A Medical Decision Analysis for the Use of Donation after Cardiac Death Donors for Simultaneous Liver-Kidney Transplant
Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 146
Keywords: Donation, Donors, Kidney/liver transplantation, non-heart-beating
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Liver - Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:42pm-4:54pm
Presentation Time: 4:42pm-4:54pm
Location: Room 6B
For patients on the simultaneous liver-kidney transplant (SLKT) waitlist, acceptance of donation after cardiac death (DCD) organs may facilitate earlier transplantation thereby reducing waitlist mortality, but may also lead to reduced organ survival. The purpose of this analysis was to determine if in SLKT, overall quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) are improved by accepting a DCD donor now versus waiting for a donation after neurologic death (DND) donor, and to determine if chosen treatment strategy is modified by MELD score at the time of listing.
A Markov model was used to examine discounted QALYs over a 10 year time horizon. Model heterogeneity was analyzed using first order Monte Carlo microsimulation. Patients could enter the model at MELD 15-20, MELD 21-30 or MELD >30, and for each MELD category, could be transplanted, die on the waitlist, or progress/regress to another MELD category during a 30 day cycle. Parameter uncertainty was assessed using a probabilistic sensitivity analysis and 2-way sensitivity analyses for probability of death on waitlist and probability of transplantation, stratified by MELD score.
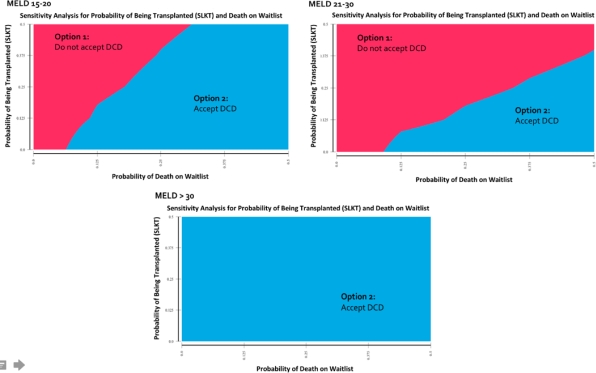
For MELD ≤30, not accepting a DCD donor (waiting for DND-SLKT) was the preferred treatment strategy (4.28 QALYs versus 3.55 QALYs for MELD 15-20; 3.94 QALYs versus 3.52 QALYs for MELD 21-30), with an incremental value (IV) of 0.42-0.73 QALYs/10 years. For MELD >30, accepting a DCD donor became the preferred strategy (3.57 QALYs versus 3.29 QALYs). The treatment strategy “not accepting a DCD” was favoured 70% of the time for a MELD score of 15-20, whereas it was only favoured 29% of the time for MELD >30. In 2-way sensitivity analysis, accepting a DCD-SLKT was the preferred treatment strategy irrespective of waitlist mortality and transplant rate for MELD >30, figure 1.
In conclusion, the benefit of waiting for DND-SLKT decreases with higher MELD scores, however the IV of waiting for DND-SLKT is small even at lower MELD scores. Thus, the use of DCD-SLKT should be encouraged in patients with advanced liver-kidney disease to improve overall QALYs (patient perspective) and organ supply (societal perspective).
CITATION INFORMATION: Miller A., Tennankore K., Kiberd B. A Medical Decision Analysis for the Use of Donation after Cardiac Death Donors for Simultaneous Liver-Kidney Transplant Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Miller A, Tennankore K, Kiberd B. A Medical Decision Analysis for the Use of Donation after Cardiac Death Donors for Simultaneous Liver-Kidney Transplant [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-medical-decision-analysis-for-the-use-of-donation-after-cardiac-death-donors-for-simultaneous-liver-kidney-transplant/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress