Antithymocyte Globulin Induction Is Associated with Improved Graft Survival and Reduced Ischemic Cholangiopathy after DCD Liver Transplantation as Compared to Basiliximab
Transplant Surgery, University of California, San Diego, CA
Transplant Surgery, University of Washington, Seattle, WA
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 280
Utilization of donation after cardiac death (DCD) hepatic allografts is limited by ischemia related biliary complications and graft loss. This report updates the originial UW experience (2003-2006) which now encompasses 89 DCD liver transplants performed between 2003 and 2011. (minimum followup period of 1 year)
To date, risk factors for increased graft loss have focused on donor and recipient factors that may identify organs or recipients at increased risk for biliary complications, however there has been no report regarding the potential effect of immunosuppression modification on the outcomes for DCD liver donor recipients. Our program has almost exclusively utilized either ATG or Basiliximab induction (86/89) for DCD liver transplants allowing us to retrospectively review any impact that alternative immunosuppression protocols may have on DCD graft outcome.
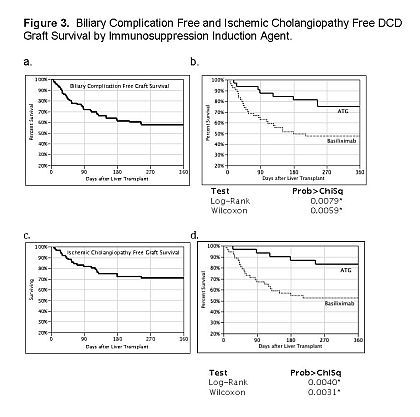
Since beginning the UW DCD program in 2003, we have achieved Kaplan-Meier estimated 5 year patient and graft survival rates of 81.6% and 75.6% respectively with the great majority of patient and graft losses occurring in the first year post transplant from ischemic cholangiopathy. Analysis of the impact of immunosuppression induction demonstrated a dramatic effect favoring ATG over Basiliximab with improved graft survival of 96.9% at one year vs. 75.9% for Basiliximab. (p=0.005). While the rate of rejection was statistically identical (21.9%/22.2%) between the two groups, the rate of IC was 35.2% in the Basiliximab group compared to 12.5% in the ATG group at one year. (p=0.017). Multivariate analysis demonstrated a stronger association for ATG with improved outcome than commonly identified risk factors of Donor age >50, Donor WIT >30min, Donor weight >100kg, Donor CIT >9hrs,Recipient HCV and HTK Preservation for predicting 1 year graft survival and 1 year IC free graft survival.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Halldorson J, Bakthavatsalam R, Dick A, Rayhill S, Perkins J, Reyes J. Antithymocyte Globulin Induction Is Associated with Improved Graft Survival and Reduced Ischemic Cholangiopathy after DCD Liver Transplantation as Compared to Basiliximab [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/antithymocyte-globulin-induction-is-associated-with-improved-graft-survival-and-reduced-ischemic-cholangiopathy-after-dcd-liver-transplantation-as-compared-to-basiliximab/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
