Associations of Immunosuppression Regimen with Fracture Risk After Kidney Transplant in High-Risk Populations: Identifying Targets for Risk-Reduction
K. Lentine1, S. Kupacchi2, W. Cheungpasitporn3, R. Li4, Y. Caliskan4, M. Schnitzler4, M. McAdams-DeMarco5, J. Ahn5, S. Bae6, G. Hess7, D. Segev5, D. Axelrod2
1Saint Louis University Center for Abdominal Transplantation, St. Louis, MO, 2U Iowa, Iowa City, IA, 3Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, 4Saint Louis University, Saint Louis, MO, 5Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MD, 6Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MO, 7Drexel, Philadelphia, MO
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 223
Keywords: Elderly patients, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Metabolic complications
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 35 - Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications II
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:40pm-4:50pm
Presentation Time: 4:40pm-4:50pm
Location: Hynes Veterans Auditorium
*Purpose: Disorders of bone and mineral metabolism frequently develop with advanced kidney disease, may be exacerbated by immunosuppression (ISx) after kidney transplant (KTx), and may increase the risk of fracture. We examined relationships between fractures and ISx among older and younger adults in a national sample of Medicare beneficiaries.
*Methods: We examined SRTR data (2005-2017) to explore associations of ISx regimens (within 6 mo) with osteoporosis and fracture diagnoses >6 mo-to-3 yr post-KTx among Medicare-insured younger (age <55) and older (aged ≥ 55) adults. We used multivariate Cox regression with inverse propensity weighting to compare cancer risk (adjusted hazard ratio, 95% LCL aHR 95% UCL) vs. reference regimen of Thymoglobulin (TMG) or Alemtuzumab (ALEM) + Tacrolimus (Tac) + mycophenolic acid (MPA) + prednisone [Pred
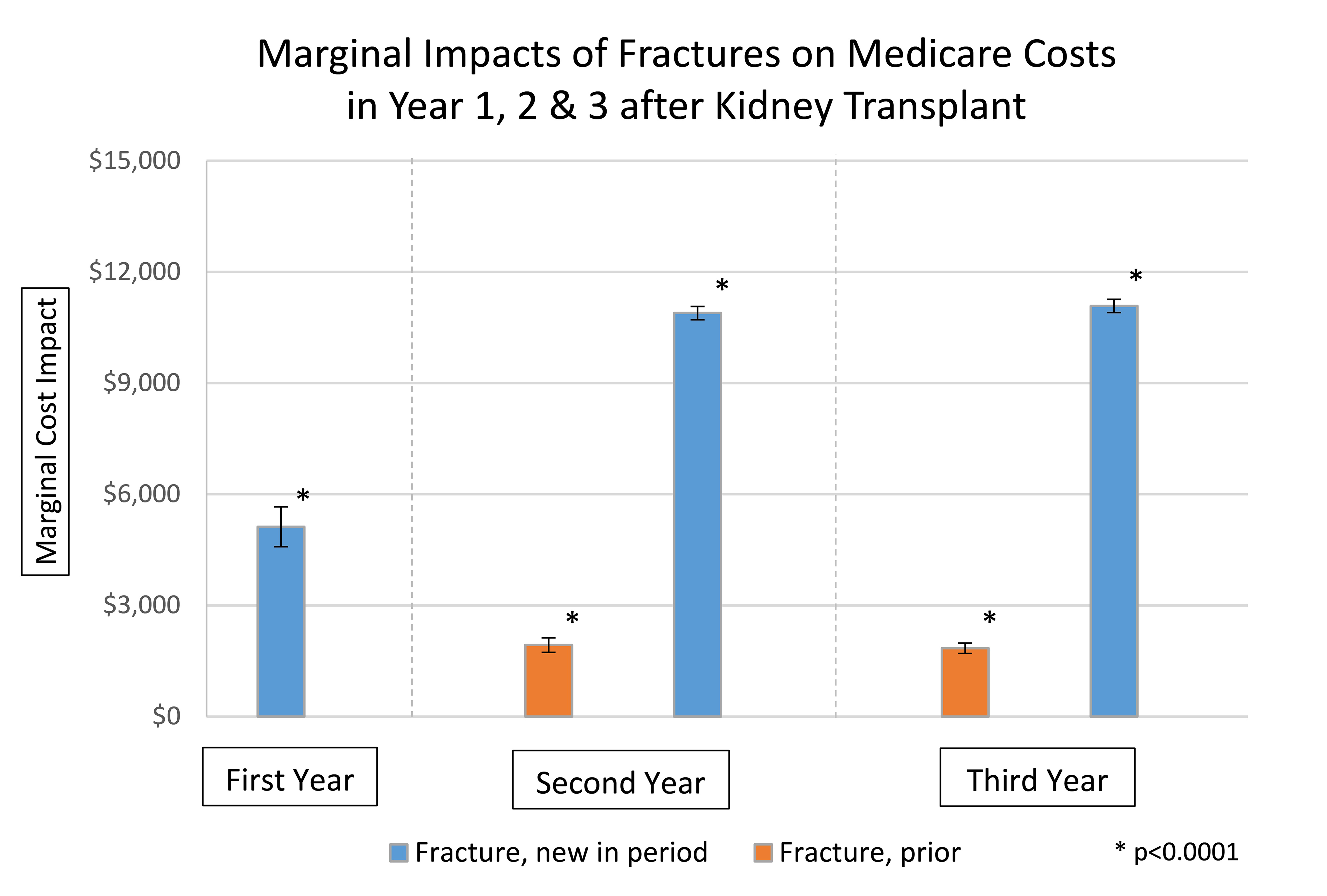
*Results: Fractures were identified in 7.5% of KTx (women: 8.8% vs. men: 6.7%; age<55 years: 5.9% vs ≥55 years: 9.3%) during observation. In time-varying regression, fractures were associated with substantially increased risk of subsequent death within 3 months of diagnosis (aHR, 2.453.063.81). Fractures were also associated with increased Medicare spending (fracture in the 1st year: $5122.5, p<.0001, 2nd year: $10,890, 3rd year: $11,082) (Fig 1).
