An Evaluation of Pjp Prophylaxis and Anemia Among Renal Transplant Recipients
J. Hedvat, N. Poladi, D. Salerno, G. Dube, N. Lange
NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 738
Keywords: Infection, Kidney transplantation, Prophylaxis
Topic: Clinical Science » Infectious Disease » All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Dapone and atovaquone are therapeutic options for PJP prophylaxis in renal transplant recipients. The objective of this study was to evaluate the incidence of anemia in renal transplant recipients receiving these agents.
*Methods: This was an IRB-approved, single-center retrospective analysis of adult renal transplant recipients who received either dapsone or atovaquone for PJP prophylaxis between July 2012 and August 2019. The primary endpoint was the change in hemoglobin within 90 days of drug initiation. Other endpoints of interest included incidence and management of anemia at multiple time points post-transplant. Categorical variables were compared with Pearson’s chi-squared or Fischer’s exact test and continuous data were compared utilizing Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Statistical analyses were performed using Stata 14.2.
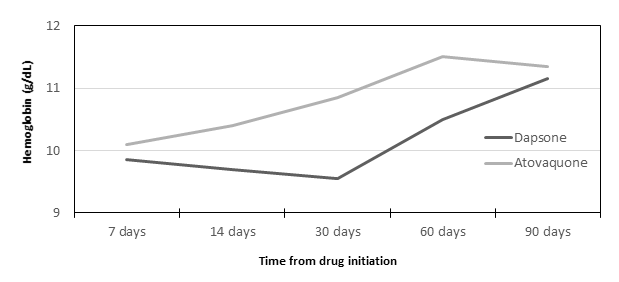
*Results: 100 patients were included in the final cohort; 50 patients in each the dapsone and atovaquone groups. In the dapsone and atovaquone groups, the median age was 52 and 50.5 years, 44% and 42% were Caucasian, and median time to treatment initiation was 27 and 39 days post-transplant, respectively. All patients receiving dapsone had normal G6PD function. There was no difference in baseline hemoglobin between groups (9.7 g/dL versus 9.8 g/dL, p=0.83). The median nadir hemoglobin values were 8.6 g/dL and 9.6 g/dL in the dapsone and atovaquone groups, respectively (p=0.047). The median decrease in hemoglobin from baseline to nadir was 1.3 g/dL in dapsone patients and 0.2 g/dL in atovaquone patients (p=0.001). Dapsone was discontinued in 46% of patients, whereas atovaquone was discontinued in 18% (p=0.001).
*Conclusions: Among renal transplant recipients with normal G6PD activity, dapsone is associated with greater hemoglobin reductions and rates of drug discontinuation as compared to atovaquone.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hedvat J, Poladi N, Salerno D, Dube G, Lange N. An Evaluation of Pjp Prophylaxis and Anemia Among Renal Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/an-evaluation-of-pjp-prophylaxis-and-anemia-among-renal-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress