Assessment of Proteinuria Reported as Adverse Events in De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients Receiving an Everolimus-Based Regimen: 24-Month Results from TRANSFORM
1TRANSFORM Study Group, Basel, Switzerland, 2Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A257
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Proteinuria, Renal function, Safety
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
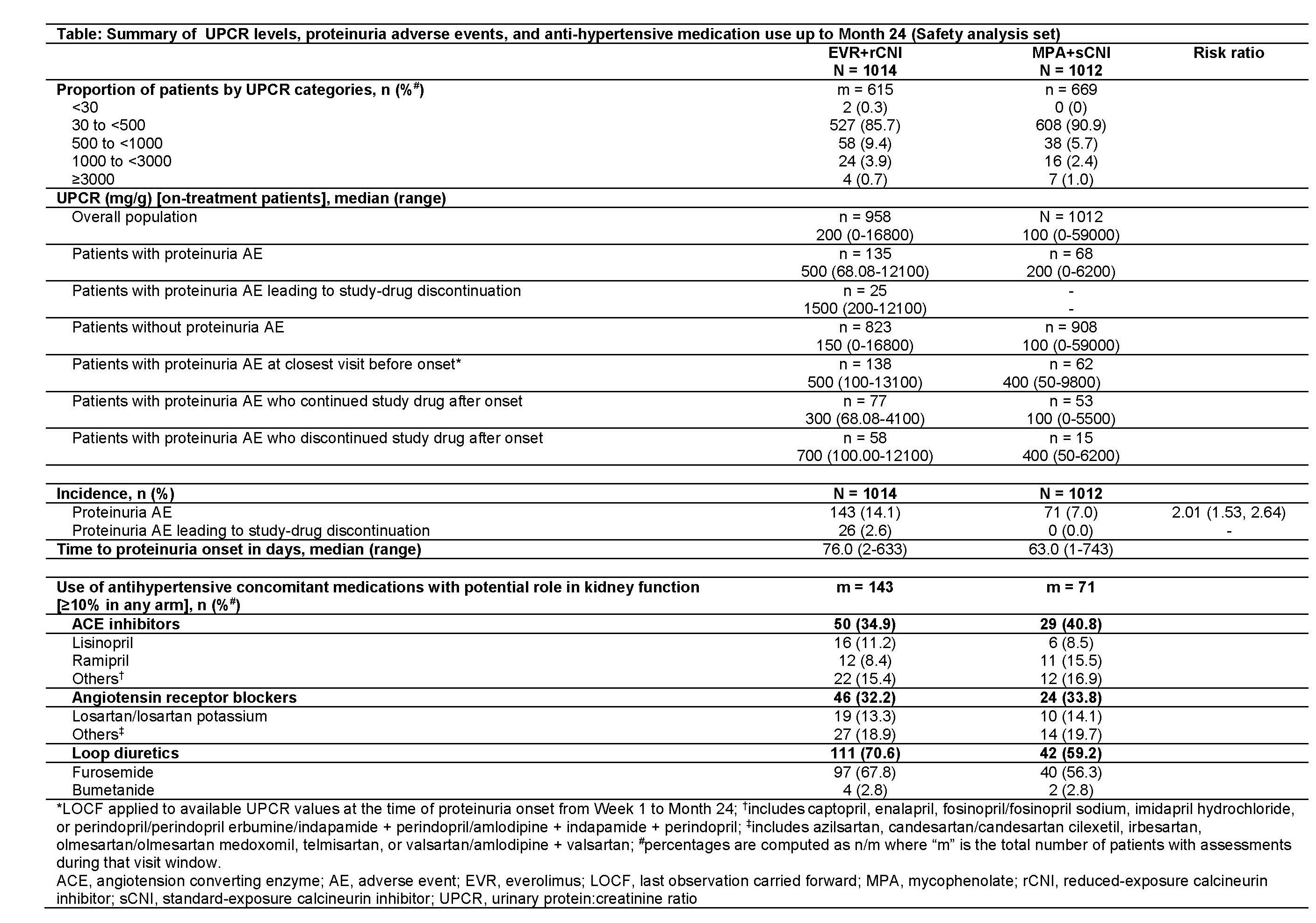
*Purpose: mTOR inhibitors (eg, everolimus [EVR]), are thought to increase the risk of post-transplant (Tx) proteinuria (PU). Here, we assess PU onset and outcomes in de novo renal Tx recipients (RTxRs) receiving EVR+reduced CNI (EVR+rCNI) or mycophenolate+standard CNI (MPA+sCNI) from the TRANSFORM study.
*Methods: In this 24-month (M), multicenter, open-label study (NCT01950819), RTxRs were randomized to EVR+rCNI (N=1022) or MPA+sCNI (N=1015) + induction and steroids. EVR trough level (C0), urine protein:creatinine ratio (UPCR), antihypertensive medication use and onset time in patients with PU adverse events (AEs) were assessed up to M24.
*Results: At M24, proportion of patients in both arms was similar across UPCR categories (<500 mg/g: >85% in both; 500-<3000 mg/g: 13.3% [EVR+rCNI] and 8.07% [MPA+sCNI]; and >3000 mg/g: ~1% in both). Incidence of PU as an AE was 14.1% (EVR+rCNI) and 7.0% (MPA+sCNI). Median time to onset was 76 vs 63 days with EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI. Drug discontinuation due to PU AE was noted in 26 vs 0 patients in EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI (Table). Among RTxRs with PU, baseline demographics were mostly balanced, except for higher proportion of RTxRs with cold ischemia time >20 h in EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI arm (18.9% vs 9.9%). In patients with PU AE, though mean EVR C0 was within target range from M1-M6, it was slightly lower in patients who continued (5.4-6.1 ng/mL) vs those who discontinued (5.9-7.0 ng/mL). Between-arm difference in median UPCR up to M24 was 2.5-fold higher in EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI arm among patients with PU. Median UPCR of patients discontinuing study drug was higher than that of those continuing study drug in both arms. Use of loop diuretics was more frequent in EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI arm.
*Conclusions: Although EVR+rCNI regimen was associated with a high incidence of PU AEs, these were not associated with EVR C0 outside target range and rarely led to drug discontinuation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Legendre C, Berger S, Oppenheimer F, Wiseman A, Steinberg S, Viklicky O, Russ G, Danguilan R, Basic-Jukic N, Mor E, Narvekar P, Gutierrez MPHernandez, Bernhardt P, Sommerer C. Assessment of Proteinuria Reported as Adverse Events in De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients Receiving an Everolimus-Based Regimen: 24-Month Results from TRANSFORM [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/assessment-of-proteinuria-reported-as-adverse-events-in-de-novo-renal-transplant-recipients-receiving-an-everolimus-based-regimen-24-month-results-from-transform/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress