A Pilot Study of the mDOT Platform for Immunosuppression Adherence in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients
J. Langlee, L. Lees, A. Saha, D. Helfer, M. Waldram, A. Love, F. Rivera, A. Massie, D. Segev, D. Brennan, M. Henderson
Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D324
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Monitoring, Psychosocial
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Psychosocial and Treatment Adherence
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: The leading predictor of rejection, de novo DSA, graft loss, and death among adult kidney transplant (KT) recipients is immunosuppressive medication nonadherence. An estimated one-third of KT recipients reportedly experience medication nonadherence. To understand if asynchronous, video directly observed therapy can be leveraged in adult KT recipients to improve medication adherence, we adapted a smartphone app (mDOT) previously shown to increase medication adherence among tuberculous patients and are testing the feasibility of this technology among transplant patients in a pilot randomized control trial (RCT).
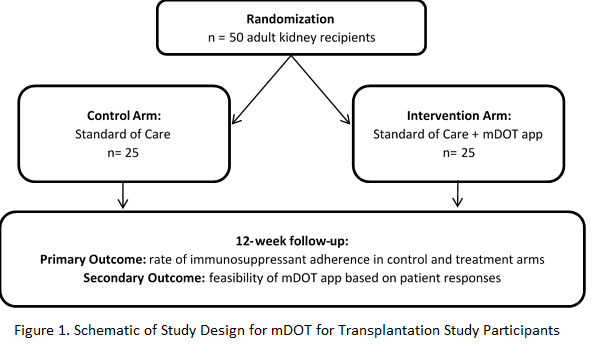
*Methods: Key features of mDOT for transplantation include a HIPAA-compliant patient-facing smartphone app and transplant provider-facing web portal, symptom and side-effect tracking and reporting, dose-by dose medication tracking capability, SMS notifications, and two-way in-app secure messaging. We are conducting an ongoing pilot RCT to evaluate mDOT on rates of post-transplant medication adherence, in preparation for a fully-powered multi-site clinical trial (NCT03427008). Participants are randomized to the intervention (mDOT) or control arm (standard of care) using block randomization (Figure 1). Immunosuppression is tracked over time through medical record abstraction and the self-reported immunosuppressant therapy adherence instrument.
*Results: We have enrolled ten patients (N =10) as of October 2018. 50% of the patients identify as white and 50% as black. 70% of these patients are male and median age is 57.5 (IQR: 45.0, 61.0) (Table 1). Feedback from patients and video reviewers have allowed us to optimize the app to foster greater patient-provider communication and user-friendliness. More clinical outcomes will be available at the time of ATC.
*Conclusions: Designed to facilitate immunosuppression adherence and engagement with transplant providers, mDOT may be a promising technology for adult KT recipients in the post-transplant period.
| Patient Characteristic | Value |
| N | 10 |
| Age, median (IQR) | 57.5 (45.0, 61.0) |
| Race – Black(%) | 50 |
| Race – White (%) | 50 |
| Female (%) | 30 |
| Male (%) | 70 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Langlee J, Lees L, Saha A, Helfer D, Waldram M, Love A, Rivera F, Massie A, Segev D, Brennan D, Henderson M. A Pilot Study of the mDOT Platform for Immunosuppression Adherence in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-pilot-study-of-the-mdot-platform-for-immunosuppression-adherence-in-adult-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress