A Multi-Center Study Assessing the Association of Frailty with Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients
M. Malinis1, M. Abidi2, E. Benamu2, N. Jakharia3, N. Law4, R. Sigler4, R. Nog5, S. Olivier5, S. Taimur6, N. Theodoropoulos7, J. Schaenman8
1Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, 2University of CO, Aurora, CO, 3Stanford, Palo Alto, CA, 4UCSD, San Diego, CA, 5Westchester Med Ctr, Westchester, NY, 6Mount Sinai SOM, New York, NY, 7Univ of MA, Worcester, MA, 8UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 548
Keywords: Infection, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 25 - Kidney Infectious Non-Polyoma & Non-Viral Hepatitis
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Transplant Infections
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:10pm-6:20pm
Presentation Time: 6:10pm-6:20pm
Location: Hynes Ballroom B
*Purpose: Frailty is a multi-dimensional characterization of decreased reserve and diminished response to stressors in older adults. Frailty at the time of transplant has been associated with worse outcomes in kidney transplant recipients (KTR), including graft failure and rehospitalization. Association of pre-transplant frailty measured by modified frailty index (MFI) with infections in older KTR (age ≥ 65 years) was limited to a single-center study. However, there was no prior evaluation that included a younger cohort. Our multi-center study aims to evaluate frailty measured by MFI as a predictor of infection after kidney transplant (KT) in older (≥ 65 years) and younger (50-64 years) adult cohorts.
*Methods: We conducted a multi-center, retrospective, observational study of primary KTR age ≥50 years between 2017-2019 through the AST IDCOP working group. Demographics, co-morbidities, transplant-related data, and infections within 1-year of KT were collected by medical record review. Frailty at the time of KT was defined by MFI ≥ 0.27. Primary outcome measured was infection within 1 year of KT. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to evaluate factors associated with post-KT infection.
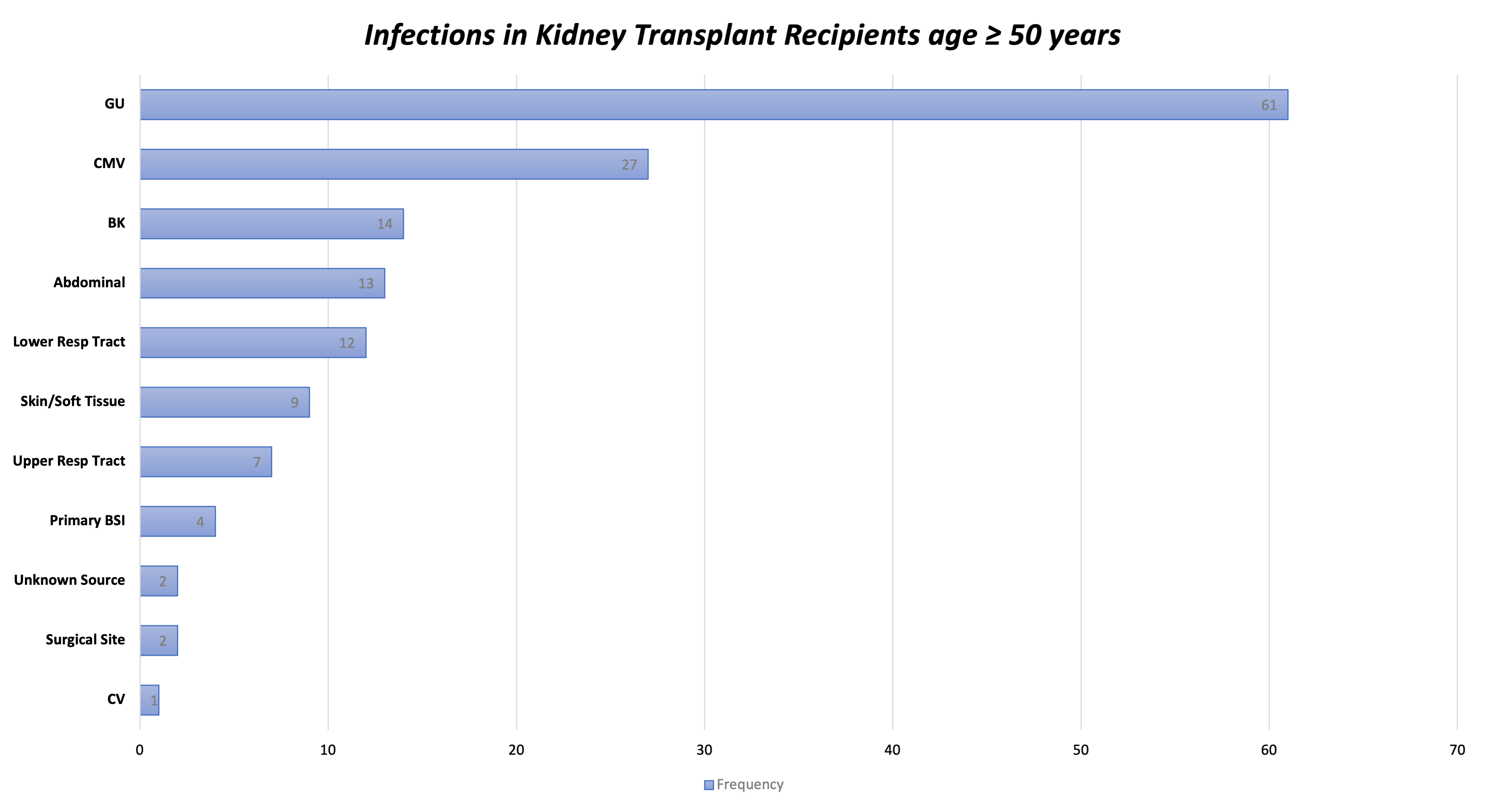
*Results: 155 KTR were evaluated. The mean age at time of KT was 62.16 (SD 7.30) years with a mean calculated panel reactive antibodies of 0.81 (SD 1.14). Fifty (32%) of the KT cohort were age ≥ 65 years. The majority were male (65%) and white (61%). Diabetes (34%) and hypertension (31%) were common KT indication. The mean MFI was 0.19 (SD 0.12). The mean follow-up from time of KT was 1325 days with patient and graft survivals of 94% and 92%, respectively. Ninety-one of 155 KTR (58%) experienced ≥ 1 infection at a mean of 103 days (SD 99) after KT. Genitourinary (40%), Cytomegalovirus (CMV) (18%), BK Polyomavirus (9%) infections were common (Figure 1). The proportion of patients with infections in age groups 50-64 and ≥ 65 years was similar (55% vs 66%, p=0.22). Frailty was significantly associated with infection in KTR age ≥ 65 years (p=0.006). However, frailty did not reveal any significant association with infection in KTR age 50-64 years.
*Conclusions: Infections were common in KTR. Frail older adults ≥ 65 years of age are at increased for infections following KT. Future, larger-scale, prospective studies are needed to validate our findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Malinis M, Abidi M, Benamu E, Jakharia N, Law N, Sigler R, Nog R, Olivier S, Taimur S, Theodoropoulos N, Schaenman J. A Multi-Center Study Assessing the Association of Frailty with Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-multi-center-study-assessing-the-association-of-frailty-with-infection-in-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress