Anti-CD3 Accelerated Diabetes in Transgenic Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) Mice Expressing miRNA Decoy Sequence(s)
Medicine, SUNY at Buffalo
Surgery, SUNY, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A742
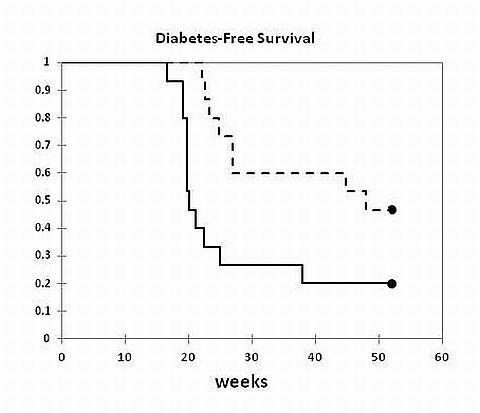
Microinhibitory RNAs (miRNAs) are short sequences that regulate post-transcriptional mRNA and protein expression. miRNA decoy genes alter gene expression by interfering with miRNA binding to the 3’untranslated regions (3’UTR) of mRNA targets. We have shown that transgenic (TG) expression of a short (240bp) fragment derived from the 3’UTR of the Wiskott-Aldrich Interacting Family 2 (WIPF2) gene blocks miRNA146a binding and murine T cell activation induced Wipf2 downregulation. This results in enhanced CD8 cytotoxicity (Eur.J.Imm. 2012.42:2409). We now examine Wipf2 regulation and the in vivo effects of this “decoy” transgene in NOD mice, a CD8 cytotoxic lymphocyte dependent model of human IDDM. Methods: Nucleotides 1,681-2,015 of WIPF2 3’UTR were cloned into pCD2-LCR containing vector thereby limiting expression to lymphocytes. C57 TG mice were generated by homologous recombination of this sequence into the HPRT site on the X chromosome. The transgene was then bred onto the NOD background. All tests were done on BC15 mice. Results: In stark contrast to the 75% decrease in Wipf2 gene expression seen in activated C57 T cells in vitro, Wipf2 levels increase by approximately 90% in anti-CD3/CD28 stimulated wild type (WT) NOD T cells. The presence of the decoy transgene in TG NODBC15 mice reverted Wipf2 expression to lower levels observed in TG C57mice. The incidence of spontaneous diabetes in TG BC15 NOD mice is similar to that in WT NOD mice. However, contrary to our expectations, when activated by injecting anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody (5mcg/dose) at weeks 8, 12 and 16, TG NOD mice demonstrated an accelerated rate of diabetes (WT n=12 dashed line vs. TG n=15 solid line, p<0.001) (Fig.1). Conclusions: Compared to C57 mice, NOD T cells demonstrate enhanced of Wipf2 gene expression which may reflect underlying miRNA defects. However, anti-CD3 stimulation in vivo accelerated diabetes in TG NOD mice indicating that this effect does not depend on increased Wipf2 expression. Preliminary data suggests that the expression of this potential miRNA decoy may alter a miRNA network enhancing CTL relevant genes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pankewycz O, Xuan J, Shen L, Ambrus J, Laftavi M. Anti-CD3 Accelerated Diabetes in Transgenic Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) Mice Expressing miRNA Decoy Sequence(s) [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/anti-cd3-accelerated-diabetes-in-transgenic-non-obese-diabetic-nod-mice-expressing-mirna-decoy-sequences/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