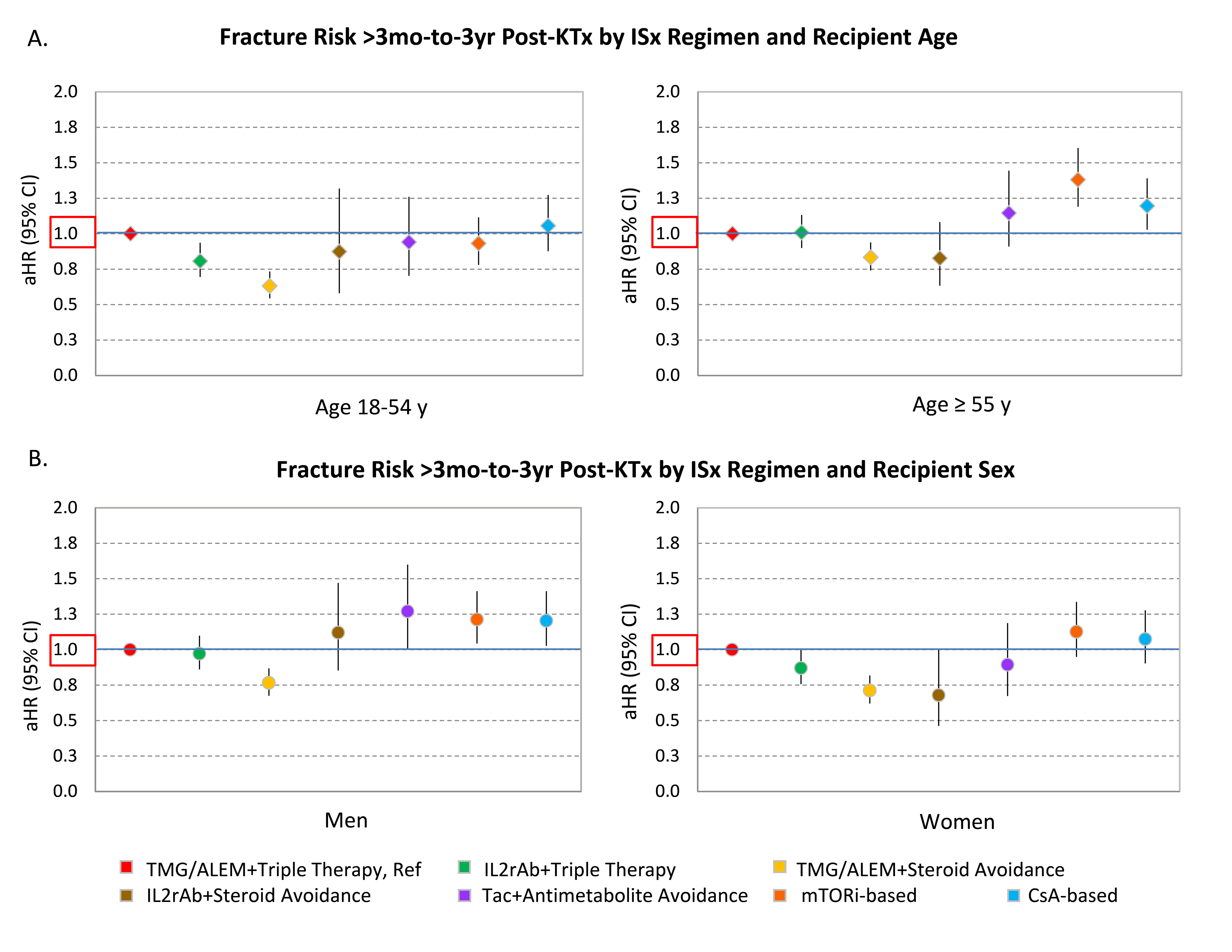
Cell-depleting induction and early steroid withdrawal/avoidance (ESW) ISx significantly reduced fracture risk in younger (aHR, 0740.830.94) and older (aHR, 0.540.630.73) patients (Fig 2A). ESW with any induction was associated with reduced fracture risk in women (Fig 2B).
*Conclusions: Fracture after KTx is associated with significantly increased clinical complications and costs. ESW after induction with TMG/ALEM reduces the risk of fracture after KTx and should be considered for high-risk patients including older adults and women.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lentine K, Kupacchi S, Cheungpasitporn W, Li R, Caliskan Y, Schnitzler M, McAdams-DeMarco M, Ahn J, Bae S, Hess G, Segev D, Axelrod D. Associations of Immunosuppression Regimen with Fracture Risk After Kidney Transplant in High-Risk Populations: Identifying Targets for Risk-Reduction [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/associations-of-immunosuppression-regimen-with-fracture-risk-after-kidney-transplant-in-high-risk-populations-identifying-targets-for-risk-reduction/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress