A Prognostic Drug Development Tool to Assess the Transplantability at the Time of Listing for Kidney Transplant Candidates
1Terasaki Research Institute, Los Angeles, CA, 2Hansa Medical AB, Lund, Sweden
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B38
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Prediction models, Waiting lists
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: At time of listing for kidney transplant (KT), a patient is not informed of the probabilities of KT, death, or remaining on the waiting list (WL) within the next year. To aid decision making, we developed an algorithm to prognosticate clinical scenario likelihood at listing.
*Methods: Data obtained from the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients on adult KT candidates registered on the WL between 1/09 thru 12/14 were used to construct a random survival forests model for selection of predictors and subsequent prediction. The aim was to predict if a patient is (a) transplantable (KT or does not need KT) or (b) At-risk (death/too sick for KT OR still on WL at 1 year post-listing. Patients removed from the WL for other reasons were censored. Variables with <85% capture were excluded. Cause-specific cumulative incidence was examined as a predictor of outcome 1-year post-listing.
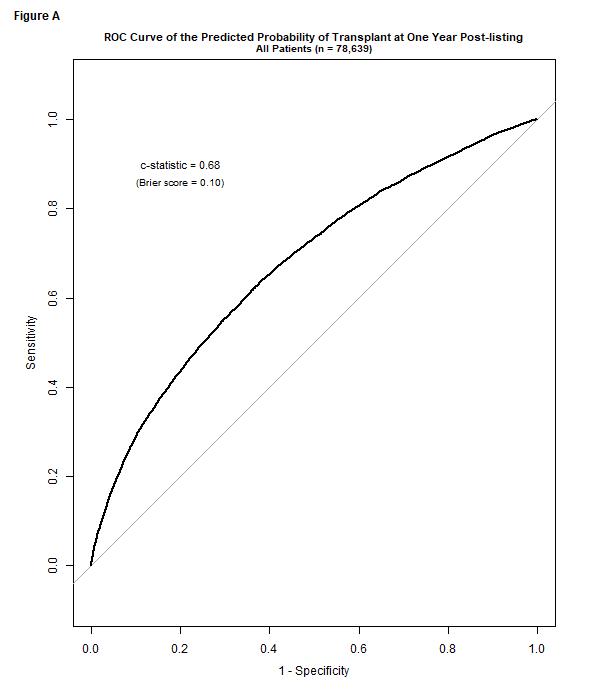
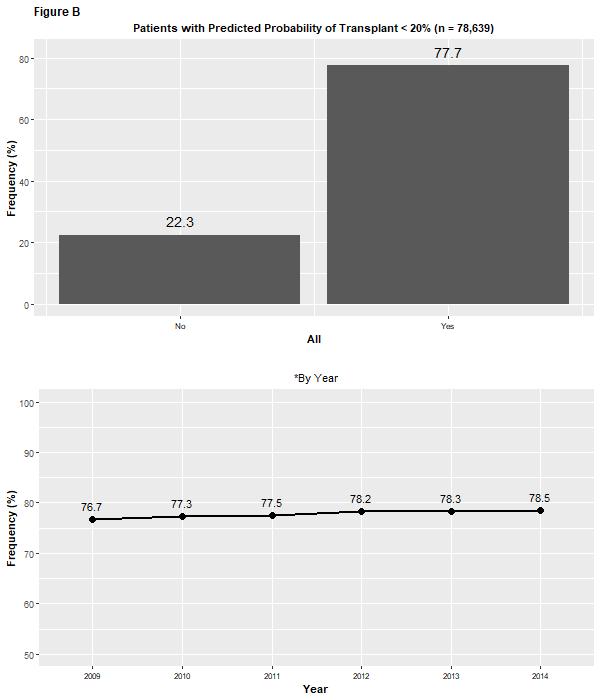
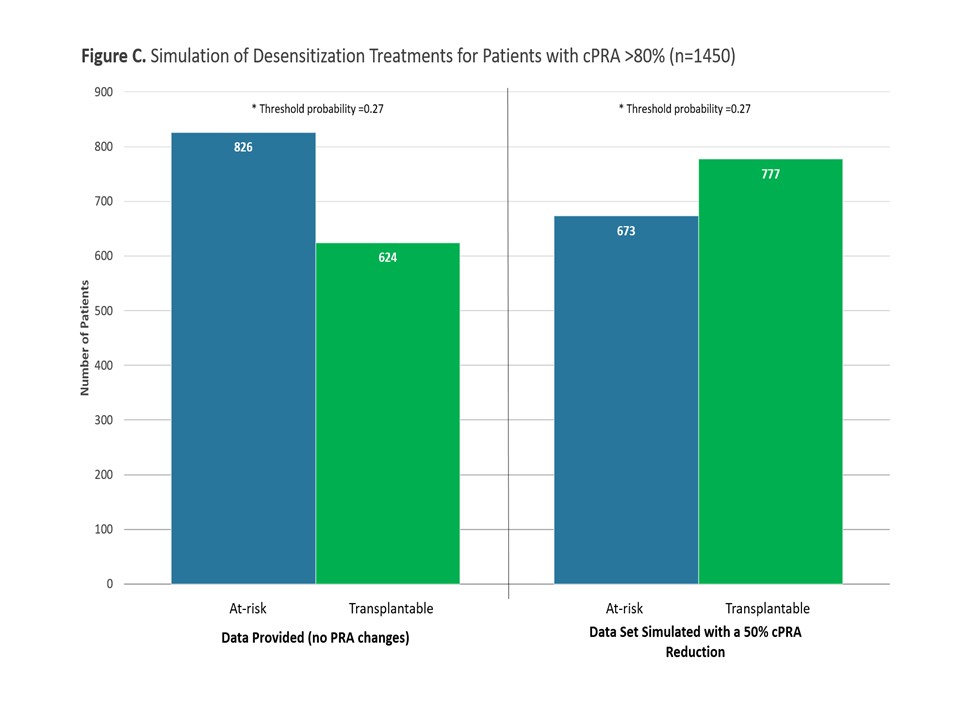
*Results: Thirteen potential predictors were identified. The overall prediction model exhibited a c-statistic of 0.68 (Figure A). Of these predictors, only 2 were medically modifiable (total albumin and cPRA) after listing. 78% of all patients had a predicted probability of KT < 20% by 1 year post-listing. The proportion remained relatively constant throughout the study period (Figure B). Within high PRA patients, 57% were At-Risk (Figure C). Simulation of a decrease in PRA by 50% showed that KT rates could increase by 25%, if therapy was used to address the high PRA/HLA antibodies.
*Conclusions: This machine learning based clinical scenario prognostic tool allows for a way to assess death/long-wait time risk at the time of listing. Simulations in the high PRA patients informs us that KT rate could be improved if therapy addressed the HLA antibody barrier.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kawakita S, Hidalgo-Semlek L, Beaumont JL, Lee J, Everly MJ. A Prognostic Drug Development Tool to Assess the Transplantability at the Time of Listing for Kidney Transplant Candidates [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-prognostic-drug-development-tool-to-assess-the-transplantability-at-the-time-of-listing-for-kidney-transplant-candidates/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress