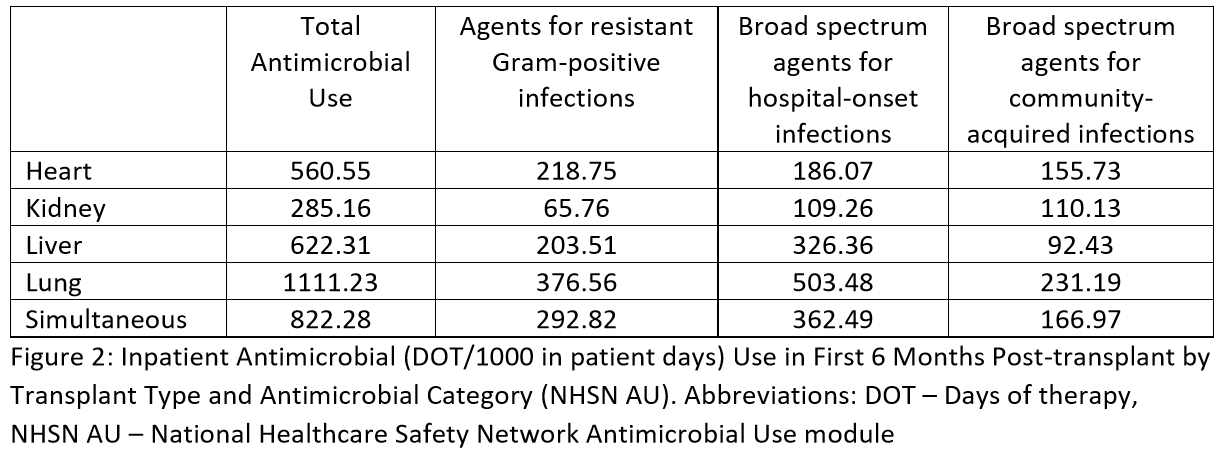
*Results: 1,845 patients were included (293 Heart, Kidney 531, 426 Liver, 595 Lung). Table 1 includes the baseline characteristics of the study population. Total inpatient AU was substantial and varied by transplant type: heart 560.55, kidney 285.16, liver 622.32, lung 1111.23, and simultaneous 822.28 (Table 2). In multiple linear regression, we identified key variables associated with inpatient AU by organ type (Table 3).
*Conclusions: SOT recipients at our institution had substantial AU in the first 6 months post-transplant and specific baseline predictors were associated with higher AU. Further research is needed to assess appropriateness of AU and develop targeted strategies for antimicrobial stewardship in SOT recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Govil M, Xie D, Hynan LS, Spitznogle SL, Monogue ML, Sanders J, Bae E, Cutrell JB, Hoz RMLa. Baseline Predictors of Antimicrobial Utilization in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/baseline-predictors-of-antimicrobial-utilization-in-solid-organ-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress